
Student Solutions Manual for Zumdahl/Zumdahl/DeCoste?s Chemistry, 10th Edition
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957510
Author: ZUMDAHL, Steven S.; Zumdahl, Susan A.; DeCoste, Donald J.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 15, Problem 20Q
Consider the following two acids:
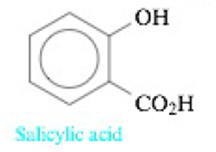
pKa1 = 2.98; pKa2 = 13.40
HO2CCH2CH2CH2CH2CO2H
Adipic acid
pKa1 = 4.41; pKa2 = 5.28
In two separate experiments the pH was measured during the titration of 5.00 mmol of each acid with 0.200 M NaOH. Each experiment showed only one stoichiometric point when the data were plotted. In one experiment the stoichiometric point was at 25.00 mL added NaOH, and in the other experiment the stoichiometric point was at 50.00 mL NaOH. Explain these results.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
8
00
6
= 10
10
Decide whether each of the molecules in the table below is stable, in the exact form in which it is drawn, at pH = 11.
If
you decide at least one molecule is not stable, then redraw one of the unstable molecules in its stable form below the table. (If more than
unstable, you can pick any of them to redraw.)
Check
OH
stable
HO
stable
Ounstable
unstable
O
OH
stable
unstable
OH
80
F6
F5
stable
Ounstable
X
Save For Later
Sub
2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C
ཀྭ་
A
F7
매
F8
F9
4
F10
Just try completing it and it should be straightforward according to the professor and TAs.
The grading is not on correctness, so if you can just get to the correct answers without perfectionism that would be great. They care about the steps and reasoning and that you did something. I asked for an extension, but was denied the extension.
Chapter 15 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual for Zumdahl/Zumdahl/DeCoste?s Chemistry, 10th Edition
Ch. 15 - What is meant by the presence of a common ion? How...Ch. 15 - Define a buffer solution. What makes up a buffer...Ch. 15 - One of the most challenging parts of solving...Ch. 15 - A good buffer generally contains relatively equal...Ch. 15 - Draw the general titration curve for a strong acid...Ch. 15 - Instead of the titration of a strong acid by a...Ch. 15 - Sketch the titration curve for a weak acid...Ch. 15 - Sketch the titration curve for a weak base...Ch. 15 - What is an acidbase indicator? Define the...Ch. 15 - Why does an indicator change from its acid color...
Ch. 15 - What are the major species in solution after...Ch. 15 - A friend asks the following: Consider a buffered...Ch. 15 - Mixing together solutions of acetic acid and...Ch. 15 - Sketch two pH curves, one for the titration of a...Ch. 15 - Sketch a pH curve for the titration of a weak acid...Ch. 15 - You have a solution of the weak acid HA and add...Ch. 15 - You have a solution of the weak acid HA and add...Ch. 15 - The common ion effect for weak acids is to...Ch. 15 - Prob. 12QCh. 15 - A best buffer has about equal quantities of weak...Ch. 15 - Consider the following pH curves for 100.0 mL of...Ch. 15 - An acid is titrated with NaOH. The following...Ch. 15 - Consider the following four titrations. i. 100.0...Ch. 15 - Figure 14-4 shows the pH curves for the titrations...Ch. 15 - Acidbase indicators mark the end point of...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of 100.0 mL of 0.10 M...Ch. 15 - Consider the following two acids: pKa1 = 2.98;...Ch. 15 - How many of the following are buffered solutions?...Ch. 15 - Which of the following can be classified as buffer...Ch. 15 - A certain buffer is made by dissolving NaHCO3 and...Ch. 15 - A buffer is prepared by dissolving HONH2 and...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of each of the following...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of each of the following...Ch. 15 - Compare the percent dissociation of the acid in...Ch. 15 - Compare the percent ionization of the base in...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH after 0.020 mole of HCl is added...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH after 0.020 mole of HCl is added...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH after 0.020 mole of NaOH is added...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH after 0.020 mole of NaOH is added...Ch. 15 - Which of the solutions in Exercise 21 shows the...Ch. 15 - Prob. 34ECh. 15 - Calculate the pH of a solution that is 1.00 M HNO2...