Concept explainers
Consider the following bromination:
a. Calculate
b. Draw out a stepwise mechanism for the reaction, including the initiation, propagation, and termination steps.
c. Calculate
d. Draw an energy diagram for the propagation steps.
e. Draw the structure of the transition state of each propagation step.
(a)
Interpretation: The value of
Concept introduction: The value of
Answer to Problem 15.53P
The value of
Explanation of Solution
The given bromination reaction is,
In the given reaction,
The value of
Where,
•
•
The bond dissociation energy of
The bond dissociation energy of
The bond dissociation energy of
The bond dissociation energy of
Substitute the bond dissociation energy of
Therefore, the value of
The value of
(b)
Interpretation: The stepwise mechanism for the given reaction which includes initiation, propagation and termination steps is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The general steps followed by free-radical reaction are stated below:
1. First step is initiation that involves formation of radical.
2. Second step is propagation.
3. Third step is the termination that involves the formation of stable bond.
Answer to Problem 15.53P
The stepwise mechanism for the given reaction which includes initiation, propagation and termination steps is,
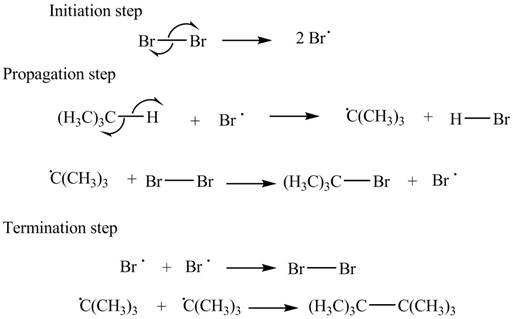
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
The initiation step involves the generation of bromine radical by hemolytic cleavage of
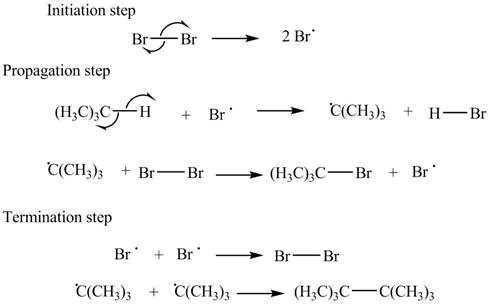
Figure 1
The stepwise mechanism for the given reaction which includes initiation, propagation and termination steps is shown in Figure 1.
(c)
Interpretation: The value of
Concept introduction: The general steps followed by free-radical reaction are stated below:
1. First step is initiation that involves formation of radical.
2. Second step is propagation.
3. Third step is the termination that involves the formation of stable bond.
Answer to Problem 15.53P
The value of
Explanation of Solution
The propagation step of given reaction involves two steps. In the first step
The value of
Where,
•
•
The bond dissociation energy of
The bond dissociation energy of
The bond dissociation energy of
The bond dissociation energy of
The value of
The value of
The value of
(d)
Interpretation: The energy level diagram for the propagation steps is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The graphical representation of chemical reaction in which x-axis represents energy of the reaction and y-axis represents the reaction coordinate is called energy profile diagram.
Answer to Problem 15.53P
The energy level diagram for the propagation steps is,
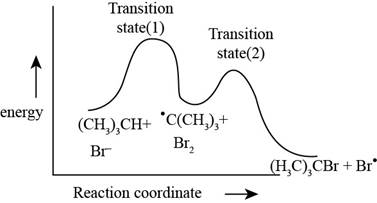
Figure 2
Explanation of Solution
The energy level diagram for the propagation steps is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2
The energy level diagram for the propagation steps is shown in Figure 2.
