
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The given reaction has to be completed by drawing its product structure.
Concept Introduction:
Hydrolysis of Ester:
The reaction in which a bond is broken by the addition of water molecule is called as hydrolysis.
Hydrolysis of esters yields the
The general reaction of ester hydrolysis is shown below,
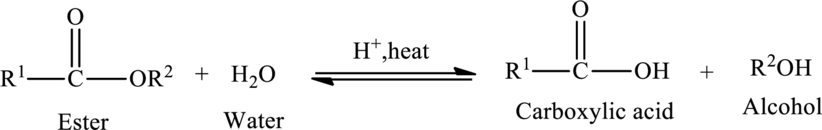
In case of base-catalyzed hydrolysis of an ester, the carboxylic acid does not exist. The reaction results in the formation of salt of carboxylic acid containing the cation of the base catalyst.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given reaction has to be completed by drawing its product structure.
Concept Introduction:
Hydrolysis of Ester:
The reaction in which a bond is broken by the addition of water molecule is called as hydrolysis.
Hydrolysis of esters yields the carboxylic acid and an alcohol. The heat is required to initiate the reaction and a small amount of acid
The general reaction of ester hydrolysis is shown below,
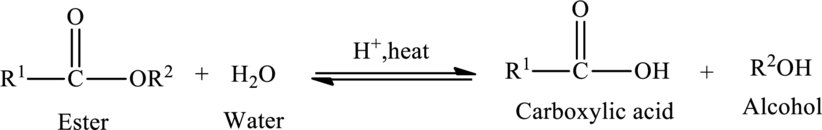
In case of base-catalyzed hydrolysis of an ester, the carboxylic acid does not exist. The reaction results in the formation of salt of carboxylic acid containing the cation of the base catalyst.
(c)
Interpretation:
The given reaction has to be completed by drawing its product structure.
Concept Introduction:
Hydrolysis of Ester:
The reaction in which a bond is broken by the addition of water molecule is called as hydrolysis.
Hydrolysis of esters yields the carboxylic acid and an alcohol. The heat is required to initiate the reaction and a small amount of acid
The general reaction of ester hydrolysis is shown below,
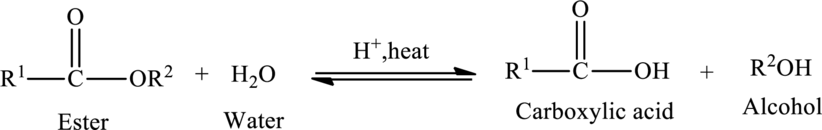
In case of base-catalyzed hydrolysis of an ester, the carboxylic acid does not exist. The reaction results in the formation of salt of carboxylic acid containing the cation of the base catalyst.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given reaction has to be completed by drawing its product structure.
Concept Introduction:
Hydrolysis of Ester:
The reaction in which a bond is broken by the addition of water molecule is called as hydrolysis.
Hydrolysis of esters yields the carboxylic acid and an alcohol. The heat is required to initiate the reaction and a small amount of acid
The general reaction of ester hydrolysis is shown below,
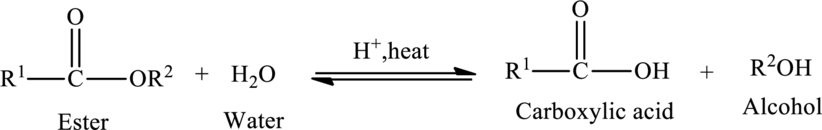
In case of base-catalyzed hydrolysis of an ester, the carboxylic acid does not exist. The reaction results in the formation of salt of carboxylic acid containing the cation of the base catalyst.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
GENERAL, ORGANIC, BIOCHEM (LL W/ ACCESS)
- The reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forwardWhich of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forwardWhich of the following is true for a particular reaction if ∆G° is -40.0 kJ/mol at 290 K and –20.0 kJ/mol at 390 K?arrow_forward
- Choose the major product of the reaction with correct regio- and stereochemistry. Br2 H₂O O "Br Br & O 'Br OH Br 吡 O OH OH Br "OH Brarrow_forwardSelect the major product of the following reaction. & Br (CH)CONa (CH₂),COH 0 OC(CH) O &arrow_forwardDraw the products of the hydrolysis reaction between the ester molecule and water. Determine the products of the following reaction.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





