
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of 4-methylhexane has to be drawn and correct name has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
The hydrocarbons which contains only single bonds are said to be
The Alkanes are named following some rules:
- The name of the alkane is given by the number of carbon atoms present in the chain. It is said to be Root of the alkane.
Root = number of carbon atoms in chain.
- To name the root, for one carbon atom, the root name use is meth-. For two carbon atoms, the root name is eth-, for three carbon atoms, it is prop-, for four carbon atoms, it is but-, for five carbon atoms, it is pent- and so on.
- The carbon chain is numbered in a way that the substituents get lowest number possible.
- The root name is followed by Suffix. Suffix indicates the
functional group present in the compound. It is placed after the root name.
Suffix = name of the functional group present in the compound.
- The root name also contains Prefix. Prefix is the groups attached to the root. It indicates the branched carbon atoms on the root chain and name according to the root specifying the carbon number on which it is placed. It contains –yl in name end. The prefix is placed before the root name.
Prefix = name of the branched carbon atoms on chain.
- The name of the alkane is given in the form
Prefix + Root + Suffix
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 4-methylhexane.
The structure of 4-methylhexane is given as the six carbon chain with a methyl group as substituent at fourth carbon. The structure will be given as
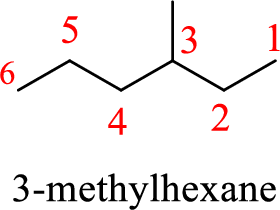
According to systematic nomenclature, the carbon chain should be numbered in a way that the substituents get lowest number possible. Hence, in hexane six carbons are there in a chain and the methyl group attached to the chain will get third number on the chain. So, the correct name is 3-methylhexane.
The name of the compound based on systematic nomenclature should be 3-methylhexane.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of 2-ethylpentane has to be drawn and correct name has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
The hydrocarbons which contains only single bonds are said to be Alkanes. The general formula for alkanes can be given as
The Alkanes are named following some rules:
- The name of the alkane is given by the number of carbon atoms present in the chain. It is said to be Root of the alkane.
Root = number of carbon atoms in chain.
- To name the root, for one carbon atom, the root name use is meth-. For two carbon atoms, the root name is eth-, for three carbon atoms, it is prop-, for four carbon atoms, it is but-, for five carbon atoms, it is pent- and so on.
- The carbon chain is numbered in a way that the substituents get lowest number possible.
- The root name is followed by Suffix. Suffix indicates the functional group present in the compound. It is placed after the root name.
Suffix = name of the functional group present in the compound.
- The root name also contains Prefix. Prefix is the groups attached to the root. It indicates the branched carbon atoms on the root chain and name according to the root specifying the carbon number on which it is placed. It contains –yl in name end. The prefix is placed before the root name.
Prefix = name of the branched carbon atoms on chain.
- The name of the alkane is given in the form
Prefix + Root + Suffix
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 2-ethylpentane.
The structure of 2-ethylpentane is given as the five carbon chain with an ethyl group as substituent at second carbon. The structure will be given as
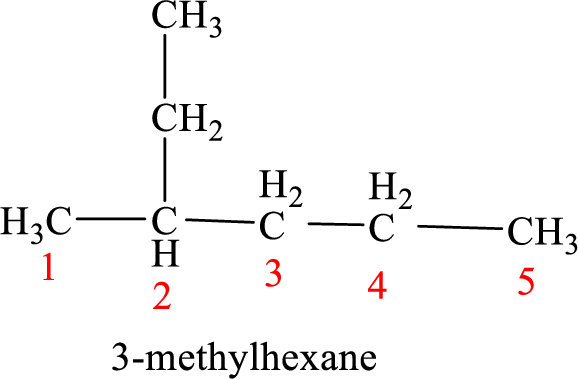
According to systematic nomenclature, the carbon chain should be numbered in a way that the carbon chain should consists of more carbon atoms and substituents get lowest number possible.
In 2-ethylpentane, the carbon chain consists only five carbons with an ethyl group on second carbon. But according to the nomenclature, the carbon chain will be hexane and the substituent group is methyl on third carbon. The correct structure of the compound can be given as
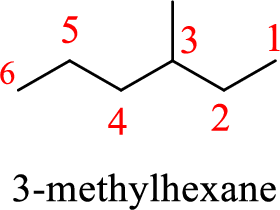
The name of the compound based on systematic nomenclature should be 3-methylhexane.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of 2-methylcyclohexane has to be drawn and correct name has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
The hydrocarbons which contains only single bonds are said to be Alkanes. The general formula for cycloalkanes can be given as
The cycloalkanes are named following some rules:
- The name of the cycloalkane is given by the number of carbon atoms present in the ring. It is said to be Root of the cycloalkane.
Root = number of carbon atoms in ring.
- To name the root, for one carbon atom, the root name use is meth-. For two carbon atoms, the root name is eth-, for three carbon atoms, it is prop-, for four carbon atoms, it is but-, for five carbon atoms, it is pent- and so on.
- The carbon ring is numbered in a way that the carbon with substituents get the first number in the ring.
- The root name is followed by Suffix. Suffix indicates the functional group present in the compound. It is placed after the root name.
Suffix = name of the functional group present in the compound.
- The root name also contains Prefix. Prefix is the groups attached to the root. It indicates the branched carbon atoms on the root chain and name according to the root specifying the carbon number on which it is placed. It contains –yl in name end. The prefix is placed before the root name.
Prefix = name of the branched carbon atoms on chain.
- The name of the alkane is given in the form
Prefix + Root + Suffix
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 2-methylcyclohexane.
The structure of 2-methylcyclohexane is given as the six carbon ring with a methyl group as substituent at second carbon. The structure will be given as
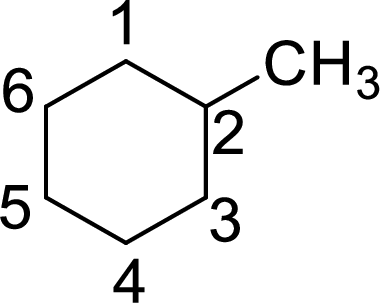
According to systematic nomenclature, the carbon ring should be numbered in a way that the substituent containing carbon is considered as first carbon.
In 2-methylcyclohexane, methyl group on second carbon. But according to the nomenclature, the carbon with methyl group as substituent will be first carbon in the ring. The correct structure of the compound can be given as
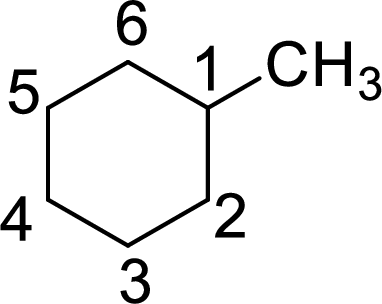
The name of the compound based on systematic nomenclature should be 1-methylcyclohexane. But it is not necessary to mention the number of the substituent on the ring (if only one substituent is present) as it will get the first position. The name of the compound can be given as methylcyclohexane.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of 3,3-methyl-4-ethyloctane has to be drawn and correct name has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
The hydrocarbons which contains only single bonds are said to be Alkanes. The general formula for alkanes can be given as
The Alkanes are named following some rules:
- The name of the alkane is given by the number of carbon atoms present in the chain. It is said to be Root of the alkane.
Root = number of carbon atoms in chain.
- To name the root, for one carbon atom, the root name use is meth-. For two carbon atoms, the root name is eth-, for three carbon atoms, it is prop-, for four carbon atoms, it is but-, for five carbon atoms, it is pent- and so on.
- The carbon chain is numbered in a way that the substituents get lowest number possible.
- The root name is followed by Suffix. Suffix indicates the functional group present in the compound. It is placed after the root name.
Suffix = name of the functional group present in the compound.
- The root name also contains Prefix. Prefix is the groups attached to the root. It indicates the branched carbon atoms on the root chain and name according to the root specifying the carbon number on which it is placed. It contains –yl in name end. The prefix is placed before the root name.
Prefix = name of the branched carbon atoms on chain.
- The name of the alkane is given in the form
Prefix + Root + Suffix
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 3,3-methyl-4-ethyloctane.
The structure of 3,3-methyl-4-ethyloctane is given as the eight carbon chain with two methyl groups as substituents at third carbon and an ethyl group as substituent at fourth carbon. The structure will be given as
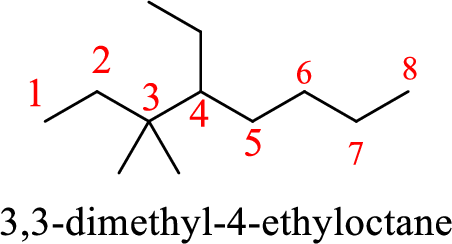
According to systematic nomenclature, the carbon chain should be numbered in a way that the carbon chain should consists of more carbon atoms and substituents get lowest number possible. If two same groups are present as substituents on same carbon atom or different carbon atoms, prefix –di is used to mention the number of groups along with the carbon chain number on which they are present.
The structure of the given compound is correct but the name is wrong. The two methyl groups are present on the same carbon atom in the chain. To mention the number of methyl group’s present prefix –di- has to be added to the methyl.
The name of the compound based on systematic nomenclature should be 3,3-dimethyl-4-ethyloctane.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
CHEM 212:CHEMISTSRY V 2
- Done 19:17 www-awu.aleks.com Chapter 12 HW Question 29 of 39 (6 points) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimited .III LTE סוי 27 28 = 29 30 31 32 = 33 34 35 Consider this structure. CH3CH2CH2 Part 1 of 3 3 CH2 CH2CH3 - C-CH2CH 3 H CH₂ Give the IUPAC name of this structure. 3-ethyl-3,4-dimethylheptane Part: 1/3 Part 2 of 3 Draw the skeletal structure. Skip Part < Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Save For Later Submit © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Хarrow_forward18:57 .III LTE www-awu.aleks.com Chapter 12 HW Question 31 of 39 (8 points) | Question Attem... Give the IUPAC name of each compound. Part 1 of 4 Part 2 of 4 Х Х Check Save For Later Submit © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. TOMS OF US vacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? CH3-C-CH2-NH2 + R - CH3 O: 0 CH3-N-CH2-C-NH-CH2-C-CH3 + H2O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume no products other than those shown above are formed. Explanation Check Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accesarrow_forward
- Done 18:17 • www-awu.aleks.com Chapter 12 HW Question 24 of 39 (4 points) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimited ▼ 20 ✓ 21 × 22 23 24 25 26 raw the structure corresponding to each IUPAC name. Part 1 of 2 .III LTE 22 27 28 סוי 29 29 3 A skeletal structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-ethyl-4-methylhexane. Part 2 of 2 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. A condensed structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 2,2,4- trimethylpentane. Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. Check Save For Later Submit < Х ப: G © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility : Garrow_forwardDone 18:25 www-awu.aleks.com .III LTE Chapter 12 HW Question 29 of 39 (6 points) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimi... Oli 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Consider this structure. CH2 CH2CH2 CH2CH2CH₂ C -C. -CH2CH3 H CH Part: 0 / 3 Part 1 of 3 Give the IUPAC name of this structure. Skip Part < Check ☑ Save For Later © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility ....................arrow_forwardCalculate Ecell at 25.0 oC using the following line notation. Zn(s)|Zn+2(aq, 0.900 M)||Cu+2(aq, 0.000200 M)|Cu(s)arrow_forward
- Predict the product of this organic reaction: O OH + H + OH A P + H2O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of P. If there isn't any P because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X G ☐ :arrow_forward0.0994 g of oxalic acid dihydrate is titrated with 10.2 mL of potassium permanganate. Calculate the potassium permanganate concentration. Group of answer choices 0.0433 M 0.135 M 0.0309 M 0.193 Marrow_forwardExperts...can any one help me solve these problems?arrow_forward
- According to standard reduction potential data in Lecture 4-1, which of the following species is the most difficult to reduce? Group of answer choices Zn2+ AgCl(s) Al3+ Ce4+arrow_forwardWhich Group 1 metal reacts with O2(g) to form a metal peroxide (M2O2)? Group of answer choices Li K Rb Naarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is true regarding the reaction between Group 1 metals and water? Group of answer choices These reactions result in a basic solution. The metals do not actually react easily with water due to the metals' lack of conductivity. These reaction result in an acidic solution. The metals need their outer coatings of metal oxides to react.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





