
The dependence of the equilibrium constant of a reaction on temperature is given by the van't Hoff equation:
where C is a constant. The following table gives the equilibrium constant
KP |
138 |
5.12 |
0.436 |
0.0626 |
0.0130 |
TOO |
600 |
700 |
800 |
900 |
1000 |
(a) Determine graphically the
How does this equation support the prediction based on Le Châ�telier's principle about the shift in equilibrium with temperature? (c) The vapor pressures of water are 31.82 mmHg at
Interpretation:
The
Concept Introduction:
Achemical equilibrium is a state of the chemical reaction when the rate of forward reaction becomes equal to the rate of reverse reaction and the concentrations of the products and reactants become constant, which are known as equilibrium concentrations.
When energy is released in a reaction, the reaction is called exothermic, and the reactions in which energy is absorbed are endothermic reactions.
According to Le Chatelier’s Principle, when a system at equilibrium is subjected to any change, the system tries to undo the effect of that change by shifting its equilibrium in the desired direction.
The van't Hoff equation provides information about the temperature dependence of the equilibrium constant.
Answer to Problem 125AP
Solution:
(a)
(b)
According to Le Chatelier’s principles, increase in temperature favors the forward endothermic reaction, and decrease in temperature favors an exothermic reaction.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
a)The
The
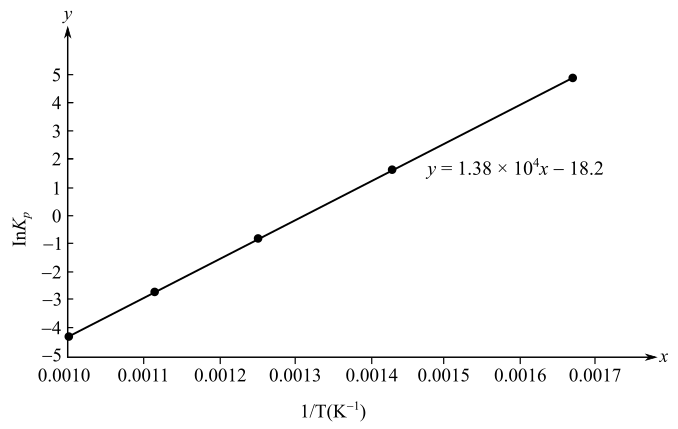
The slope of the plot is
Here,
Substitute the values of
The
b)The following equation support the prediction based on Le-Chatelier’s principle about the shift in equilibrium with temperature
The vant Hoff’s equation at two different temperatures is
Here,
From (1) and (2):
An endothermic reaction has
Then, temperature is
In a reversible reaction at equilibrium, when the equilibrium constant is more, the products are also more or the rate constant of forward reaction is more, and hence the products are more. According to LeChatelier’s principle, an increase in temperature favors endothermic reaction, and a decrease in temperature favors exothermic reaction.
c) Molar heat of vaporization of water
The vapor pressure of water is
From vant’s Hoff equation,
Here,
Substitute the values of
On further solving
The molar heat ofvaporization of water is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Chemistry
- Gramicidin A can adopt more than one structure; NMR spectroscopy has revealed an “end-to-end” dimer form, and x-ray crystallography has revealed an “anti-parallel double- helical” form. Briefly outline and describe an experimentalapproach/strategy to investigate WHICH configuration (“end-to-end dimer” vs “anti-paralleldouble helical”) gramicidin adopts in an actual lipid bilayer.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forwardCHEM2323 Problem 2-24 Tt O e: ל Predict the product(s) of the following acid/base reactions. Draw curved arrows to show the formation and breaking of bonds. If the bonds needed are not drawn out, you should redraw them. + BF3 (a) (b) HI + (c) OH -BF Problem 2-25 Use curved arrows and a proton (H+) to draw the protonated form of the following Lewis bases. Before starting, add all missing lone pairs. (a) (b) :0: (c) N 1 CHEM2323 PS CH02 Name:arrow_forward
- CHEM2323 Problem 2-26 Tt O PS CH02 Name: Use the curved-arrow formalism to show how the electrons flow in the resonance form on the left to give the one on the right. (Draw all lone pairs first) (a) NH2 NH2 + (b) Problem 2-27 Double bonds can also act like Lewis bases, sharing their electrons with Lewis acids. Use curved arrows to show how each of the following double bonds will react with H-Cl and draw the resulting carbocation. (a) H2C=CH2 (b) (c) Problem 2-28 Identify the most electronegative element in each of the following molecules: (a) CH2FCI F Problem 2-29 (b) FCH2CH2CH2Br (c) HOCH2CH2NH2 (d) CH3OCH2Li F 0 0 Use the electronegativity table in Figure 2.3 to predict which bond in the following pairs is more polar and indicate the direction of bond polarity for each compound. (a) H3C-Cl or Cl-CI (b) H3C-H or H-CI (c) HO-CH3 or (CH3)3Si-CH3 (d) H3C-Li or Li-OHarrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- at 32.0 °C? What is the osmotic pressure (in atm) of a 1.46 M aqueous solution of urea [(NH2), CO] at 3 Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardReagan is doing an atomic absorption experiment that requires a set of zinc standards in the 0.4-1.6 ppm range. A 1000 ppm Zn solution was prepared by dissolving the necessary amount of solid Zn(NO3)2 in water. The standards can be prepared by diluting the 1000 ppm Zn solution. Table 1 shows one possible set of serial dilutions (stepwise dilution of a solution) that Reagan could perform to make the necessary standards. Solution A was prepared by diluting 5.00 ml of the 1000 ppm Zn standard to 50.00 ml. Solutions C-E are called "calibration standards" because they will be used to calibrate the atomic absorption spectrometer. a. Compare the solution concentrations expressed as ppm Zn and ppm Zn(NO3)2. Compare the concentrations expressed as M Zn and M Zn(NO3)2 - Which units allow easy conversion between chemical species (e.g. Zn and Zn(NO3)2)? - Which units express concentrations in numbers with easily expressed magnitudes? - Suppose you have an analyte for which you don't know the molar…arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781285199030Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781285199030Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning





