
Concept explainers
Dominique Fouque owns and operates Dominique’s Doll House. She has a small shop in which she sells new and antique dolls. She is particularly well known for her collection of antique Ken and Barbie dolls. A completed spreadsheet for 20-3 is shown on page 610. Fouque made no additional investments during the year and the long-term note payable is due in 20-9. No portion of the long-term note is due within the next year. Net credit sales for 20-3 were $38,000, and receivables on January 1 were $3,000.
REQUIRED
- 1. Prepare a multiple-step income statement.
- 2. Prepare a statement of owner’s equity.
- 3. Prepare a
balance sheet . - 4. Compute the following measures of performance and financial condition for 20-3:
- (a)
Current ratio - (b) Quick ratio
- (c)
Working capital - (d) Return on owner’s equity
- (e)
Accounts receivable turnover and average number of days required to collect receivables - (f) Inventory turnover and the average number of days required to sell inventory
- (a)
- 5. Prepare
adjusting entries and indicate which should be reversed and why. - 6. Open an Income Summary account. Post adjusting and closing entries (prepared in 7) to this account.
- 7. Prepare closing entries.
- 8. Prepare reversing entries for the adjustments where appropriate.
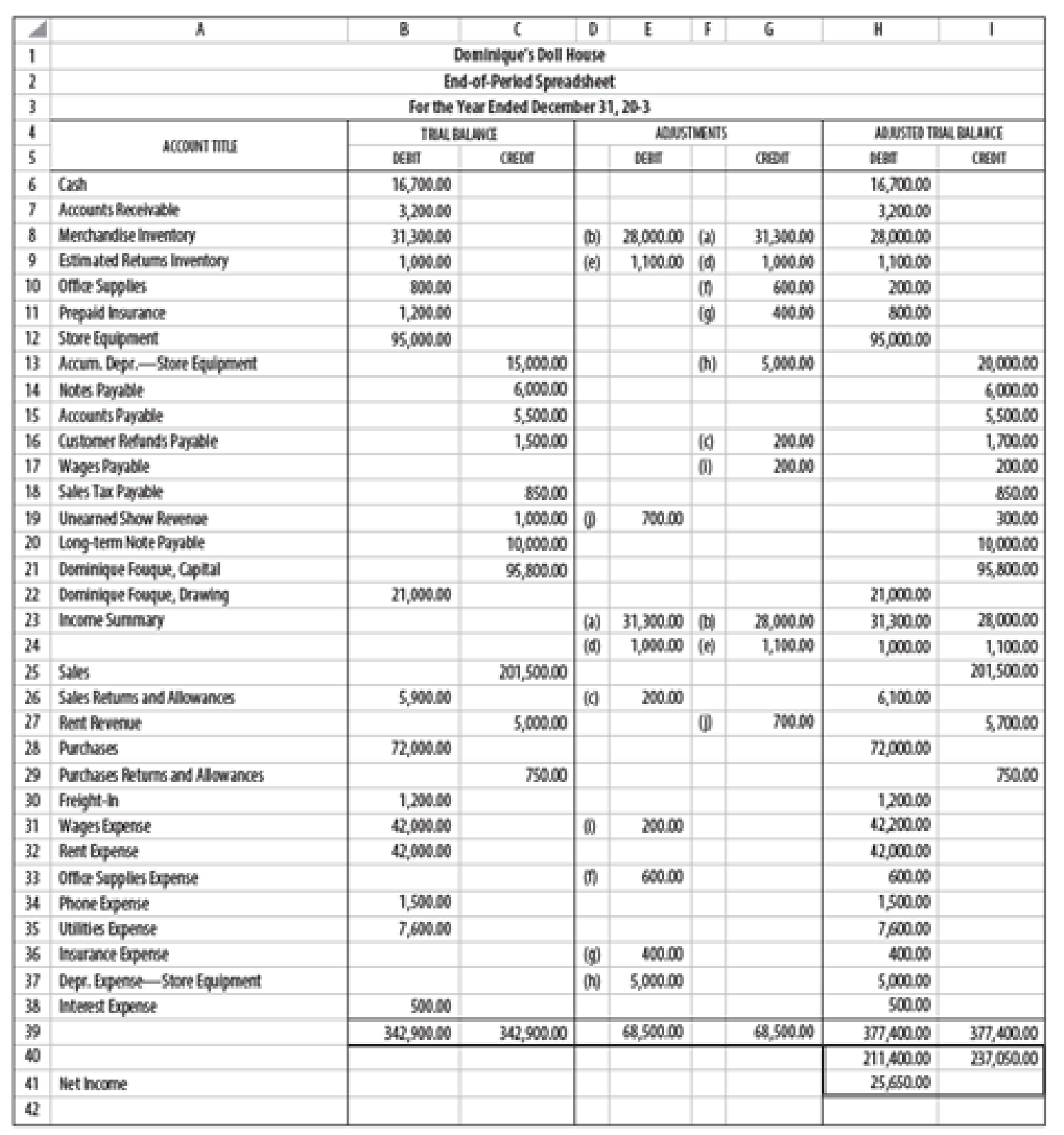
1.
