
Concept explainers
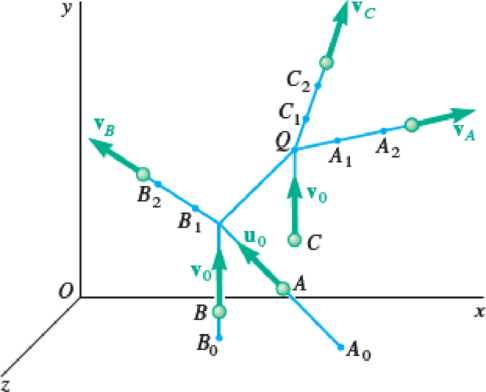
In the scattering experiment of Prob. 14.26, it is known that the alpha particle is projected from A0(300, 0, 300) and that it collides with the oxygen nucleus C at Q(240, 200, 100), where all coordinates are expressed in millimeters. Determine the coordinates of point B0 where the original path of nucleus B intersects the zx plane. (Hint: Express that the angular momentum of the three particles about Q is conserved.)
14.26 In a scattering experiment, an alpha particle A is projected with the velocity u0 = −(600 m/s)i + (750 m/s)j − (800 m/s)k into a stream of oxygen nuclei moving with a common velocity v0 = (600 m/s)j. After colliding successively with the nuclei B and C, particle A is observed to move along the path defined by the points A1 (280, 240, 120) and A2 (360, 320, 160), while nuclei B and C are observed to move along paths defined, respectively, by B1 (147, 220, 130) and B2 (114, 290, 120), and by C1 (240, 232, 90) and C2 (240, 280, 75). All paths are along straight lines and all coordinates are expressed in millimeters. Knowing that the mass of an oxygen nucleus is four times that of an alpha particle, determine the speed of each of the three particles after the collisions.
Fig. P14.26
The coordinates of point
Answer to Problem 14.48P
The coordinates of point
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The velocity of the alpha particle A is
The common velocity of oxygen nuclei is
The alpha particle A projected from
The position of the alpha particle A is
The position of the nuclei B is
The position of the nuclei C is
The mass of an oxygen nucleus is four times that of an alpha particle.
The alpha particle collides with the oxygen nucleus C at
Calculation:
Provide the positions of each point in vector form as shown below.
Sketch the scattering of the alpha and nuclei particles as shown in Figure 1.
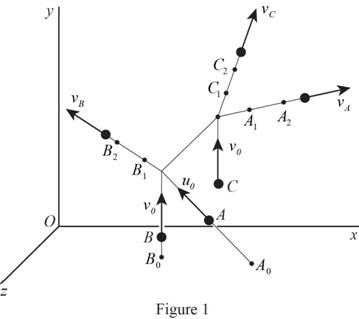
Refer to Figure 1.
Calculate the position vectors as shown below.
Calculate
Substitute
Calculate
Substitute
Calculate
Substitute
Calculate
Substitute
Calculate
Substitute
Calculate
Calculate the unit vector
Substitute
Calculate the unit vectors
Substitute
Calculate the unit vectors
Substitute
Provide the velocity vectors after the collisions as shown below.
Apply the conservation of momentum as shown below.
Substitute
Substitute
Equating the components of
Solve the Equations to get the speed of the particles.
Calculate the velocity vector
Substitute
Apply the conservation of momentum about Q as shown below.
Substitute
Equating the components of
Refer to Figure 1.
Calculate the coordinates of
Coordinate of along x direction.
Substitute
Coordinate of along y direction.
Coordinate of along z direction.
Substitute
Therefore, the coordinates of point
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
VECTOR MECHANIC
- Please sovle this for me and please don't use aiarrow_forwardPlease sovle this for me and please don't use aiarrow_forward3. The cold-drawn AISI 1040 steel bar shown in the figure is subjected to a completely reversed axial load fluctuating between 28 kN in compression to 28 kN in tension. Estimate the fatigue factor of safety based on achieving infinite life (using Goodman line) and the yielding factor of safety. If infinite life is not predicted, estimate the number of cycles to failure. 25 mm + 6-mm D. 10 mmarrow_forward
- CORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE 1. The truss shown is supported by hinge at A and cable at E.Given: H = 4m, S = 1.5 m, α = 75⁰, θ = 33⁰.Allowable tensile stress in cable = 64 MPa.Allowable compressive stress in all members = 120 MPaAllowable tensile stress in all members = 180 MPa1.Calculate the maximum permissible P, in kN, if the diameter of the cable is 20 mm.2.If P = 40 kN, calculate the required area (mm2) of member BC.3. If members have solid square section, with dimension 15 mm, calculate the maximum permissible P (kN) based on the allowable strength of member HI.ANSWERS: (1) 45.6 kN; (2) 83.71 mm2; (3) 171.76 kNarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE 2: A wire 4 meters long is stretched horizontally between points 4 meters apart. The wire is 25 mm2 in cross-section with a modulus of elasticity of 200 GPa. A load W placed at the center of the wire produces a sag Δ.1.Calculate the tension (N) in the wire if sag Δ = 30 mm.2.Calculate the magnitude of W, in N, if sag Δ = 54.3 mm.3. If W is 60 N, what is the sag (in mm)?ANSWERS: (1) 562 N, (2) 100 N, (3) 45.8 Narrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE 4 : A cable and pulley system at D is used to bring a 230-kg pole (ACB) to a vertical position as shown. The cable has tensile force T and is attached at C. The length of the pole is 6.0 m, the outer diameter is d = 140 mm, and the wall thickness t = 12 mm. The pole pivots about a pin at A. The allowable shear stress in the pin is 60 MPa and the allowable bearing stress is 90 MPa. The diameter of the cable is 8 mm.1.Find the minimum diameter (mm) of the pin at A to support the weight of the pole in the position shown.2.Calculate the elongation (mm) of the cable CD.3.Calculate the vertical displacement of point C, in mm.ANSWERS: (1) 6 mm, (2) 1.186 mm, (3) 1.337 mm--arrow_forward
- 1. Derive an expression for H(w) filter or bandpass/reject filter. = for the circuit below. Qualitatively determine if it's a high/lowpass L ell R ww Voarrow_forward2. Obtain the transfer function, H(w) = 0 for the circuit below for R₁ = 1 kQ2, R2 = 10 kQ, and Vi C = 1 μF. What role, if any, does the capacitor play? Explain. R₁ R2 + C + Voarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE 3 (15 points): A 12-meter-long precast pile segment is to be lifted from a trailer down to the ground and then set in place prior to driving by a crane.1. If two slings are to be used in lifting the pile to the ground, at what distance from the ends must the slings be placed for minimum bending due to its own weight?2. At what distance from the ends must the slings be placed for minimum shear due to its own weight?3. Using one sling to set the pile in a vertical position before driving at what distance from one end must the sling be placed for minimum bending due to its own weight?ANSWERS: (1) 2.48 m, (2) 3.00 m, (3) 3.51 marrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





