
(a).
To Find: The nature of changes in the daily high temperature recorded for a week by a weather observatory in a city.
(a).
Answer to Problem 53E
The daily high temperature has increased from Sunday to Monday.
Explanation of Solution
Given Information: The high temperature of a city on Sunday is
Method Used: If two numbers are plotted on the number line, the number to the right is the higher number and the number to the left is the lower number.
Plot
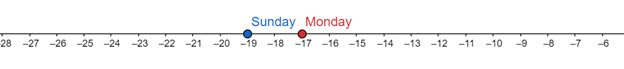
On the above number line, the high temperature corresponding to Monday is to the right of the high temperature corresponding to Sunday. Hence, high the temperature has increased from Sunday to Monday.
(b).
To Find: The nature of changes in the daily high temperature recorded for a week by a weather observatory in a city.
(b).
Answer to Problem 53E
The daily high temperature has decreased from Friday to Saturday.
Explanation of Solution
Given Information: The high temperature of a city on Friday is
Method Used: If two numbers are plotted on the number line, the number to the right is the higher number and the number to the left is the lower number.
Plot
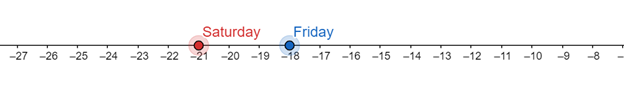
On the above number line, the high temperature corresponding to Saturday is to the left of the high temperature corresponding to Friday. Hence, the high temperature has decreased from Friday to Saturday.
(c).
To Find: The warmest and coldest day of the city in a week from the temperatures recorded by a weather observatory
(c).
Answer to Problem 53E
The hottest day is Wednesday and the coldest day is Saturday.
Explanation of Solution
Given Information: The temperature recordings for each day of the week.
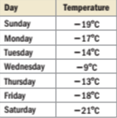
Method: When a group of numbers are plotted on a number line, the highest number is the rightmost number and the lowest number is the leftmost number.
Plot the daily high temperatures of all the seven days of the week on a number line.
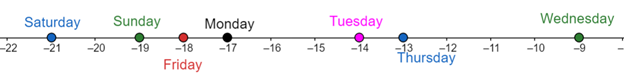
The leftmost number is
The rightmost number is
(d).
To Find: Periods of two or more days of consecutive increase or decrease in daily high temperature, if any, from the temperatures recorded for a week by a weather observatory in a city.
(d).
Answer to Problem 53E
The daily high temperature has increased for three consecutive days from Sunday to Wednesday and then it decreased for three consecutive days from Wednesday to Saturday.
Explanation of Solution
Given: The daily high temperatures recorded on seven days of a week were plotted in the previous sub-part as shown below.
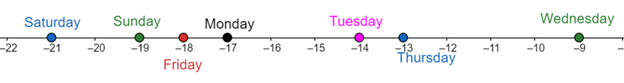
Method: If two numbers are plotted on the number line, the number to the right is the higher number and the number to the left is the lower number.
In the above number line, the temperature corresponding to
- Monday is to the right of Sunday.
- Tuesday is to the right of Monday.
- Wednesday is to the right of Tuesday.
So, the daily high temperature has consistently increased for
Also, in the above number line, the temperature corresponding to
- Thursday is to the left of Wednesday.
- Friday is to the left of Thursday.
- Saturday is to the left of Friday.
So, the daily high temperature has consistently decreased for
Chapter 1 Solutions
EP PRE-ALGEBRA,COMMON CORE-1 YEAR CODE
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- Safari File Edit View History Bookmarks Window Help Ο Ω OV O mA 0 mW ర Fri Apr 4 1 222 tv A F9 F10 DII 4 F6 F7 F8 7 29 8 00 W E R T Y U S D பட 9 O G H J K E F11 + 11 F12 O P } [arrow_forwardSo confused. Step by step instructions pleasearrow_forwardIn simplest terms, Sketch the graph of the parabola. Then, determine its equation. opens downward, vertex is (- 4, 7), passes through point (0, - 39)arrow_forward
- In simplest way, For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. a) y = x 2 + 16 x + 39 b) y = 5 x2 - 50 x - 120arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step Write each quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = - 4( x + 6)2 + 36arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. 1) y = - 2 x2 - 28 x + 64 2) y = 6 x2 + 36 x - 42arrow_forward
- Write each relation in standard form a)y = 5(x + 10)2 + 7 b)y = 9(x - 8)2 - 4arrow_forwardIn simplest form and step by step Write the quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = 3(x - 1)2 - 147arrow_forwardStep by step instructions The path of a soccer ball can be modelled by the relation h = - 0.1 d 2 + 0.5 d + 0.6, where h is the ball’s height and d is the horizontal distance from the kicker. a) Find the zeros of the relation.arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





