
Concept explainers
Introduction:
To make large quantities of recombinant plasmid DNA, bacterial cells are mixed with recombinant plasmid DNA. Some bacteria take up the recombinant plasmid DNA through a process called transformation. Brief heating or short electric pulse creates openings in the plasma membrane of bacterial cells which allow recombinant plasmid DNA to enter the bacterial cells. However some bacterial cells do not take up the plasmid DNA.
Answer to Problem 3STP
Correct answer :
The correct answer is option C. Cells without new plasmid will die after exposure to an antibiotic
Explanation of Solution
Explanation/justification for the correct answer:
Option C. Cells without new plasmid will die after exposure to an antibiotic - The illustration given below shows bacteria that were transformed after they were mixed with the recombinant DNA. Cells A and B do not have the new recombinant DNA plasmid. After transformation the bacteria are allowed to grow on a plate containing an antibiotic. The transformed bacteria are able to survive as they contain the gene for antibiotic resistance and the normal bacteria die. Hence this is the correct option.
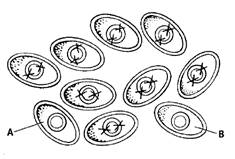
Explanation for incorrect answer:
Option A. Cells with new plasmid will die after exposure to an antibiotic - The illustration given below shows bacteria that were transformed after they were mixed with the recombinant DNA. Cells A and B do not have the new recombinant DNA plasmid. After transformation the bacteria are allowed to grow on a plate containing an antibiotic. The transformed bacteria are able to survive as they contain the gene for antibiotic resistance and the normal bacteria die.
Hence this is not the correct option.
Option B. Cells with the new plasmid will replicate quicker - The illustration given below shows bacteria that were transformed after they were mixed with the recombinant DNA. Cells A and B do not have the new recombinant DNA plasmid. After transformation the bacteria are allowed to grow on a plate containing an antibiotic. The transformed bacteria are able to survive as they contain the gene for antibiotic resistance and the normal bacteria die. Hence this is not the correct option.
Option D. Cells without the new plasmid will replicate more quickly − The illustration given below shows bacteria that were transformed after they were mixed with the recombinant DNA. Cells A and B do not have the new recombinant DNA plasmid. After transformation the bacteria are allowed to grow on a plate containing an antibiotic. The transformed bacteria are able to survive as they contain the gene for antibiotic resistance and the normal bacteria die. Hence this is not the correct option.
Chapter 14 Solutions
Glencoe Biology, Florida Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
- What are functions of cuboidal cells in the kidney? Select all that apply. Concentration of gases Dilution of chemicals Secretion of molecules Nutrition to tissues Support of tissues Absorption of moleculesarrow_forwardquestion1 In plants, epithelial tissue is only found as the outermost cell layer and acts as a barrier. In humans, epithelial tissue is found inside the body as well as on the surface. What function(s) does/do epithelial tissue carry out in humans? Select all that apply. Waste storage Filtration Oxygen transport Protection Diffusion Osmosis Absorptionarrow_forwardWhat words best describes this organism? a. Unicellular/nonmotile Ob. unicellular/motile c. colonial/nonmotile d. colonial/motile e. multicelluar O f. siphonous g. none of thesearrow_forward
- Identify the phylum or class. a. Euglenophyta b. Dinoflagellata c. Bacillariophyceae d. Oomycetes e. Phaeophyceae O f. Myxomycota g. Xanthophyceae ○ h. Chrysophyceae i. Dictyosteliomycota O j. Rhodophyta Ok. Chlorophyceaens I. Charophyceaensarrow_forwardWhat is produced inside the indicated structure (Fucus). a. eggs O b. antheridia ○ c. sperm d. zygotes e. none of thesearrow_forwardGreen Algae, as a group, is actually paraphyletic with one subgroup more closely related to higher plants than the other. Which of the following green algae groups is more closely related to higher plants: a. Charophyceans b. Chlorophyceans c. Rhodophyta d. Xanthophyceansarrow_forward
- A single-celled green algal genus that is motile with 2 flagella, has a cup shaped chloroplast, and an eyespot: a. Volvox b. Chlamydomonas c. Euglena d. Codiumarrow_forwardA[n] ___ is produced by members of the Myxomycota when there is a lack of moisture. a. plasmodiocarp b. aethalium c. sclerotium d. plasmodiumarrow_forwardWhich of the following is not true about the life-cycle of Fucus. a. 8 eggs per oogonium b. 64 sperm per antheridium c. eggs are flagellated d. sperm are flagellatedarrow_forward
- Green Algae, as a group, is actually paraphyletic with one subgroup more closely related to higher plants than the other. Which of the following green algae groups is more closely related to higher plants: a. Charophyceans b. Chlorophyceans c. Rhodophyta d. Xanthophyceansarrow_forwardCertain toxic terpenoids in this group is thought to deter herbivory but may also have some anti-tumor activity? a. green algae b. brown algae c. red algae d. golden algae e. none of thesearrow_forwardIn the cellular slime molds, the most common phase is: a. plasmodium b. pseudoplasmodial c. single cells as myxamoebae d. moundingarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





