
State the null and alternative hypothesis.
Find the degrees of freedom for the
Find the critical value of chi-square from Appendix E or from Excel’s
Calculate the chi-square test statistics at 0.05 level of significance.
Interpret the p-value.
Check whether the conclusion is sensitive to the level of significance chosen, identify the cells that contribute to the chi-square test statistic and check for the small expected frequencies.
Perform a two-tailed, two-sample z test for
Answer to Problem 30CE
The null hypothesis is:
And the alternative hypothesis is:
The degrees of freedom for the contingency table is 1.
The critical-value using EXCEL is 3.841.
The chi-square test statistics at 0.05 level of significance is 1.50.
The p-value for the hypothesis test is 0.221.
There is enough evidence to conclude that the correct response and type of cola are independent.
The conclusion is not sensitive to the level of significance chosen.
The cells (1, 1) and (1, 2) contribute the most to the chi-square test statistic.
There is no expected frequencies that are too small.
It is verified that
Explanation of Solution
The table summarizes the grade and order of papers handed in.
The claim is to test whether the data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that the grade and order handed in are independent. If the claim is rejected, then the grade and order handed in are not independent.
The test hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
Alternative hypothesis:
The degrees of freedom can be obtained as follows:
Substitute 2 for r and 2 for c.
Thus, the degrees of freedom for the contingency table is 1.
Procedure for critical-value using EXCEL:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain critical-value using EXCEL software is as follows:
- Open an EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula “=CHISQ.INV.RT(0.05,1)”
- Output using EXCEL software is given below:
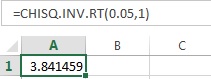
Thus, the critical-value using EXCEL is 3.841.
Test statistic:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain the chi-square test statistics and p-value using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Tables >Cross Tabulation and Chi-Square.
- Choose Row data (categorical variables).
- In Rows, choose Grade.
- In Columns, choose Order handed in.
- In Frequencies, choose Count.
- In Display, select Counts.
- In chi-square, select Chi-square test, Expected cell counts and Each cell’s contribution to chi-square.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
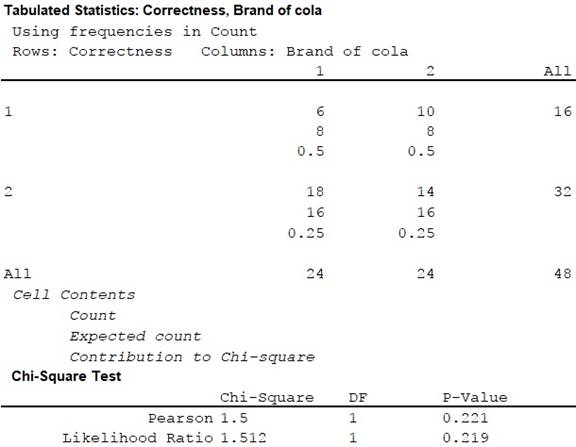
Thus, the test statistic is 1.50 and the p-value for the hypothesis test is 0.221.
Rejection rule:
If the p-value is less than or equal to the significance level, then reject the null hypothesis
Conclusion:
Here, the p-value is greater than the level of significance.
That is,
Therefore, the null hypothesis is not rejected.
Thus, the data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that the correct response and type of cola are independent.
Take
Here, the p-value is greater than the level of significance.
That is,
Therefore, the null hypothesis is not rejected.
Thus, the data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that the correct response and type of cola are independent.
Thus, the conclusion is same for both the significance levels.
Hence, the conclusion is not sensitive to the level of significance chosen.
The cells (1, 1) and (1, 2) contribute the most to the chi-square test statistic.
Since all
Two-tailed, two-sample z test:
The test hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
Alternative hypothesis:
The proportion of “yes” responses to the regular cola is denoted as
Where
The proportion of number of “yes” responses to the diet cola is denoted as
Where
The pooled proportion is denoted as
Test statistic:
The z-test statistics can be obtained as follows:
Thus, the z-test statistic is –1.22.
The square of the z-test statistic is,
Thus the square of the z-test statistic is same as the chi-square statistics.
Procedure for p-value using EXCEL:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain p-value using EXCEL software is as follows:
- Open an EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula “=2*(1-NORM.S.DIST(–1.22,1))”
- Output using EXCEL software is given below:
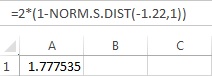
Thus, the p-value using EXCEL is 1.778, which is not same as the p-value obtained in chi-square test. But the square of the z-test statistic is same as the chi-square statistics.