Prepare a multiple income statement of DD.
Explanation of Solution
Multi-step income statement: The income statement represented in multi-steps with several subtotals, to report the income from principal operations, and separate the other expenses and revenues which affect net income, is referred to as multi-step income statement.
Prepare a multiple income statement of DD.
| DD | ||||
| Income Statement | ||||
| For Year Ended December 31, 20-3 | ||||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount | Amount | Amount |
| Revenue from Sales: | ||||
| Sales | $201,500 | |||
| Less: Sales returns and allowances | $6,100 | |||
| Net sales | $195,400 | |||
| Less: Cost of goods sold: | ||||
| Opening merchandise inventory | $31,300 | |||
| Opening estimated returns inventory | $1,000 | |||
| Purchases | $72,000 | |||
| Less: Purchases returns and allowances | $750 | |||
| Net purchases | $71,250 | |||
| Add: Freight in | $1,200 | |||
| Cost of goods purchased | $72,450 | |||
| Goods available for sale | $104,750 | |||
| Less: Ending merchandise inventory | $28,000 | |||
| Ending estimated returns inventory | $1,100 | |||
| Cost of goods sold | $75,650 | |||
| Gross profit | $119,750 | |||
| Less: Operating expenses: | ||||
| Wages expense | $42,200 | |||
| Advertising expense | $42,000 | |||
| Office supplies expense | $600 | |||
| Phone expense | $1,500 | |||
| utilities expense | $7,600 | |||
| Insurance expense | $400 | |||
| Depreciation expense - Store Equipment | $5,000 | |||
| Total operating expenses | $99,300 | |||
| Income from operations | $20,450 | |||
| Add: Other revenues: | ||||
| Rent revenue | $5,700 | |||
| Less: Other expenses: | ||||
| Interest expense | $500 | |||
| Net income | $25,650 | |||
Table (1)
2.
Prepare statement of owners’ equity of DD.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of Owners’ equity: This statement reports the beginning stockholder's equity and all the changes which led to ending stockholder's equity. Additional capital, net income from income statement is added to and drawings or dividends are deducted from beginning stockholder's equity to arrive at the end result, closing balance of stockholder's equity.
Prepare statement of owners’ equity.
| DD | ||
| Statement of Owner's Equity | ||
| For Year Ended December 31, 20-3 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| DF's Opening capital | $95,800 | |
| Add: Additional investment | $0 | |
| Total investment | $95,800 | |
| Add: Net income for the year | $25,650 | |
| Less: Withdrawal for the year | $21,000 | |
| Increase in capital | $4,650 | |
| DF's Ending capital | $100,450 | |
Table (2)
3.
Prepare a balance sheet of DD.
