
Concept explainers
Suggest appropriate methods for preparing each of the following
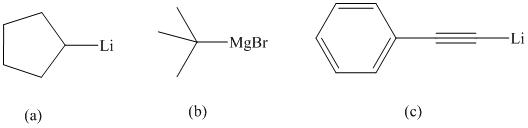
Interpretation:
The appropriate method of preparation for each of the given organometallic compounds is to be suggested.
Concept introduction:
The reaction of a metal with an organic halide is an oxidation–reduction in which the metal is the reducing agent.
lithium metal and magnesium metal in the presence of dry ether as a solvent, reacts with alkyl halides to produce the corresponding organo lithium and magnesium compounds respectively.
Organolithium reagents are used to prepare organometallic compounds analogous of terminal alkynes.
Organolithium compounds are strongly basic and react with terminal alkynes by abstracting the acidic proton and forming an alkane.
Answer to Problem 20P
Solution:
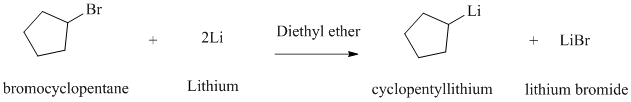

Explanation of Solution
Alkyl halides react with lithium metal in the presence of dry ether as a solvent to produce the corresponding organo lithium compound.
The product given is cyclopentyl lithium. Reaction of cyclopentyl bromide with lithium metal in the presence of diethyl ether as a solvent will produce this cyclopentyl lithium.
The reaction is shown below:

The product given is tert-butyl magnesium bromide. Tert-butyl bromide react with magnesium metal in the presence of diethyl ether as a solvent will produce this tert-butyl magnesium bromide.
The reaction is shown below:

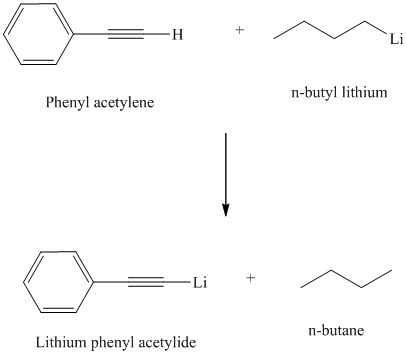
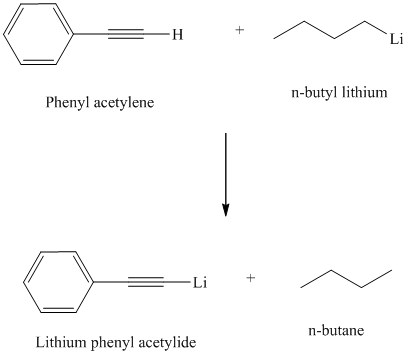
Organolithium reagents are used to prepare organometallic compounds analogous of terminal alkynes.
Organolithium compounds are strongly basic and react with terminal alkynes by abstracting the acidic proton and forming an alkane.
Thus, phenyl acetylene reacts with an organo lithium reagent like butyl lithium to produce lithium phenylacetylide and butane.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
- What is the formula of the compound 3-isopropylcyclopentane-1-carbonyl chloride?arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COONa (Sodium acetoacetate) and BrCH2COOC2H5arrow_forwardIndicate whether the product of the reaction between Naphthalene and CrO3 in acetic acid at 25ºC is 1,4 naphthoquinone or phthalic anhydride.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COOC2H5 and Na+-OC2H5.arrow_forwardPrimary, Secondary, and Tertiary Alcohols O-H O-H O-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-R₁ H R₂ R₂ Primary Alcohol Secondary Alcohol ChemistryLearner.com R stands for Carbon group like ethyl methyl propyl Tertiary Alcohol If 1 carbon group with two H attached to alcoholic carbon, then primary If 2 carbon group and 1 H are attached to alcoholic carbon, then secondary IF 3 carbon group and no H attach to alcoholic carbon then tertiary. The bottom line Starting "Weak" oxidant material PCC, DMP, Swern, etc Primary alcohol Aldehyde OH Secondary alcohol Ketone OH "Strong" oxidant KMnO4, H₂CrO4 (or equivalent) OH Carboxylic acid 요 Ketone No reaction No reaction Tertiary alcohol 1. Is ethanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of ethanol and any oxidation products of ethanol. If there is more than one oxidation product, give the structure of each of the products. 2. Is 2-propanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of 2-propanol and any…arrow_forwardFormulate the reaction: Naphthalene with CrO3 in acetic acid at 25ºCarrow_forward
- Complete the following equations please hand written pleasearrow_forwardUsing the Nernst equation to calculate nonstandard cell voltage A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 3+ 3Cu²+ (aq) +2Al(s) → 3 Cu(s)+2A1³* (aq) 2+ Suppose the cell is prepared with 5.29 M Cu in one half-cell and 2.49 M A1³+ in the other. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. x10 μ ☑ 00. 18 Ar Иarrow_forwardPlease help me solve this homework problemarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