Thus, it is verified that
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
APPLIED STAT.IN BUS.+ECONOMICS
- For each of the time series, construct a line chart of the data and identify the characteristics of the time series (that is, random, stationary, trend, seasonal, or cyclical). Date IBM9/7/2010 $125.959/8/2010 $126.089/9/2010 $126.369/10/2010 $127.999/13/2010 $129.619/14/2010 $128.859/15/2010 $129.439/16/2010 $129.679/17/2010 $130.199/20/2010 $131.79 a. Construct a line chart of the closing stock prices data. Choose the correct chart below.arrow_forwardFor each of the time series, construct a line chart of the data and identify the characteristics of the time series (that is, random, stationary, trend, seasonal, or cyclical) Date IBM9/7/2010 $125.959/8/2010 $126.089/9/2010 $126.369/10/2010 $127.999/13/2010 $129.619/14/2010 $128.859/15/2010 $129.439/16/2010 $129.679/17/2010 $130.199/20/2010 $131.79arrow_forward1. A consumer group claims that the mean annual consumption of cheddar cheese by a person in the United States is at most 10.3 pounds. A random sample of 100 people in the United States has a mean annual cheddar cheese consumption of 9.9 pounds. Assume the population standard deviation is 2.1 pounds. At a = 0.05, can you reject the claim? (Adapted from U.S. Department of Agriculture) State the hypotheses: Calculate the test statistic: Calculate the P-value: Conclusion (reject or fail to reject Ho): 2. The CEO of a manufacturing facility claims that the mean workday of the company's assembly line employees is less than 8.5 hours. A random sample of 25 of the company's assembly line employees has a mean workday of 8.2 hours. Assume the population standard deviation is 0.5 hour and the population is normally distributed. At a = 0.01, test the CEO's claim. State the hypotheses: Calculate the test statistic: Calculate the P-value: Conclusion (reject or fail to reject Ho): Statisticsarrow_forward
- 21. find the mean. and variance of the following: Ⓒ x(t) = Ut +V, and V indepriv. s.t U.VN NL0, 63). X(t) = t² + Ut +V, U and V incepires have N (0,8) Ut ①xt = e UNN (0162) ~ X+ = UCOSTE, UNNL0, 62) SU, Oct ⑤Xt= 7 where U. Vindp.rus +> ½ have NL, 62). ⑥Xn = ΣY, 41, 42, 43, ... Yn vandom sample K=1 Text with mean zen and variance 6arrow_forwardA psychology researcher conducted a Chi-Square Test of Independence to examine whether there is a relationship between college students’ year in school (Freshman, Sophomore, Junior, Senior) and their preferred coping strategy for academic stress (Problem-Focused, Emotion-Focused, Avoidance). The test yielded the following result: image.png Interpret the results of this analysis. In your response, clearly explain: Whether the result is statistically significant and why. What this means about the relationship between year in school and coping strategy. What the researcher should conclude based on these findings.arrow_forwardA school counselor is conducting a research study to examine whether there is a relationship between the number of times teenagers report vaping per week and their academic performance, measured by GPA. The counselor collects data from a sample of high school students. Write the null and alternative hypotheses for this study. Clearly state your hypotheses in terms of the correlation between vaping frequency and academic performance. EditViewInsertFormatToolsTable 12pt Paragrapharrow_forward
- A smallish urn contains 25 small plastic bunnies – 7 of which are pink and 18 of which are white. 10 bunnies are drawn from the urn at random with replacement, and X is the number of pink bunnies that are drawn. (a) P(X = 5) ≈ (b) P(X<6) ≈ The Whoville small urn contains 100 marbles – 60 blue and 40 orange. The Grinch sneaks in one night and grabs a simple random sample (without replacement) of 15 marbles. (a) The probability that the Grinch gets exactly 6 blue marbles is [ Select ] ["≈ 0.054", "≈ 0.043", "≈ 0.061"] . (b) The probability that the Grinch gets at least 7 blue marbles is [ Select ] ["≈ 0.922", "≈ 0.905", "≈ 0.893"] . (c) The probability that the Grinch gets between 8 and 12 blue marbles (inclusive) is [ Select ] ["≈ 0.801", "≈ 0.760", "≈ 0.786"] . The Whoville small urn contains 100 marbles – 60 blue and 40 orange. The Grinch sneaks in one night and grabs a simple random sample (without replacement) of 15 marbles. (a)…arrow_forwardSuppose an experiment was conducted to compare the mileage(km) per litre obtained by competing brands of petrol I,II,III. Three new Mazda, three new Toyota and three new Nissan cars were available for experimentation. During the experiment the cars would operate under same conditions in order to eliminate the effect of external variables on the distance travelled per litre on the assigned brand of petrol. The data is given as below: Brands of Petrol Mazda Toyota Nissan I 10.6 12.0 11.0 II 9.0 15.0 12.0 III 12.0 17.4 13.0 (a) Test at the 5% level of significance whether there are signi cant differences among the brands of fuels and also among the cars. [10] (b) Compute the standard error for comparing any two fuel brands means. Hence compare, at the 5% level of significance, each of fuel brands II, and III with the standard fuel brand I. [10] �arrow_forwardBusiness discussarrow_forward
- What would you say about a set of quantitative bivariate data whose linear correlation is -1? What would a scatter diagram of the data look like? (5 points)arrow_forwardBusiness discussarrow_forwardAnalyze the residuals of a linear regression model and select the best response. yes, the residual plot does not show a curve no, the residual plot shows a curve yes, the residual plot shows a curve no, the residual plot does not show a curve I answered, "No, the residual plot shows a curve." (and this was incorrect). I am not sure why I keep getting these wrong when the answer seems obvious. Please help me understand what the yes and no references in the answer.arrow_forward
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL


