
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259638091
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek, Phillip J. Cornwell, Brian Self
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14.2, Problem 14.55P
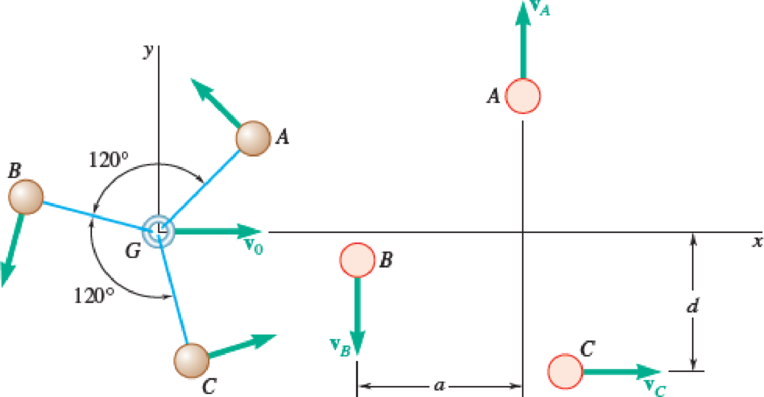
Three small identical spheres A, B, and C, which can slide on a horizontal, frictionless surface, are attached to three strings of length l, which are tied to a ring G. Initially the spheres rotate about the ring, which moves along the x axis with a velocity v0. Suddenly the ring breaks, and the three spheres move freely in the xy plane. Knowing that vA = (8.66 ft/s)j, vC = (15 ft/s)i, a = 0.866 ft, and d = 0.5 ft, determine (a) the initial velocity of the ring, (b) the length l of the strings, (c) the rate in rad/s at which the spheres were rotating about G.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
For the four-bar- linkage shown in the following figure. BC=68mm, CD=100mm, AD=120mm. Determine the range of AB to
make it a crank-rocker mechanism.
B
D
all of those 4 fi
1)Draw kinematic diagram:
2)DOF:
3)type/name of mechanism
4)evolution:
7.4 Impeller viscometer
The rheology of a Penicillium chrysogenum broth is examined using an impeller viscometer. The density of
the cell suspension is approximately 1000 kg m³. Samples of broth are stirred under laminar conditions
using a Rushton turbine of diameter 4 cm in a glass beaker of diameter 15 cm. The average shear rate
generated by the impeller is greater than the stirrer speed by a factor of about 10.2. When the stirrer shaft
is attached to a device for measuring torque and rotational speed, the following results are recorded.
Stirrer speed (s¹) Torque (Nm)
0.185
3.57 × 10-6
0.163
3.45 × 10-6
0.126
3.31 x 10-6
0.111
3.20×10-6
Can the rheology be described using a power-law model? If so, evaluate K and n.
Chapter 14 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Ch. 14.1 - A 30-g bullet is fired with a horizontal velocity...Ch. 14.1 - Two identical 1350-kg automobiles A and B are at...Ch. 14.1 - An airline employee tosses two suitcases in rapid...Ch. 14.1 - Car A weighing 4000 lb and car B weighing 3700 lb...Ch. 14.1 - Two swimmers A and B, of weight 190 lb and 125 lb,...Ch. 14.1 - A 180-lb man and a 120-lb woman stand side by side...Ch. 14.1 - A 40-Mg boxcar A is moving in a railroad...Ch. 14.1 - Two identical cars A and B are at rest on a...Ch. 14.1 - A 20-kg base satellite deploys three...Ch. 14.1 - For the satellite system of Prob. 14.9, assuming...
Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three identical 19.32-lb...Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three identical 19.32-lb...Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three particles A, B, and C....Ch. 14.1 - For the system of particles of Prob. 14.13,...Ch. 14.1 - A 13-kg projectile is passing through the origin O...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.16PCh. 14.1 - A 2-kg model rocket is launched vertically and...Ch. 14.1 - An 18-kg cannonball and a 12-kg cannonball are...Ch. 14.1 - 14.19 and 14.20 Cruiser A was traveling east at 60...Ch. 14.1 - 14.19 and 14.20 Cruiser A was traveling east at 60...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.21PCh. 14.1 - Two spheres, each of mass m, can slide freely on a...Ch. 14.1 - In a game of pool, ball A is moving with a...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.24PCh. 14.1 - Prob. 14.25PCh. 14.1 - In a scattering experiment, an alpha particle A is...Ch. 14.1 - Derive the relation HO=rmv+HG between the angular...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.28PCh. 14.1 - Prob. 14.29PCh. 14.1 - Show that the relation MA=HA, where HA is defined...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the energy lost due to friction and the...Ch. 14.2 - In Prob. 14.3, determine the energy lost (a) when...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.33PCh. 14.2 - Determine the energy lost as a result of the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.35PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.36PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.37PCh. 14.2 - Ball B is suspended from a cord of length l...Ch. 14.2 - A 15-lb block B starts from rest and slides on the...Ch. 14.2 - A 40-lb block B is suspended from a 6-ft cord...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.41PCh. 14.2 - 14.41 and 14.42 In a game of pool, ball A is...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.43PCh. 14.2 - In a game of pool, ball A is moving with the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.45PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.46PCh. 14.2 - Four small disks A, B, C, and D can slide freely...Ch. 14.2 - In the scattering experiment of Prob. 14.26, it is...Ch. 14.2 - Three identical small spheres, each weighing 2 lb,...Ch. 14.2 - Three small spheres A, B, and C, each of mass m,...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.51PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.52PCh. 14.2 - Two small disks A and B of mass 3 kg and 1.5 kg,...Ch. 14.2 - Two small disks A and B of mass 2 kg and 1 kg,...Ch. 14.2 - Three small identical spheres A, B, and C, which...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.56PCh. 14.3 - A stream of water with a density of = 1000 kg/m3...Ch. 14.3 - A jet ski is placed in a channel and is tethered...Ch. 14.3 - Tree limbs and branches are being fed at A at the...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.60PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.61PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.62PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.63PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.64PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.65PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.66PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.67PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.68PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.69PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.70PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.71PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.72PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.73PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.74PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.75PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.76PCh. 14.3 - The propeller of a small airplane has a...