
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of 3,3-dimethylbutane has to be drawn and correct name has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
The hydrocarbons which contains only single bonds are said to be
The Alkanes are named following some rules:
- The name of the alkane is given by the number of carbon atoms present in the chain. It is said to be Root of the alkane.
Root = number of carbon atoms in chain.
- To name the root, for one carbon atom, the root name use is meth-. For two carbon atoms, the root name is eth-, for three carbon atoms, it is prop-, for four carbon atoms, it is but-, for five carbon atoms, it is pent- and so on.
- The carbon chain is numbered in a way that the substituents get lowest number possible.
- The root name is followed by Suffix. Suffix indicates the
functional group present in the compound. It is placed after the root name.
Suffix = name of the functional group present in the compound.
- The root name also contains Prefix. Prefix is the groups attached to the root. It indicates the branched carbon atoms on the root chain and name according to the root specifying the carbon number on which it is placed. It contains –yl in name end. The prefix is placed before the root name.
Prefix = name of the branched carbon atoms on chain.
- The name of the alkane is given in the form
Prefix + Root + Suffix
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 3,3-dimethylbutane.
The structure of 3,3-dimethylbutane is given as the four carbon chain with two methyl groups as substituents at third carbon. According to the given name the structure will be given as
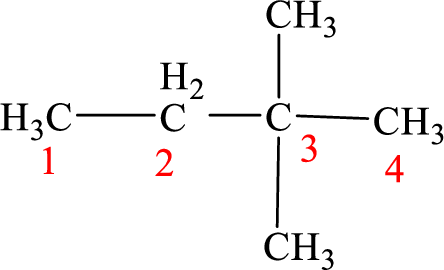
According to systematic nomenclature, the carbon chain should be numbered in a way that the substituents get lowest number possible. Hence, in butane four carbons are there in a chain and the methyl groups attached to the chain will get second number on the chain. So, the correct name is 2,2-dimethylbutane.
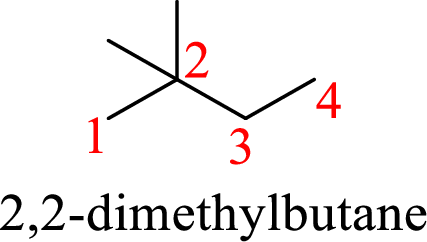
The name of the compound based on systematic nomenclature should be 2,2-dimethylbutane.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of 1,1,1-trimethylheptane has to be drawn and correct name has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
The hydrocarbons which contains only single bonds are said to be Alkanes. The general formula for alkanes can be given as
The Alkanes are named following some rules:
- The name of the alkane is given by the number of carbon atoms present in the chain. It is said to be Root of the alkane.
Root = number of carbon atoms in chain.
- To name the root, for one carbon atom, the root name use is meth-. For two carbon atoms, the root name is eth-, for three carbon atoms, it is prop-, for four carbon atoms, it is but-, for five carbon atoms, it is pent- and so on.
- The carbon chain is numbered in a way that the substituents get lowest number possible.
- The root name is followed by Suffix. Suffix indicates the functional group present in the compound. It is placed after the root name.
Suffix = name of the functional group present in the compound.
- The root name also contains Prefix. Prefix is the groups attached to the root. It indicates the branched carbon atoms on the root chain and name according to the root specifying the carbon number on which it is placed. It contains –yl in name end. The prefix is placed before the root name.
Prefix = name of the branched carbon atoms on chain.
- The name of the alkane is given in the form
Prefix + Root + Suffix
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 1,1,1-trimethylheptane.
The structure of 1,1,1-trimethylheptane is given as the seven carbon chain with three methyl groups as substituents at first carbon. The structure will be given as
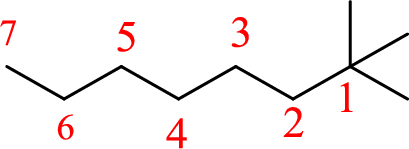
According to systematic nomenclature, the carbon chain should be numbered in a way that the carbon chain should consists of more carbon atoms and substituents get lowest number possible.