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of a solution that is 0.60 M HF...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH after 0.10 mole of NaOH is added...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH after 0.10 mole of NaOH is added...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of each of the following buffered...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of each of the following buffered...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of a buffered solution prepared...Ch. 15 - A buffered solution is made by adding 50.0 g NH4Cl...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH after 0.010 mole of gaseous HCl...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH after 0.15 mole of solid NaOH is...Ch. 15 - Some K2SO3 and KHSO3 are dissolved in 250.0 mL of...Ch. 15 - An aqueous solution contains dissolved C6H5NH3Cl...Ch. 15 - Calculate the mass of sodium acetate that must be...Ch. 15 - What volumes of 0.50 M HNO2 and 0.50 M NaNO2 must...Ch. 15 - Consider a solution that contains both C5H5N and...Ch. 15 - Calculate the ratio [NH3]/[NH4+] in...Ch. 15 - Carbonate buffers are important in regulating the...Ch. 15 - When a person exercises, muscle contractions...Ch. 15 - Consider the acids in Table 13-2. Which acid would...Ch. 15 - Consider the bases in Table 13-3. Which base would...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of a solution that is 0.40 M...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of a solution that is 0.20 M HOCl...Ch. 15 - Which of the following mixtures would result in...Ch. 15 - Which of the following mixtures would result in a...Ch. 15 - What quantity (moles) of NaOH must be added to 1.0...Ch. 15 - Calculate the number of moles of HCl(g) that must...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of a generic weak acid HA...Ch. 15 - Sketch the titration curve for the titration of a...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of 40.0 mL of 0.200 M HClO4...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of 80.0 mL of 0.100 M...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of 100.0 mL of 0.200 M...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of 100.0 mL of 0.100 M...Ch. 15 - Lactic acid is a common by-product of cellular...Ch. 15 - Repeat the procedure in Exercise 61, but for the...Ch. 15 - Repeat the procedure in Exercise 61, but for the...Ch. 15 - Repeat the procedure in Exercise 61, but for the...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH at the halfway point and at the...Ch. 15 - In the titration of 50.0 mL of 1.0 M methylamine,...Ch. 15 - You have 75.0 mL of 0.10 M HA. After adding 30.0...Ch. 15 - A student dissolves 0.0100 mole of an unknown weak...Ch. 15 - Two drops of indicator HIn (Ka = 1.0 109), where...Ch. 15 - Methyl red has the following structure: It...Ch. 15 - Potassium hydrogen phthalate, known as KHP (molar...Ch. 15 - A certain indicator HIn has a pKa of 3.00 and a...Ch. 15 - Which of the indicators in Fig. 14-8 could be used...Ch. 15 - Prob. 80ECh. 15 - Which of the indicators in Fig. 14-8 could be used...Ch. 15 - Prob. 82ECh. 15 - Estimate the pH of a solution in which bromcresol...Ch. 15 - Estimate the pH of a solution in which crystal...Ch. 15 - A solution has a pH of 7.0. What would be the...Ch. 15 - A solution has a pH of 4.5. What would be the...Ch. 15 - When a diprotic acid, H2A. is titrated with NaOH,...Ch. 15 - Consider die titration of 50.0 mL of 0.10 M H3A...Ch. 15 - Derive an equation analogous to the...Ch. 15 - a. Calculate the pH of a buffered solution that is...Ch. 15 - Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, commonly called...Ch. 15 - You make 1.00 L of a buffered solution (pH = 4.00)...Ch. 15 - You have the following reagents on hand: Solids...Ch. 15 - Prob. 94AECh. 15 - Phosphate buffers are important in regulating the...Ch. 15 - When a diprotic acid, H2A, is titrated with NaOH,...Ch. 15 - Consider the blood buffer system discussed in the...Ch. 15 - What quantity (moles) of HCl(g) must be added to...Ch. 15 - Prob. 99AECh. 15 - The following plot shows the pH curves for the...Ch. 15 - Calculate the volume of 1.50 102 M NaOH that must...Ch. 15 - Prob. 102AECh. 15 - A certain acetic acid solution has pH = 2.68....Ch. 15 - A 0.210-g sample of an acid (molar mass = 192...Ch. 15 - The active ingredient in aspirin is...Ch. 15 - One method for determining the purity of aspirin...Ch. 15 - A student intends to titrate a solution of a weak...Ch. 15 - A student titrates an unknown weak acid, HA, to a...Ch. 15 - A sample of a certain monoprotic weak acid was...Ch. 15 - The pigment cyanidin aglycone is one of the...Ch. 15 - Consider 1.0 L of a solution that is 0.85 M HOC6H5...Ch. 15 - What concentration of NH4Cl is necessary to buffer...Ch. 15 - Consider the following acids and bases: HCO2H Ka =...Ch. 15 - Consider a buffered solution containing CH3NH3Cl...