
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure of Otezla needs to be completed.
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structure shows the arrangement of total number of valence electrons in a molecule. The electrons involved in bonding are known as bonding electrons and these are represented as bonds or line between two atoms (bonded together). On the other hand, electrons which are not involved in the bonding are known as lone pair of electrons. They are represented as dots (in pair) on symbol of an atom.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is as follows:
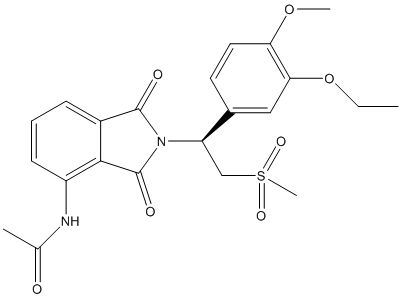
Here, C, N, O and S atoms are present. The number of valence electrons of C, N, O and S atom is 4, 5, 6 and 6 respectively.
In the given molecule, C atom will form 4 covalent bonds so all its electrons will be represented as bond pairs, O atom will form 2 lone pair and 2 bond pair of electrons, S atom will have all the valence electrons involved in bonding and N atom will have 1 lone pair of electrons and 3 bond pairs.
The distribution of valence electrons is represented as follows:
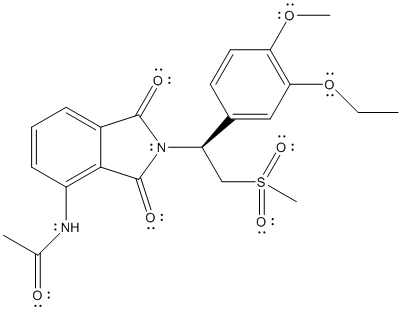
Here, all the oxygen atoms will have 2 lone pair of electrons, N atom will have 1 lone pair of electrons and there will be no valence electrons on S atom.
(b)
Interpretation:In the structure of Otezla, the atom which is exception to octet rule needs to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
In the Lewis structure of a molecule, total number of valence electrons are distributed such that all the atoms have complete octets. In complete octet, atoms have 8 valance electrons in their outermost shell (except H which has 2 electrons).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The complete Lewis structure of Otezla is as follows:
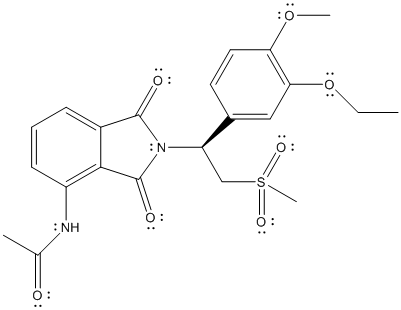
Here, all the valence electrons of C atoms are involved in bonding, oxygen atom has 2 lone pair of electrons and 2 bond pairs, N atom has 1 lone pair of electrons and 3 bond pairs. Thus, C, O and N atoms have complete octet. The only atom with exception to the octet rule is S. The total number of valence electrons on S atom is 6 thus, it can share 2 electrons with other atoms to complete the octet like O atom but, here S is involved in 2 double bonds with 2 O atoms and 2 single bonds with 2 C atom. The total number of electrons involved will be 12 which is exception to octet rule.
(c)
Interpretation: The valence-shell electron-pair repulsion model needs to be used to predict all the bond angles in Otezla.
Concept Introduction:
The valence-shell electron pair repulsion model is used to determine the hybridization, geometry and bond angles of central atoms in given structure.
To determine the hybridization, total number of bond pairs and lone pair of electrons are determined for a central atom. Depending on the total number of electron pair, hybridization is decided. Each hybridization corresponds to a geometry and respective bond angle.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The complete Lewis structure of Otezla is as follows:
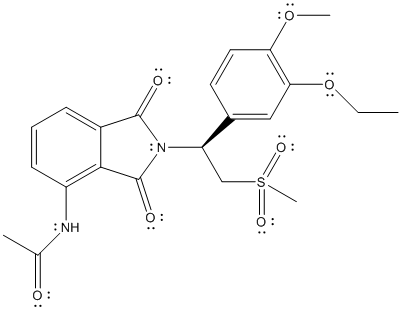 T
T
Here, the C atom with 4 single bonds is
All the bond angles are represented in Lewis structure as follows:
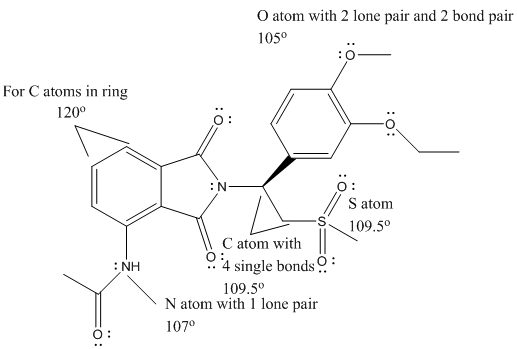
(d)
Interpretation: Whether Otezla is polar or non-polar needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction: In a molecule, if there is difference in electronegativity between atoms then it is said to be polar in nature. In other way, if polar bonds are present in the molecule, then it is considered as a polar molecule.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
A molecule is said to be polar if there are polar bonds present in it. A bond is said to be polar if there is difference in electronegativity value of two bonded atoms.
The given structure is as follows:
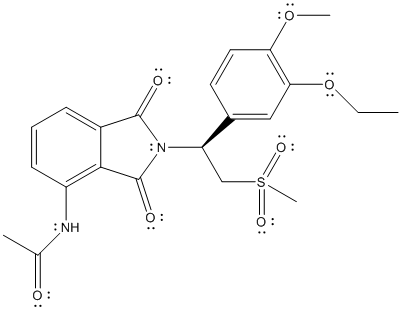
There is no electronegativity difference between C and H atom. The electronegative atoms in the above molecule are N, O and S atom.
Thus, N-C, N-H, C-O and C-S are polar bonds and molecule will be polar in nature.
(e)
Interpretation: The two resonance structures of Otezla needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction: The resonance structures are possible in a molecule if there are lone pair of electrons and alternate pi bonds are present.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
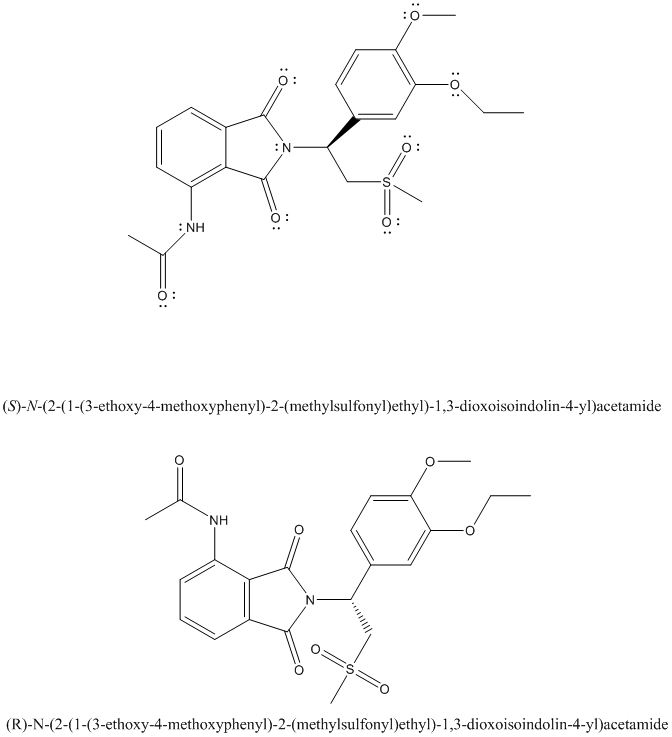
The complete Lewis structure of Otezla is as follows:
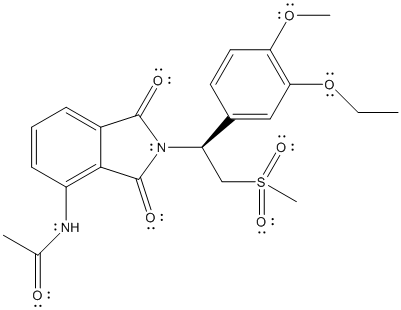
Two resonance structures are as follows:
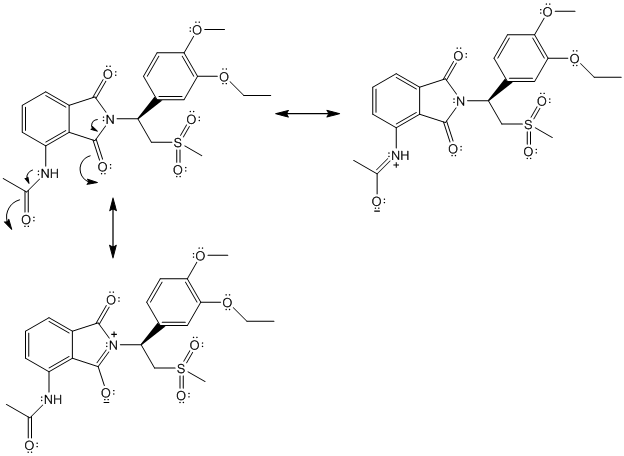
(f)
Interpretation: The molecular formula of Otezla needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: The molecular formula of a molecule can be determined from its structure. Total number of atoms of same atoms can be determined from the structure and formula can be determined.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
The complete Lewis structure of Otezla is as follows:
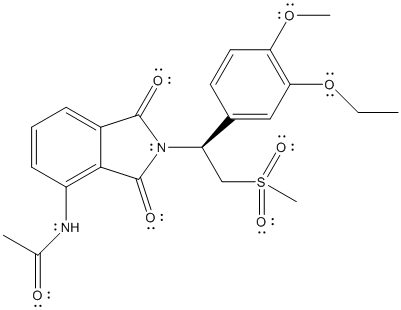
In the above structure, there are C, H, N, O and S atoms. By calculating the total number of atoms in the molecule, molecular formula can be calculated.
The molecular formula of the molecule will be
(g)
Interpretation: The intermolecular forces present between Otezla molecules needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: The intermolecular forces are type of interactions between the molecules. Non-polar molecules only have London dispersion forces and polar molecules can have other interactions as well like hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, Van der Waals forces etc.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
The complete Lewis structure of Otezla is as follows:
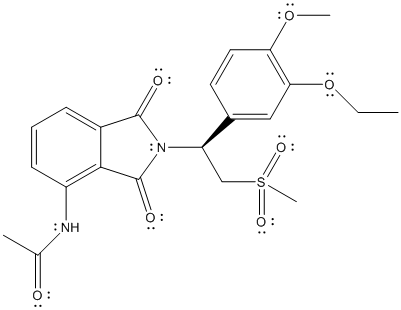
Due to the presence of non-polar bonds, London dispersion forces are present in the molecules. Also due to N-H bond, hydrogen bonding is possible between the molecules.
(h)
Interpretation: The stereocenter of Otezla needs to be identified as R or S.
Concept Introduction:
The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog system is a set of rules that allows us to unambiguously define the stereochemical configuration of any stereocenter, using the designations 'R ' (from the Latin rectus, meaning right-handed) or ' S ' (from the Latin sinister, meaning left-handed).
In the first step, priority is given to 4 different groups attached to the stereocenter. The direction of 4th priority group should be away from the observer. In the second step, direction from 1 to 3 priority group is determined. If the direction is clockwise, the configuration will be R and if it is anticlockwise, the configuration will be S.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
The complete Lewis structure is represented as follows:
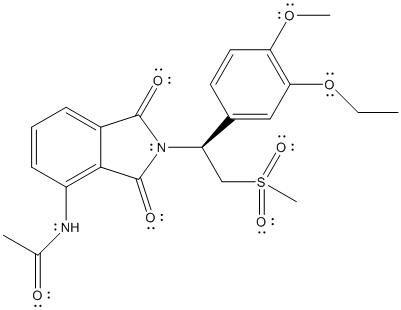
The stereocenter is point where 4 different substituents are present on a carbon atom. Molecules with stereocenter are known as chiral molecules.
The chiral center is labelled as follows:
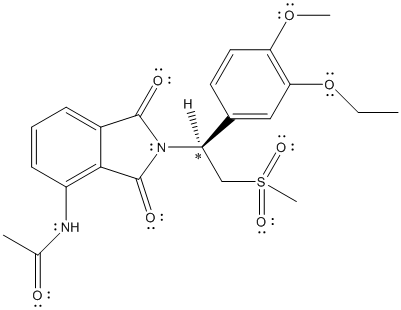
The numbering according to priority rules will be:
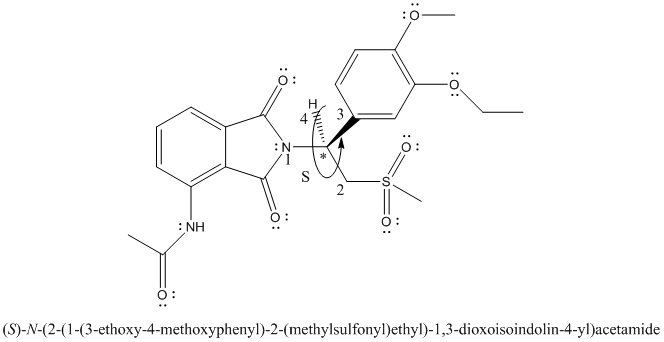
The direction from 1 to 3 priority group is anticlockwise thus, the configuration is S.
(i)
Interpretation: The enantiomer of Otezla needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The chirality in a group in a molecule results in the formation of two enantiomers. These enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror image of each other.
(i)
Explanation of Solution
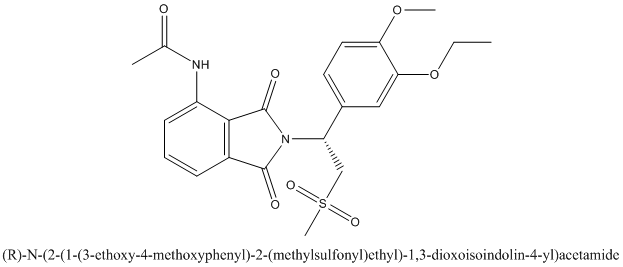
The enantiomer of Otezla will be R configuration and it is represented as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
INTRO.TO GENERAL,ORGAN...-OWLV2 ACCESS
- Assign all the carbonsarrow_forward9 7 8 C 9 8 200 190 B 5 A -197.72 9 8 7 15 4 3 0: ང་ 200 190 180 147.52 134.98 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 90 OH 10 4 3 1 2 -143.04 140. 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 CI 3 5 1 2 141.89 140.07 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 ៖- 90 129. 126.25 80 70 60 -60 50 40 10 125.19 -129.21 80 70 3.0 20 20 -8 60 50 10 ppm -20 40 128.31 80 80 70 60 50 40 40 -70.27 3.0 20 10 ppm 00˚0-- 77.17 30 20 20 -45.36 10 ppm -0.00 26.48 22.32 ―30.10 ―-0.00arrow_forwardAssign all the carbonsarrow_forward
- C 5 4 3 CI 2 the Righ B A 5 4 3 The Lich. OH 10 4 5 3 1 LOOP- -147.52 T 77.17 -45.36 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm B -126.25 77.03 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 TO LL <-50.00 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm 45.06 30.18 -26.45 22.36 --0.00 45.07 7.5 1.93 2.05 -30.24 -22.36 C A 7 8 5 ° 4 3 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 8 5 4 3 ཡི་ OH 10 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 5 4 3 2 that th 7 I 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 115 2.21 4.00 1.0 ppm 6.96 2.76 5.01 1.0 ppm 6.30 1.00arrow_forwardCurved arrows were used to generate the significant resonance structure and labeled the most significant contribute. What are the errors in these resonance mechanisms. Draw out the correct resonance mechanisms with an brief explanation.arrow_forwardWhat are the: нсе * Moles of Hice while given: a) 10.0 ml 2.7M ? 6) 10.ome 12M ?arrow_forward
- You are asked to use curved arrows to generate the significant resonance structures for the following series of compounds and to label the most significant contributor. Identify the errors that would occur if you do not expand the Lewis structures or double-check the mechanisms. Also provide the correct answers.arrow_forwardhow to get limiting reactant and % yield based off this data Compound Mass 6) Volume(mL Ben zaphone-5008 ne Acetic Acid 1. Sam L 2-propanot 8.00 Benzopin- a col 030445 Benzopin a Colone 0.06743 Results Compound Melting Point (°c) Benzopin acol 172°c - 175.8 °c Benzoping to lone 1797-180.9arrow_forwardAssign ALL signals for the proton and carbon NMR spectra on the following pages.arrow_forward
- 7.5 1.93 2.05 C B A 4 3 5 The Joh. 9 7 8 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 0.86 OH 10 4 3 5 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 CI 4 3 5 1 2 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 2.21 4.00 1.5 2.00 2.07 1.0 ppm 2.76arrow_forwardAssign the functional group bands on the IR spectra.arrow_forwardFind the pH of a 0.120 M solution of HNO2. Find the pH ignoring activity effects (i.e., the normal way). Find the pH in a solution of 0.050 M NaCl, including activityarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





