
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Chirality center of the
Concept Introduction:
Chirality is the presence of an asymmetric carbon center in a molecule and a molecule which contains a chiral center cannot superimpose on its mirror image.
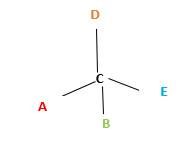
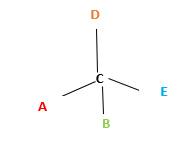
In the above diagram, where C is the chiral center/ asymmetric carbon center.
A, B, D, E are four different
Answer to Problem 30P
In
Explanation of Solution
The
(b)
Interpretation:
Chirality center of the
Concept Introduction:
Chirality is the presence of an asymmetric carbon center in a molecule and a molecule which contains a chiral center cannot superimpose on its mirror image.
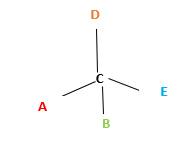
In the above diagram, where C is the chiral center/ asymmetric carbon center.
A, B, D, E are four different functional groups.
Answer to Problem 30P
The compound
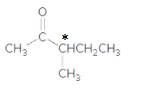
Explanation of Solution
The
The chiral center is represented as follows:
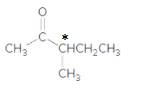
(c)
Interpretation:
Chirality center of the given molecule, should be labeled and identified.
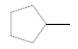
Concept Introduction:
Chirality is the presence of an asymmetric carbon center in a molecule and a molecule which contains a chiral center cannot superimpose on its mirror image.
In the above diagram, where C is the chiral center/ asymmetric carbon center.
A, B, D, E are four different functional groups.
Answer to Problem 30P
Inmolecule there are no chiral centers present.
Explanation of Solution
The
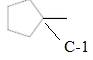
Therefore, molecule does not contain any chiral centers.
(d)
Interpretation:
Chirality center of the given molecule, should be labeled and identified.
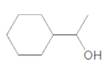
Concept Introduction:
Chirality is the presence of an asymmetric carbon center in a molecule and a molecule which contains a chiral center cannot superimpose on its mirror image.
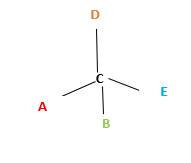
In the above diagram, where C is the chiral center/ asymmetric carbon center.
A, B, D, E are four different functional groups.
Answer to Problem 30P
Inmolecule there is only one chiral center is present. Refer the below mentioned diagram.
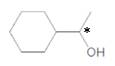
Explanation of Solution
The
C atom which bonded toone
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Loose Leaf for General, Organic and Biological Chemistry with Connect 2 Year Access Card
- Indicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COONa (Sodium acetoacetate) and BrCH2COOC2H5arrow_forwardIndicate whether the product of the reaction between Naphthalene and CrO3 in acetic acid at 25ºC is 1,4 naphthoquinone or phthalic anhydride.arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COOC2H5 and Na+-OC2H5.arrow_forward
- Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Alcohols O-H O-H O-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-R₁ H R₂ R₂ Primary Alcohol Secondary Alcohol ChemistryLearner.com R stands for Carbon group like ethyl methyl propyl Tertiary Alcohol If 1 carbon group with two H attached to alcoholic carbon, then primary If 2 carbon group and 1 H are attached to alcoholic carbon, then secondary IF 3 carbon group and no H attach to alcoholic carbon then tertiary. The bottom line Starting "Weak" oxidant material PCC, DMP, Swern, etc Primary alcohol Aldehyde OH Secondary alcohol Ketone OH "Strong" oxidant KMnO4, H₂CrO4 (or equivalent) OH Carboxylic acid 요 Ketone No reaction No reaction Tertiary alcohol 1. Is ethanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of ethanol and any oxidation products of ethanol. If there is more than one oxidation product, give the structure of each of the products. 2. Is 2-propanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of 2-propanol and any…arrow_forwardFormulate the reaction: Naphthalene with CrO3 in acetic acid at 25ºCarrow_forwardComplete the reaction hand written pleasearrow_forward
 Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