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of 150.0 mL of 0.100 M HI...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of 100.0 mL of 0.100 M HCN...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of 100.0 mL of 0.200 M...Ch. 15 - Consider the following four titrations (iiv): i....Ch. 15 - Another way to treat data from a pH titration is...Ch. 15 - A buffer is made using 45.0 mL of 0.750 M HC3H5O2...Ch. 15 - A 0.400-M solution of ammonia was titrated with...Ch. 15 - What volume of 0.0100 M NaOH must be added to 1.00...Ch. 15 - Consider a solution formed by mixing 50.0 mL of...Ch. 15 - Cacodylic acid, (CH3)2AsO2H, is a toxic compound...Ch. 15 - The titration of Na2CO3 with HCl bas the following...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration curve in Exercise 115 for...Ch. 15 - A few drops of each of the indicators shown in the...Ch. 15 - Malonic acid (HO2CCH2CO2H) is a diprotic acid. In...Ch. 15 - A buffer solution is prepared by mixing 75.0 mL of...Ch. 15 - A 10.00-g sample of the ionic compound NaA, where...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of a solution prepared by mixing...Ch. 15 - Consider a solution prepared by mixing the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Show your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers. Something that looks reasonable or correct would be sufficient. If you can get many of them correct that would be great!arrow_forwardShow your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers. Something that looks reasonable or correct would be sufficient. If you can get many of them correct that would be great!arrow_forwardTake a look at the following molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. (You can click the other tab to see the molecule without the colored regions.) with colored region plain 0= CH2-0-C-(CH2)16-CH3 =0 CH-O-C (CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)5-CH3 D CH3 | + OMPLO CH3-N-CH2-CH2-0-P-O-CH2 B CH3 A Try again * 000 Ar 8 0 ?arrow_forward
- Show your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers.arrow_forwardShow your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers.arrow_forward= 1 = 2 3 4 5 6 ✓ 7 8 ✓ 9 =10 Devise a synthesis to prepare the product from the given starting material. Complete the following reaction scheme. Part 1 of 3 -Br Draw the structure for compound A. Check Step 1 Step 2 A Click and drag to start drawing a structure. × ↓m + OH Save For Later S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privaarrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reduction: 田 Check AP + + H2 Lindlar catalyst Click an drawing 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rigarrow_forward70 Suppose the molecule below is in acidic aqueous solution. Is keto-enol tautomerization possible? • If a keto-enol tautomerization is possible, draw the mechanism for it. Be sure any extra reagents you add to the left-hand sid available in this solution. • If a keto-enol tautomerization is not possible, check the box under the drawing area. : ☐ Add/Remove step Click and drag to st drawing a structure Check Save For Late. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forwardThe problem will not be graded for correctness, but you have to get a reasonable answer something that is either correct or very closer to the correct answer. The instructor professor wants us to do something that shows the answer but everything does not have to be correct. Ideally, yes, it has to be correct. Give it your best shot.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY
Acid-base Theories and Conjugate Acid-base Pairs; Author: Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hQLWYmAFo3E;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
COMPLEXOMETRIC TITRATION; Author: Pikai Pharmacy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EQxvY6a42Dw;License: Standard Youtube License