
Concept explainers
Introduction:
To make large quantities of recombinant plasmid DNA, bacterial cells are mixed with recombinant plasmid DNA. Some bacteria take up the recombinant plasmid DNA through a process called transformation. Brief heating or short electric pulse creates openings in the plasma membrane of bacterial cells which allow recombinant plasmid DNA to enter the bacterial cells. However some bacterial cells do not take up the plasmid DNA.
Answer to Problem 3STP
Correct answer :
The correct answer is option C. Cells without new plasmid will die after exposure to an antibiotic
Explanation of Solution
Explanation/justification for the correct answer:
Option C. Cells without new plasmid will die after exposure to an antibiotic - The illustration given below shows bacteria that were transformed after they were mixed with the recombinant DNA. Cells A and B do not have the new recombinant DNA plasmid. After transformation the bacteria are allowed to grow on a plate containing an antibiotic. The transformed bacteria are able to survive as they contain the gene for antibiotic resistance and the normal bacteria die. Hence this is the correct option.
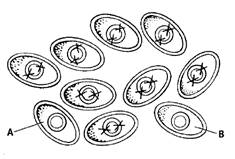
Explanation for incorrect answer:
Option A. Cells with new plasmid will die after exposure to an antibiotic - The illustration given below shows bacteria that were transformed after they were mixed with the recombinant DNA. Cells A and B do not have the new recombinant DNA plasmid. After transformation the bacteria are allowed to grow on a plate containing an antibiotic. The transformed bacteria are able to survive as they contain the gene for antibiotic resistance and the normal bacteria die.
Hence this is not the correct option.
Option B. Cells with the new plasmid will replicate quicker - The illustration given below shows bacteria that were transformed after they were mixed with the recombinant DNA. Cells A and B do not have the new recombinant DNA plasmid. After transformation the bacteria are allowed to grow on a plate containing an antibiotic. The transformed bacteria are able to survive as they contain the gene for antibiotic resistance and the normal bacteria die. Hence this is not the correct option.
Option D. Cells without the new plasmid will replicate more quickly − The illustration given below shows bacteria that were transformed after they were mixed with the recombinant DNA. Cells A and B do not have the new recombinant DNA plasmid. After transformation the bacteria are allowed to grow on a plate containing an antibiotic. The transformed bacteria are able to survive as they contain the gene for antibiotic resistance and the normal bacteria die. Hence this is not the correct option.
Chapter 14 Solutions
EP BIOLOGY 2012-STUDENTWORKS ONLINE
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
- If you transplant trunk neural crest into the cranial neural crest region of a developing embryo, will you see the donor tissue form cartilage? Does the neural crest only give rise to two cells in the developing embryo, and is essential for lamprey to develop their jaw structure? Does a multipotent neural crest cell that is receiving Wnt signals become a Chromaffin cell?arrow_forwardUsing quail and chick embryos, quail-specific antibody and fluorescent tissue-specific antibodies, design an experiment where you investigate the tissues the cranial neural crest can give rise to. What are four derivatives of the cranial neural crest that you expect to see in the resulting chimeric embryos?arrow_forwardDoes the neural crest have to undergo epithelial to mesenchymal transition prior to migration through the developing embryo? Does the neural crest differentiate into different cell types based on their axial position along the anterior and posterior axis?arrow_forward
- Using quail and chicken embryos, what kind of experiment would you conduct to test if rib forming somites have their axial identity specified before segmentation? How do we know this phenotype is due to axial identity being specified before segmentation and not due to our experimental method?arrow_forward8. Aerobic respiration of a 5 mM solution of tripeptide that is composed of the following three amino acids; alanine, leucine and isoleucine. Alanine breaks down to pyruvate, leucine breaks down to Acetyl-CoA and isoleucine breaks down to succinyl-CoA. Alanine NADH FADH2 OP ATP SLP ATP Total ATP Leucine Isoleucine Totals Show your work using dimensional analysis here: 4arrow_forward9. Aerobic respiration of one lipid molecule. The lipid is composed of one glycerol molecule connected to two fatty acid tails. One fatty acid is 12 carbons long and the other fatty acid is 18 carbons long in the figure below. Use the information below to determine how much ATP will be produced from the glycerol part of the lipid. Then, in part B, determine how much ATP is produced from the 2 fatty acids of the lipid. Finally put the NADH and ATP yields together from the glycerol and fatty acids (part A and B) to determine your total number of ATP produced per lipid. Assume no other carbon source is available. fatty acids glycerol 18 carbons 12 carbons 0=arrow_forward
- If using animals in medical experiments could save human lives, is it ethical to do so? In your answer, apply at least one ethical theory in support of your position.arrow_forwardYou aim to test the hypothesis that the Tbx4 and Tbx5 genes inhibit each other's expression during limb development. With access to chicken embryos and viruses capable of overexpressing Tbx4 and Tbx5, describe an experiment to investigate whether these genes suppress each other's expression in the limb buds. What results would you expect if they do repress each other? What results would you expect if they do not repress each other?arrow_forwardYou decide to delete Fgf4 and Fgf8 specifically in the limb bud. Explain why you would not knock out these genes in the entire embryo instead.arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





