
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
From the given compounds, compounds with higher value of solubility has to be identified and the reason for the higher value of solubility has to be explained.
The given compounds are chloroethane and methylethylamine.
Concept Introduction:
The physical properties are determined by the intermolecular forces, polarity of the compound and hydrogen bonding. If a compound is polar and have hydrogen bonding, the solubility will be more for that compound than in non-polar compounds.
Intermolecular forces:
The forces which acts in between the atoms to hold a molecule are said to be intermolecular forces. They are weak forces. Intermolecular forces are categorized as hydrogen bonding, ionic bonding, ion-induced dipole forces, ion-dipole forces and Vanderwaal forces.
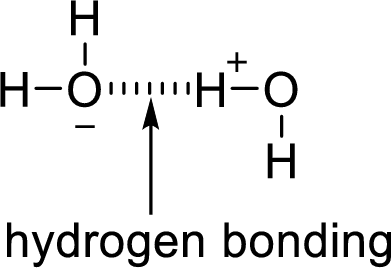
Hydrogen bonding:
The attraction between a lone pair of hydrogen atom with that of an electronegative atom forms hydrogen bonding. Two water molecules are held together by hydrogen bond.
(b)
Interpretation:
From the given compounds, compounds with higher value of melting point has to be identified and the reason for the higher value of melting point has to be explained.
The given compounds are diethyl ether and 1-butanol.
Concept Introduction:
The physical properties are determined by the intermolecular forces, polarity of the compound and hydrogen bonding. If a compound is polar and have hydrogen bonding, the melting point will be more for that compound than in non-polar compounds.
Intermolecular forces:
The forces which acts in between the atoms to hold a molecule are said to be intermolecular forces. They are weak forces. Intermolecular forces are categorized as hydrogen bonding, ionic bonding, ion-induced dipole forces, ion-dipole forces and Vanderwaal forces.
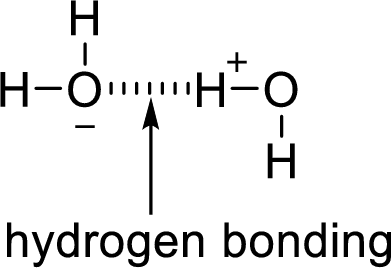
Hydrogen bonding:
The attraction between a lone pair of hydrogen atom with that of an electronegative atom forms hydrogen bonding. Two water molecules are held together by hydrogen bond.
(c)
Interpretation:
From the given compounds, compounds with higher value of boiling point has to be identified and the reason for the higher value of boiling point has to be explained.
The given compounds are trimethylamine and propylamine.
Concept Introduction:
The physical properties are determined by the intermolecular forces, polarity of the compound and hydrogen bonding. If a compound is polar and have hydrogen bonding, the boiling point will be more for that compound than in non-polar compounds.
Intermolecular forces:
The forces which acts in between the atoms to hold a molecule are said to be intermolecular forces. They are weak forces. Intermolecular forces are categorized as hydrogen bonding, ionic bonding, ion-induced dipole forces, ion-dipole forces and Vanderwaal forces.
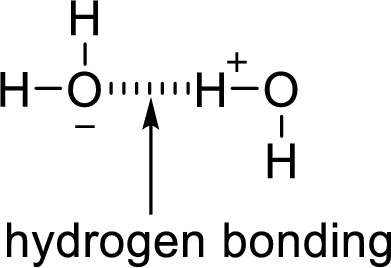
Hydrogen bonding:
The attraction between a lone pair of hydrogen atom with that of an electronegative atom forms hydrogen bonding. Two water molecules are held together by hydrogen bond.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
CHEMISTRY:MOLECULAR...V.2 W/ACCESS
- Draw a mechanism for the following synthetic transformation including reagents and any isolable intermediates throughout the process. Please clearly indicate bond cleavage/formation using curly arrows. MeO2Carrow_forwardCHEM 310 Quiz 8 Organic Chemistry II Due: Tuesday, April 25th, at 11:59 pm. This quiz is open textbook / open notes - but you must work alone. You cannot use the internet or the solutions manual for the book. Scan in your work and record an explanation of your mechanism. You may record this any way that you like. One way would be to start an individual Zoom meeting, start recording, "share your screen" and then talk through the problem. This will be converted to an .mp4 file that you can upload into Canvas using the "record/upload media" feature. Pyridine, benzoic acid and benzene are dissolved in ethyl acetate. Design and provide a plan / flow chart for separating and isolating each of these components. Pyridine and benzene are liquids at room temperature. Benzoic acid is a solid. You have ethyl acetate, 2M NaOH, 2M HCI and anhydrous MgSO4 available, as well as all the glassware and equipment that you used in the organic lab this year. Provide accurate acid/base reactions for any…arrow_forwardCan anyone help me solve this step by step. Thank you in advaarrow_forward
- Please draw the mechanism for this Friedel-crafts acylation reaction using arrowsarrow_forwardDraw the Fischer projection of D-fructose. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Skip Part Check AP 14 tv SC F1 F2 80 F3 a F4 ! 2 # 3 CF F5 75 Ax MacBook Air 894 $ 5olo % Λ 6 > W F6 K F7 &arrow_forwardConsider this step in a radical reaction: Y What type of step is this? Check all that apply. Draw the products of the step on the right-hand side of the drawing area below. If more than one set of products is possible, draw any set. Also, draw the mechanism arrows on the left-hand side of the drawing area to show how this happens. ionization propagation initialization passivation none of the abovearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