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.78PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.79PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.80PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.81PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.82PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.83PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.84PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.85PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.86PCh. 14.3 - Solve Prob. 14.86, assuming that the chain is...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.88PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.89PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.90PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.91PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.92PCh. 14.3 - A rocket sled burns fuel at the constant rate of...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.94PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.95PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.96PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.97PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.98PCh. 14.3 - Determine the distance traveled by the spacecraft...Ch. 14.3 - A rocket weighs 2600 lb, including 2200 lb of...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the altitude reached by the spacecraft...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.102PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.103PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.104PCh. 14 - Three identical cars are being unloaded from an...Ch. 14 - A 50-kg mother and her 26-kg son are sledding down...Ch. 14 - An 80-Mg railroad engine A coasting at 6.5 km/h...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.108RPCh. 14 - Mass C, which has a mass of 4 kg, is suspended...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.110RPCh. 14 - A 6000-kg dump truck has a 1500-kg stone block...Ch. 14 - For the ceiling-mounted fan shown, determine the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.113RPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.114RPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.115RPCh. 14 - A chain of length l and mass m falls through a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (read image)arrow_forward(read image) Answer Providedarrow_forwardThis is part B Part A's question and answer was find moment of inertia (Ix = 3.90×10^5) and radius of gyration (kx = 21.861) Determine the centroid ( x & y ) of the I-section, Calculate the moment of inertia of the section about itscentroidal x & y axes. How or why is this result different fromthe result of a previous problem?arrow_forward
- Determine by direct integration the moment of inertia of theshaded area of figure with respect to the y axis shownarrow_forwardConsider the feedback controlled blending system shown below, which is designed to keep theoutlet concentration constant despite potential variations in the stream 1 composition. The density of all streamsis 920 kg/m3. At the nominal steady state, the flow rates of streams 1 and 2 are 950 and 425 kg/min,respectively, the liquid level in the tank is 1.3 m, the incoming mass fractions are x1 = 0.27, x2 = 0.54. Noticethe overflow line, indicating that the liquid level remains constant (i.e. any change in total inlet flow ratetranslates immediately to the same change in the outlet flow rate). You may assume the stream 1 flowrate andthe stream 2 composition are both constant. Use minutes as the time unit throughout this problem. Identify any controlled variable(s) (CVs), manipulated variable(s) (MVs),and disturbance variable(s) (DVs) in this problem. For each, explain how you know that’show it is classified.CVs: ___________, MVs: _____________, DVs: ______________ b) Draw a block diagram…arrow_forwardA heat transfer experiment is conducted on two identical spheres which are initially at the same temperature. The spheres are cooled by placing them in a channel. The fluid velocity in the channel is non-uniform, having a profile as shown. Which sphere cools off more rapidly? Explain. V 1arrow_forward
- My ID# 016948724 last 2 ID# 24 Last 3 ID# 724 Please help to find the correct answer for this problem using my ID# first write le line of action and then help me to find the forces {fx= , fy= mz= and for the last find the moment of inertial about the show x and y axes please show how to solve step by steparrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724 last 2 ID# 24 Last 3 ID# 724 Please help to find the correct answer for this problem using my ID# first write le line of action and then help me to find the forces and the tension {fx= , fy= mz=arrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724 last 2 ID# 24 Last 3 ID# 724 Please help to find the correct answer for this problem using my ID# first write le line of action and then help me to find the forces {fx= , fy= mz=arrow_forward
- my ID is 016948724 Last 2 ID# 24 Last 3 ID# 724 please help me to solve this problem step by step show me how to solve first wirte the line actions and then find the forces {fx=, fy=, mz= and for the last step find the support reactions and find forcesarrow_forwardUppgift 1 (9p) 3 m 3 m 3 m 3 m H G F 3 m ↑ Dy D B AAY 30° 8 kN Ay Fackverket i figuren ovan är belastat med en punktlast. Bestäm normalkraften i stängerna BC, BG och FG.arrow_forwardThe cardiovascular countercurrent heat exchnager mechanism is to warm venous blood from 28 degrees C to 35 degrees C at a mass flow rate of 2 g/s. The artery inflow temp is 37 degrees C at a mass flow rate of 5 g/s. The average diameter of the vein is 5 cm and the overall heat transfer coefficient is 125 W/m^2*K. Determine the overall blood vessel length needed too warm the venous blood to 35 degrees C if the specific heat of both arterial and venous blood is constant and equal to 3475 J/kg*K.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY