
(a)
Interpretation:
The molecular geometry, polarity and the strongest intermolecular force present in
Concept introduction:
Geometry of a molecule is the arrangement of atoms of a molecule in space. Geometry is dependent on the number of bond pairs, lone pairs and valence electrons of central atom. Polarity is defined as the tendency of atoms of a molecule to attract the electrons of the bond pairs towards itself.
Answer to Problem 15.3TC
The geometry, polarity and intermolecular force present in
Geometry is tetrahedral.
Polarity of methane is zero. It means
The strongest intermolecular force present is induced dipole.
Explanation of Solution
Methane,
Structure of methane is shown below.
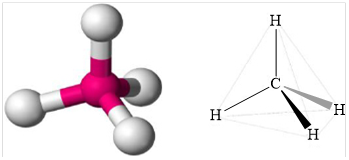
Figure 1
Therefore, methane is tetrahedral, non-polar and strongest intermolecular forces are induced dipole.
Geometry of methane is tetrahedral methane is non polar and the strongest intermolecular force present in methane is induced dipole.
(b)
Interpretation:
The geometry, polarity and the strongest intermolecular force present in
Concept introduction:
Geometry of a molecule of a molecule is the arrangements of atoms of a molecule in space. Geometry is depends on the number of bond pairs, lone pairs and valence electrons of central atom. Polarity is defined as the tendency of atoms of a molecule to attract the bond pairs towards itself.
Answer to Problem 15.3TC
The geometry, polarity and the strongest intermolecular force present in
Geometry is linear.
Polarity of carbon dioxide is zero. It means
Strongest intermolecular force present is induced dipole.
Explanation of Solution
Carbon dioxide
Structure of carbon dioxie is shown below.
![]()
Figure 2
Therefore, carbon dioxide is linear, non-polar and the strongest intermolecular force present is induced dipole.
Geometry of carbon dioxide is linear, polarity is zero means non polar molecule and the strongest intermolecular force present is induced dipole.
(c)
Interpretation:
The geometry, polarity and the strongest intermolecular force present in
Concept introduction:
Geometry of a molecule of a molecule is the arrangements of atoms of a molecule in space. Geometry is depends on the number of bond pairs, lone pairs and valence electrons of central atom. Polarity is defined as the tendency of atoms of a molecule to attract the bond pairs towards itself.
Answer to Problem 15.3TC
The geometry, polarity and intermolecular force present in
Geometry is bent.
Polarity of
Strongest intermolecular force present in
Explanation of Solution
Oxygen difluoride
Structure of oxygen difluoride is shown below.
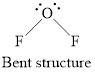
Figure 3
Therefore, oxygen difluoride is bent, polar, and the strongest intermolecular force present is dipole-dipole.
Geometry of oxygen difluoride is bent, polarity is non-zero means polar molecule and the strongest intermolecular force present is dipole dipole interaction.
(d)
Interpretation:
The geometry, polarity and the strongest intermolecular force present in
Concept introduction:
Geometry of a molecule of a molecule is the arrangements of atoms of a molecule in space. Geometry is depends on the number of bond pairs, lone pairs and valence electrons of central atom. Polarity is defined as the tendency of atoms of a molecule to attract the bond pairs towards itself.
Answer to Problem 15.3TC
The geometry, polarity and intermolecular force present in
Geometry is bent.
Polarity of
The strongest intermolecular force present is hydrogen bonding.
Explanation of Solution
Chloric acid
Structure of chloric acid is shown below.
![]()
Figure 4
Therefore, chloric acid is bent, polar and the strongest force present is hydrogen bonding.
Geometry of chloric acid is bent, polarity is non-zero means polar molecule and the strongest intermolecular force present is hydrogen bonding.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning





