
(a)
Interpretation: The reagents are to be identified for Synthesis of Racemic mixture of
Concept Introduction:
Epoxides are obtained by the conversion of
Epoxides from Peroxy acids:
The commonly used Peroxy acids are meta-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid (MCPBA) and Peroxyacetic acid. This process is stereospecific.
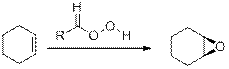
Specifically, the substituent are cis to each other in starting Alkene remains cis to each other in Epoxide, and the substituent’s are trans to each other in starting Alkene remains trans to each other in Epoxide.
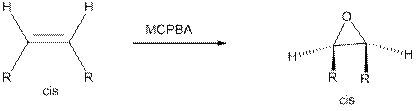
Epoxides from Halohydrins:
Epoxides can be obtained by the conversion of Alkene to Halohydrins. Halohydrins are formed when an Alkene is treated with halogen in presence of Water. Halohydrins formed are later treated with strong base to from Epoxides.
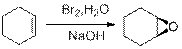
(b)
Interpretation: The reagents are to be identified for Synthesis of Racemic mixture of Epoxides.
Concept Introduction:
Epoxides are obtained by the conversion of Alkene using Peroxy acids and Halohydrins
Epoxides from Peroxy acids:
The commonly used Peroxy acids are meta-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid (MCPBA) and Peroxyacetic acid. This process is stereospecific.
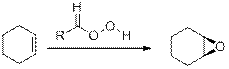
Specifically, the substituent are cis to each other in starting Alkene remains cis to each other in Epoxide, and the substituent’s are trans to each other in starting Alkene remains trans to each other in Epoxide.
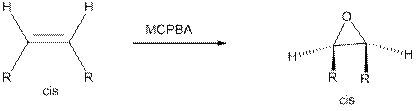
Epoxides from Halohydrins:
Epoxides can be obtained by the conversion of Alkene to Halohydrins. Halohydrins are formed when an Alkene is treated with halogen in presence of Water. Halohydrins formed are later treated with strong base to from Epoxides.
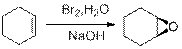
(c)
Interpretation: The reagents are to be identified for Synthesis of Racemic mixture of Epoxides.
Concept Introduction:
Epoxides are obtained by the conversion of Alkene using Peroxy acids and Halohydrins
Epoxides from Peroxy acids:
The commonly used Peroxy acids are meta-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid (MCPBA) and Peroxyacetic acid. This process is stereospecific.
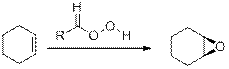
Specifically, the substituent are cis to each other in starting Alkene remains cis to each other in Epoxide, and the substituent’s are trans to each other in starting Alkene remains trans to each other in Epoxide.
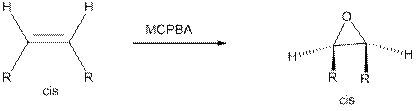
Epoxides from Halohydrins:
Epoxides can be obtained by the conversion of Alkene to Halohydrins. Halohydrins are formed when an Alkene is treated with halogen in presence of Water. Halohydrins formed are later treated with strong base to from Epoxides.
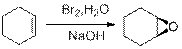
(d)
Interpretation: The reagents are to be identified for Synthesis of Racemic mixture of Epoxides.
Concept Introduction:
Epoxides are obtained by the conversion of Alkene using Peroxy acids and Halohydrins
Epoxides from Peroxy acids:
The commonly used Peroxy acids are meta-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid (MCPBA) and Peroxyacetic acid. This process is stereospecific.
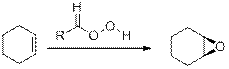
Specifically, the substituent are cis to each other in starting Alkene remains cis to each other in Epoxide, and the substituent’s are trans to each other in starting Alkene remains trans to each other in Epoxide.
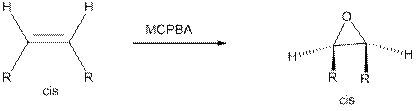
Epoxides from Halohydrins:
Epoxides can be obtained by the conversion of Alkene to Halohydrins. Halohydrins are formed when an Alkene is treated with halogen in presence of Water. Halohydrins formed are later treated with strong base to from Epoxides.
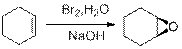
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Binder Ready Version
- What would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forward
- Please complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forwardWhat would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forwardWhat would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forward
- For benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





