
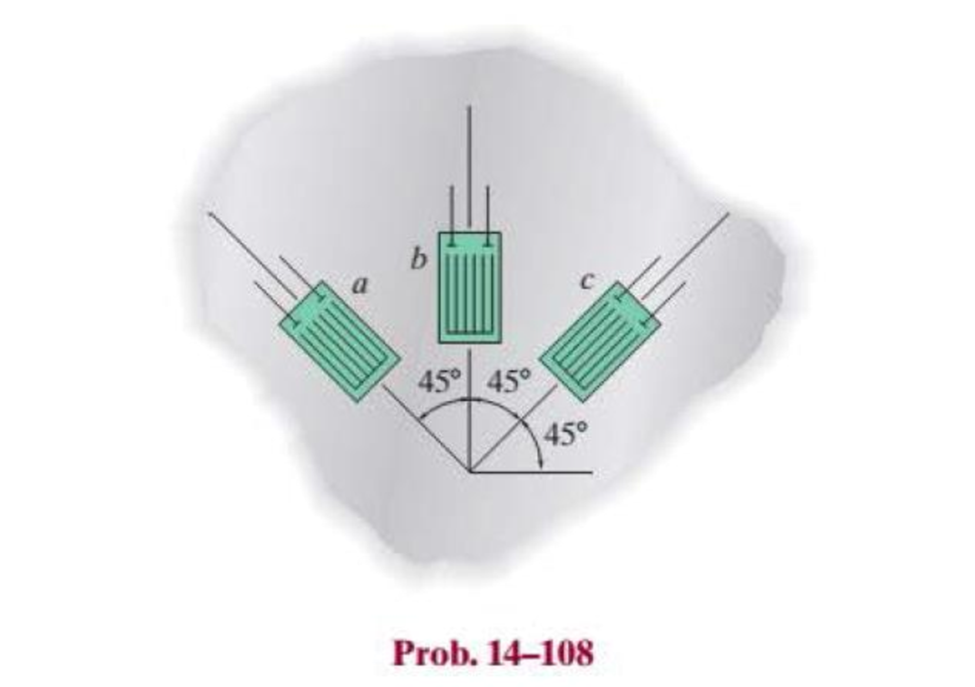
The 45° strain rosette is mounted on the surface of a shell. The following readings are obtained for each gage:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
- A press that delivers 115 strokes per minute, each stroke providing a force of 7826 N throughout a distance of 18 mm. The press efficiency is 90% and is driven by a 1749-rpm motor. Determine average torque that must be provided by the motor in the units of N-m.arrow_forward·3) find the force (P) for the figures (1) and (2) 15cm 10cm 15 h=10mm h2=6mm // Call = 90 N/2 P Agate Fig (i) Ans: 1)P=112614N 2) P=1956.5 N 25cm 25 cm الفترة أو الحجم تمر بالتي عثر اكو تورشن (ک Fig (2) h₁ = 10mm 42=6mm Cmarrow_forwardI want a human solutionarrow_forward
- (Read Image)arrow_forward47 14 16 12 34 10 12 12 33arrow_forward3. A steam power plant has an average monthly net power delivery of 740 MW over the course of a year. This power delivery is accomplished by burning coal in the boiler. The coal has a heating value of 9150 Btu/lbm. The cost of the coal is $14.20/ton. The overall thermal efficiency of the plant is, nth = Wnet Qboiler = 0.26 = 26% Determine the annual cost of the coal required to deliver the given average monthly power.arrow_forward
- 47 14 16 12 34 10 12 12 33arrow_forward= The forces F₁ = 590 lb, F₂ = 380 lb, F3 = 240 lb and F 330 lb. Determine the forces in each member of the truss. Use positive values to indicate tension and negative values to indicate compression. a a a D b F₁ A 000 B. 779977 F₂V H G E F4 b BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 6 ft b 10.1 ft The force in member AB is lb. The force in member AH is lb. The force in member GH is lb. The force in member BH is lb. The force in member BC is lb. The force in member BG is lb. The force in member EG is lb. The force in member CD is lb. The force in member DE is lb. The force in member CE is lb. The force in member CG is lb.arrow_forwardMultiple Choice Circle the best answer to each statement. 1. Which type of surface deviation is controlled by a cy- lindricity tolerance but not by a circularity tolerance? A. B. C. Ovality Taper Lobing D. None of the above 2. When verifying a cylindricity tolerance, the inspec- tion method must be able to collect a set of points and determine the: A. Distance between two coaxial cylinders that con- tain the set of points B. Cylinder that circumscribes the set of points C. Cylinder that inscribes the set of points D. Distance between two coaxial circles that contain the set of points 3. Where Rule #1 applies to a cylindrical regular feature of size, the tolerance value of a cylindricity tolerance applied to the feature of size must be tolerance. A. Less than B. Equal to C. Greater than D. None of the above the size 4. Which of the following modifiers may be applied with a cylindricity tolerance? A. M B. C. ℗ D. Ø 5. Which geometric tolerance can provide an indirect cylindricity…arrow_forward
- The beam AB is attached to the wall in the xz plane by a fixed support at A. A force of F = (−129î + 69.0ĵ + 3591) N is applied to the end of the beam at B. The weight of the beam can be modeled with a uniform distributed load of intensity w = 85.0 N/m acting in the negative z direction along its entire length. Find the support reactions at A. Z с A b a B F y Cc 10 BY NC SA 2016 Eric Davishahl X Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following. table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 5.60 m b 5.00 m C 3.70 m A II = MA = ( m 2.> ~.> + + k) N k) N-arrow_forwardneed help?arrow_forwardA bent pipe is attached to a wall with brackets as shown. A force of F = 180 lb is applied to the end of the tube with direction indicated by the dimensions in the figure. Determine the support reactions at the brackets B, C, and D. Model these brackets as journal bearings (only force reactions perpendicular to the axis of the tube) and neglect couple moment reactions. Assume the distance between the supports at B and C and the tube bends nearby are negligible such that the support at C is directly above the support at D and the dimension g gives the distance between supports B and C. Enter your answers in Cartesian components. 2013 Michael Swanbom cc 10 BY NC SA g h א B 8° У A C x каж Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the table below. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 6.72 in b 11.8 in с 14.8 in d 42.0 in h 26.6 in g 28.0 in → The reaction at B is B = lb. The reaction at C is C = lb. The reaction at D is D = lb. + << + + 2. + + 557 〈んarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