(e)
Interpretation: The structure of transition state of each propagation step is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The general steps followed by free-radical reaction are stated below:
1. First step is initiation that involves formation of radical.
2. Second step is propagation.
3. Third step is the termination that involves the formation of stable bond.
Answer to Problem 15.53P
The structure of transition state of first and second propagation step is,
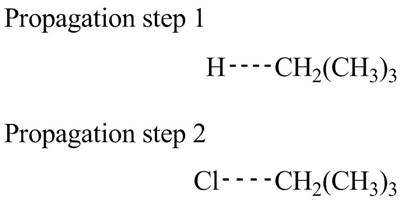
Figure 3
Explanation of Solution
The propagation step of given reaction involves two steps. In the first step
The transition state of the first propagation step is,
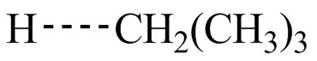
Figure 4
The transition state of the first propagation step is,
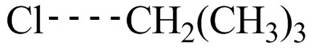
Figure 5
The structure of transition state of first and second propagation step is shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5, respectively.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
PKG ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- -Page: 8 nsition metal ions have high-spin aqua complexes except one: [Co(HO)₁]". What is the d-configuration, oxidation state of the metal in [Co(H:O))"? Name and draw the geometry of [Co(H2O)]? b) Draw energy diagrams showing the splitting of the five d orbitals of Co for the two possible electron configurations of [Co(H2O)]: Knowing that A = 16 750 cm and Пl. = 21 000 cm, calculate the configuration energy (.e., balance or ligand-field stabilization energy and pairing energy) for both low spin and high spin configurations of [Co(H2O)]. Which configuration seems more stable at this point of the analysis? (Note that 349.76 cm = 1 kJ/mol) Exchange energy (IT) was not taken into account in part (d), but it plays a role. Assuming exchange an occur within t29 and within eg (but not between tz, and ea), how many exchanges are possible in the low in configuration vs in the high spin configuration? What can you say about the importance of exchange energy 07arrow_forwardDraw everything please on a piece of paper explaining each steparrow_forwardDefine crystalline, polycrystalline and amorphous materials What crystal system and Bravais lattices are shown in the figure immediately below? What do a, b, C, a, ẞ and y represent and what are their values? You can label the Bravais lattices directly above or under the figure. C aarrow_forward
- 32. The diagrams below show the band structure of an intrinsic semiconductor at absolute zero and room temperature. Room Temperature EF E OK Ep- a) In the space below, sketch a similar pair of diagrams for an n-type semiconductor. D) Give the definition and an example of (i) an intrinsic semiconductor and (ii) an n-type semiconductor.arrow_forward29. a) i Which energy diagram best represents the d-electrons in tetrahedral [Co(NH3)4]²+? b) ii c) iii d) iv 11 ་ ↑↓ ↑t t ↑↓ ↑↓ e) none of these ii In1 According to Slater's rules, what is the effective nuclear charge experienced by a 3d electron in 30. Ge? a) 32.00 b) 21.15 c) 16.05 d) 14.00 e) 10.85arrow_forwardRegarding Lowis structuros and geometrios, Draw Lewis structures for the following: SOF4, SO, ICI, XeO2F4, SeF and XeO3. For each one, indicate the observed molecular geometry it adopts.arrow_forward
- Explain the following statements with equations: - The fusion product of an organic compund with sodium metal is an alkaline solution - The test for elements should be done before the solubility tests. - Using less sodium than the organic compound in the ignition test might cause a problem to detect the presence of the nitrogen and sulfur - Formation of colored product when adding ferric acid chloride to phenol solutionarrow_forward31 Indicate the symbol, mass number and the atomic number of the missing product in each of the following nuclear reactions. a) 13/3 N 41 b) 11 Ca 20 c) 90 38 Sr → 133 C + ? + - 6 0 e →? 90 Y + ? 39 11 d) 22 Na → ? + + 1 B +1 β Toarrow_forwardPlease drawarrow_forward
- 9. compore the Following two Venctions IN termy Of Ronction Rate and explan in detail the reasoning that led to your conclusion +He p₁₂ 11- ㅐ 15 .. +He H #H H / H b. Compare the Following too reactions 14 terms of reaction Rate and explain in detail the reasoning that led to your conclusion Н d-C- tłu Na +2446 е -ll +2n "Harrow_forwarda. •Write all of the possible products For the Following ronction А ----- H - H H + H₂0 H+ Н b. in Rite the complete reaction Mechaniszn For the Formation of each product. ·C. Suggest what Reaction conditions could Result in each product being the major Product of the veaction:arrow_forwarda. Write the product For each of the Following reactions H 6-836-6 레 +H₂ N A H A-C-C=C-C-CH + 2 Na +2 NH3 - H H b. Write the reaction Mechanism For. reaction eacharrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