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet: Balance Sheet is one of the financial statements that summarize the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Prepare a balance sheet of DD.
| DD | |||
| Balance sheet | |||
| For Year Ended December 31, 20-3 | |||
| Assets | |||
| Current assets: | |||
| Cash | $16,700 | ||
| Accounts receivable | $3,200 | ||
| Merchandise inventory | $28,000 | ||
| Estimated returns inventory | $1,100 | ||
| office supplies | $200 | ||
| Prepaid insurance | $800 | ||
| Total current assets | $50,000 | ||
| Property, plant and Store Equipment: | |||
| Store Equipment | $95,000 | ||
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | $20,000 | $75,000 | |
| Total Assets | $125,000 | ||
| Liabilities | |||
| Current liabilities: | |||
| Notes payable | $6,000 | ||
| Accounts payable | $5,500 | ||
| Customer refunds payable | $1,700 | ||
| Wages payable | $200 | ||
| sales tax payable | $850 | ||
| Unearned show revenue | $300 | ||
| Total current liabilities | $14,550 | ||
| Long-term liabilities: | |||
| Notes payable | $10,000 | ||
| Total liabilities | $24,550 | ||
| Owner's Equity: | |||
| DD's capital | $100,450 | ||
| Total liabilities and Owner's equity | $125,000 | ||
Table (3)
4.
Calculate the following measures of performance and financial condition for 20-3:
- (a) Current ratio
- (b) Quick ratio
- (c) Working capital
- (d) Return on owners’ equity
- (e) Accounts receivable and average collection period
- (f) Inventory turnover and average number of days required to sell inventory
Explanation of Solution
(a)
Current ratio: The financial ratio which evaluates the ability of a company to pay off the debt obligations which mature within one year or within completion of operating cycle is referred to as current ratio. This ratio assesses the liquidity of a company.
Calculate current ratio.
(b)
Calculate quick ratio.
Quick ratio: The financial ratio which evaluates the ability of a company to pay off the instant debt obligations is referred to as quick ratio. Quick assets are cash, marketable securities, and accounts receivables. This ratio assesses the short-term liquidity of a company.
(c)
Calculate working capital.
Working capital: Working capital refers to the excess amount of current assets over its current liabilities of a business. It measures the excess funds that are required for the companies to carry out their day to day operations, excluding any new funds that have been invested during the year.
(d)
Calculate the return on owner’s equity.
(e)
Calculate accounts receivable turnover.
Calculate average collection period.
(f)
Calculate inventory turnover.
Calculate average number of days required to sell inventory.
6.
Open an income summary account, and post adjusting entries and closing entries in the income summary account.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and balance sheet accounts (assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity) to maintain the records according to accrual basis principle.
Prepare adjusting entries.
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| December 31 | Income summary | $31,300 | |
| Merchandise inventory | $31,300 | ||
| December 31 | Merchandise inventory | $28,000 | |
| Income summary | $28,000 | ||
| December 31 | Sales returns and allowances | $200 | |
| Customer refunds payable | $200 | ||
| December 31 | Income summary | $1,000 | |
| Estimated returns inventory | $1,000 | ||
| December 31 | Estimated returns inventory | $1,100 | |
| Income summary | $1,100 | ||
| December 31 | Office supplies expense | $600 | |
| Office Supplies | $600 | ||
| December 31 | Insurance expense | $400 | |
| Prepaid insurance | $400 | ||
| December 31 | Depreciation expense - Store equipment | $5,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation - Store equipment | $5,000 | ||
| December 31 | Wages expense | $200 | |
| Wages payable | $200 | ||
| December 31 | Unearned show revenue | $700 | |
| Rent revenue | $700 |
Table (4)
Prepare income summary account.
| INCOME SUMMARY ACCOUNT | |||||
| Date | Item | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Debit | Credit | ||||
| December 31 | Adjusting entry | $31,300 | $31,300 | ||
| December 31 | Adjusting entry | $28,000 | ($3,300) | ||
| December 31 | Adjusting entry | $1,000 | ($4,300) | ||
| December 31 | Adjusting entry | $1,100 | ($3,200) | ||
| December 31 | Closing entry | $207,950 | $204,750 | ||
| December 31 | Closing entry | $179,100 | $25,650 | ||
| December 31 | Closing entry | $25,650 | |||
Table (5)
7.
Prepare closing entries of DD.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries: The journal entries prepared to close the temporary accounts to Retained Earnings account are referred to as closing entries. The revenue, expense, and dividends accounts are referred to as temporary accounts because the information and figures in these accounts is held temporarily and consequently transferred to permanent account at the end of accounting year.