In 1,1,1-trimethylheptane, the carbon chain consists only seven carbons with three methyl groups on first carbon. But according to the nomenclature, the carbon chain will be octane and the substituent groups are methyl groups on second carbon. The correct structure of the compound can be given as
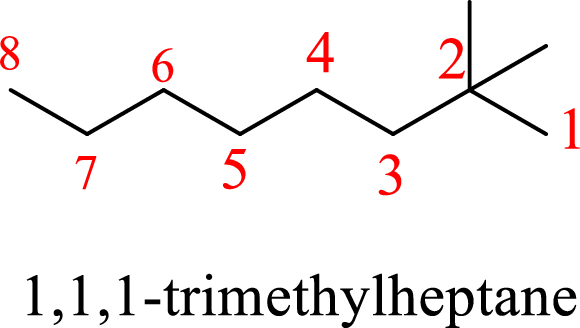
The name of the compound based on systematic nomenclature should be 2,2-dimethyloctane.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of 1,4-diethylcyclopentane has to be drawn and correct name has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
The hydrocarbons which contains only single bonds are said to be Alkanes. The general formula for cycloalkanes can be given as
The cycloalkanes are named following some rules:
- The name of the cycloalkane is given by the number of carbon atoms present in the ring. It is said to be Root of the cycloalkane.
Root = number of carbon atoms in ring.
- To name the root, for one carbon atom, the root name use is meth-. For two carbon atoms, the root name is eth-, for three carbon atoms, it is prop-, for four carbon atoms, it is but-, for five carbon atoms, it is pent- and so on.
- The carbon ring is numbered in a way that the carbon with substituents get the first number in the ring.
- The root name is followed by Suffix. Suffix indicates the functional group present in the compound. It is placed after the root name.
Suffix = name of the functional group present in the compound.
- The root name also contains Prefix. Prefix is the groups attached to the root. It indicates the branched carbon atoms on the root chain and name according to the root specifying the carbon number on which it is placed. It contains –yl in name end. The prefix is placed before the root name.
Prefix = name of the branched carbon atoms on chain.
- The name of the alkane is given in the form
Prefix + Root + Suffix
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 1,4-diethylcyclopentane.
The structure of 1,4-diethylcyclopentane is given as the five carbon ring with two ethyl groups as substituents at first and fourth carbon atoms. The structure will be given as
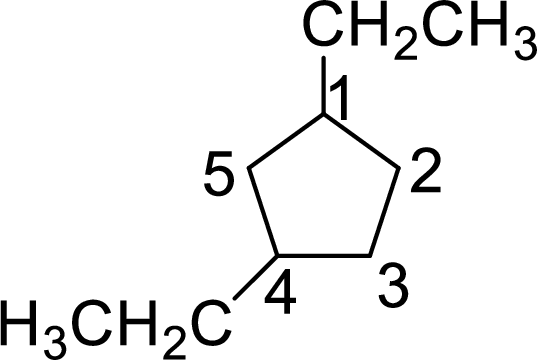
According to systematic nomenclature, the carbon ring should be numbered in a way that the substituent containing carbon is considered as first carbon and the second substituent should get the lowest number possible in the ring.
In 1,4-diethylcyclopentane, one ethyl group is on first carbon and other ethyl group is on fourth carbon. But according to the nomenclature the substituent containing carbon is considered as first carbon and the second substituent should get the lowest number possible in the ring. The correct structure of the compound can be given as
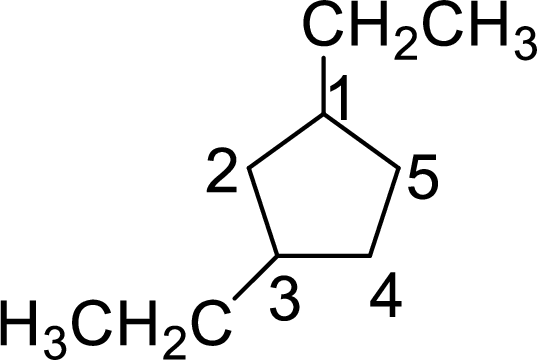
The name of the compound based on systematic nomenclature should be 1,3-diethylcyclopentane.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of 1-propylcyclohexane has to be drawn and correct name has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
The hydrocarbons which contains only single bonds are said to be Alkanes. The general formula for cycloalkanes can be given as
The cycloalkanes are named following some rules:
- The name of the cycloalkane is given by the number of carbon atoms present in the ring. It is said to be Root of the cycloalkane.
Root = number of carbon atoms in ring.
- To name the root, for one carbon atom, the root name use is meth-. For two carbon atoms, the root name is eth-, for three carbon atoms, it is prop-, for four carbon atoms, it is but-, for five carbon atoms, it is pent- and so on.
- The carbon ring is numbered in a way that the carbon with substituents get the first number in the ring.
- The root name is followed by Suffix. Suffix indicates the functional group present in the compound. It is placed after the root name.
Suffix = name of the functional group present in the compound.
- The root name also contains Prefix. Prefix is the groups attached to the root. It indicates the branched carbon atoms on the root chain and name according to the root specifying the carbon number on which it is placed. It contains –yl in name end. The prefix is placed before the root name.
Prefix = name of the branched carbon atoms on chain.
- The name of the alkane is given in the form
Prefix + Root + Suffix
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 1-propylcyclohexane.
The structure of 1-propylcyclohexane is given as the six carbon ring with a propyl group as substituent at first carbon atom. The structure will be given as
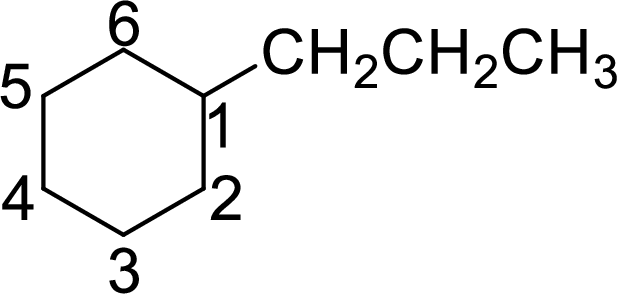
According to systematic nomenclature, the carbon ring should be numbered in a way that the substituent containing carbon is considered as first carbon.
The name of the compound based on systematic nomenclature should be 1-propylcyclohexane. But it is not necessary to mention the number of the substituent on the ring (if only one substituent is present) as it will get the first position. Hence, the name of the compound will be propylcyclohexane.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
CHEMISTRY(LOOSELEAF) W/CONNECT+EBOOK
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. LDA (-78°C) ? 2. Br Some notes: • Draw only the major product, or products. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. . • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds where necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • If there are no products, just check the box under the drawing area. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardPlease draw the structuresarrow_forwardDraw the missing intermediates 1 and 2, plus the final product 3, of this synthesis: 0 1. Eto 1. Eto- 1 2 2. MeBr 2. EtBr H3O+ A 3 You can draw the three structures in any arrangement you like. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- Draw the missing intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this synthesis: 1. MeO- H3O+ 1 2 2. PrBr Δ You can draw the two structures in any arrangement you like. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the differences between: Glyceride and phosphoglyceride Wax and Fat Soap and Fatty acid HDL and LDL cholesterol Phospho lipids and sphingosine What are the types of lipids? What are the main lipid components of membrane structures? How could lipids play important rules as signaling molecules and building units? The structure variety of lipids makes them to play significant rules in our body, conclude breifly on this statement.arrow_forwardWhat is the differences between DNA and RNA for the following: - structure - function - type What is the meaning of: - replication - transcription - translation show the base pair connection(hydrogen bond) in DNA and RNAarrow_forward
- What is the IP for a amino acid- give an example what are the types of amino acids What are the structures of proteins The N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Try-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val- Tyr- Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forwardWhat is the IP for a amino acid- give an example what are the types of amino acids What are the structures of proteins The N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Try-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val- Tyr- Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forward> aw the missing intermediates 1 and 2, plus the final product 3, of this synthesis: 1. Eto 1. EtO¯ H3O+ 1 2 2. PrBr 2. PrBr Δ You can draw the three structures in any arrangement you like. 3 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Explanation Check 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacarrow_forward
- There are various factors that affect an equilibrium. Give 3 of these factors and explain using examples andequations how an equilibrium is affected by these factors. Please remember that this is a communication question so that you are communicating your understanding of the factors that affect and equilibrium.arrow_forwardEEZE LETCHUP ID Draw the most likely conjugate base resulting from this acid-base reaction. Include all lone pairs. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Drawing く NaOCH2CH3 :0: :0: 狗arrow_forwardAnswerarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