Prepare closing entries of DD.
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| December 31 | Rent Revenue | $5,700 | |
| Sales | $201,500 | ||
| Purchase returns and allowances | $750 | ||
| Income summary | $207,950 | ||
| December 31 | Income summary | $179,100 | |
| Sales returns and allowances | $6,100 | ||
| Purchases | $72,000 | ||
| Rent expense | $42,000 | ||
| Freight in | $1,200 | ||
| Wages expense | $42,200 | ||
| Office supplies expense | $600 | ||
| Phone expense | $1,500 | ||
| Utilities expense | $7,600 | ||
| Insurance expense | $400 | ||
| Depreciation expense - Store Equipment | $5,000 | ||
| Interest expense | $500 | ||
| December 31 | Income summary | $25,650 | |
| DD's Capital | $25,650 | ||
| December 31 | DD's Capital | $21,000 | |
| DD's Drawings | $21,000 |
Table (6)
8.
Prepare reversing entries for the adjustments where appropriate.
Explanation of Solution
Reversing entry: Entries made on the first day of the next accounting cycle, and it abridges the recording transactions in the different period. It is an opposite of adjusting entry.
Prepare reversing entries.
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| January 1 -20-4 | Wages payable | $200 | |
| Wages expense | $200 |
Table (7)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
College Accounting - Study Guide / Working Papers 1-15
- Calculate the number of units that must be sold in order to realize an operating income of $150,000 when fixed costs are $480,000 and the unit contribution margin is $25. Right Answerarrow_forwardCompute the predetermined overhead rate for the yeararrow_forwardVector Industries used 8,200 machine hours (Driver) on Job #25. Total machine hours are 24,500. Assume Job #25 is the only job sold during the accounting period. What is the overhead applied in COGS if the total overhead applied is $156,500?arrow_forward
- A company produces a single product. Variable production costs are $15.5 per unit, and variable selling and administrative expenses are $5.0 per unit. Fixed manufacturing overhead totals $60,000, and fixed selling and administration expenses total $55,000. Assuming a beginning inventory of zero, production of 6,000 units, and sales of 4,500 units, the dollar value of the ending inventory under variable costing would be_. Currect answerarrow_forwardA company produces a single product. Variable production costs are $15.5 per unit, and variable selling and administrative expenses are $5.0 per unit. Fixed manufacturing overhead totals $60,000, and fixed selling and administration expenses total $55,000. Assuming a beginning inventory of zero, production of 6,000 units, and sales of 4,500 units, the dollar value of the ending inventory under variable costing would be_. Want a solutionarrow_forwardOverhead costs:960000, direct materials costs:320000arrow_forward
- The Blue Jay Corporation has annual sales of $5,200, total debt of $1,500, total equity of $2,800, and a profit margin of 8 percent. What is the return on assets? Accurate Answerarrow_forwardThe Blue Jay Corporation has annual sales of $5,200, total debt of $1,500, total equity of $2,800, and a profit margin of 8 percent. What is the return on assets? Don't Use Aiarrow_forwardAt the beginning of the year, manufacturing overhead for the year was estimated to be $810,000. At the end of the year, actual direct labor hours for the year were 40,000 hours, the actual manufacturing overhead for the year was $780,000, and the manufacturing overhead for the year was overapplied by $30,000. If the predetermined overhead rate is based on direct labor hours, then the estimated direct labor hours at the beginning of the year used in the predetermined overhead rate must have been ____ hours. ANSWERarrow_forward
- Compute the company's plantwide predetermined overhead rate for the yeararrow_forwardSuppose in its 2022 annual report that Burger Haven Corporation reports beginning total assets of $32.80 billion, ending total assets of $35.40 billion, net sales of $25.60 billion, and net income of $5.20 billion. What is Burger Haven's return on assets and asset turnover? Need helparrow_forwardSuppose in its 2022 annual report that Burger Haven Corporation reports beginning total assets of $32.80 billion, ending total assets of $35.40 billion, net sales of $25.60 billion, and net income of $5.20 billion. What is Burger Haven's return on assets and asset turnover? Accurate Answerarrow_forward
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT





