
Concept explainers
A 215-kg robotic arm at an assembly plant is extended horizontally (Fig. P14.32). The massless support rope attached at point B makes an angle of 15.0° with the horizontal, and the center of mass of the arm is at point C. a. What is the tension in the support rope? b. What are the magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the hinge A on the robotic arm to keep the arm in the horizontal position?
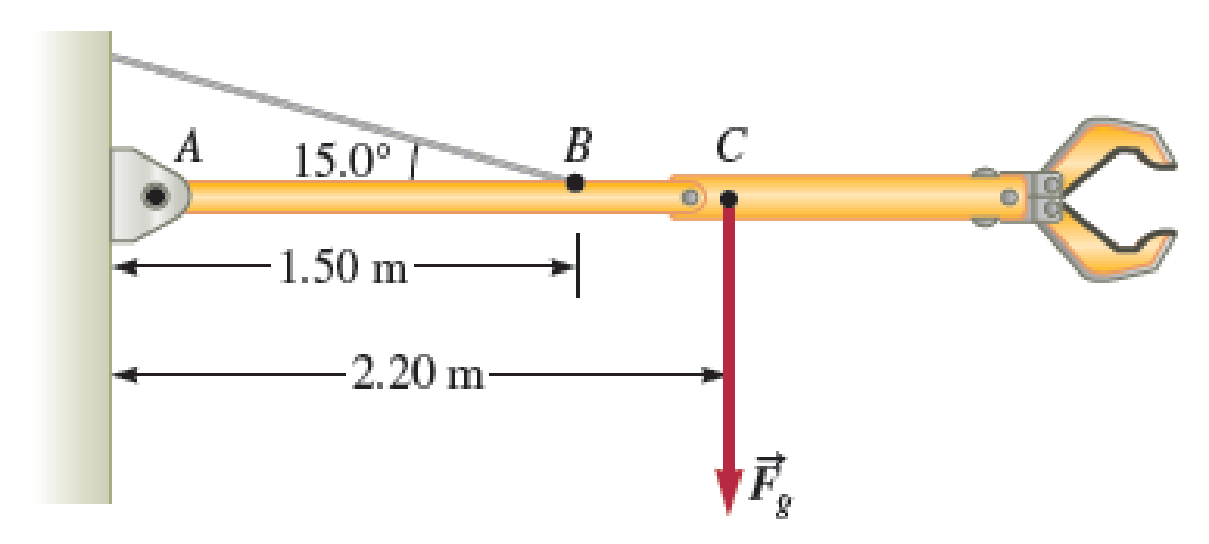
FIGURE P14.32
(a)
Tension in the support rope.
Answer to Problem 32PQ
The tension in the support rope is
Explanation of Solution
The figure given below is the free body diagram of the robotic arm.
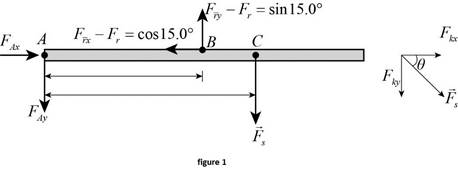
In the equilibrium state of the system, the net torque experienced by the robotic arm is zero. Take shoulder joint at point A as the pivot point. The forces acting on the body are the force of tension on the rope and the force at robotic arm due to gravitational field. Torque acts on the arm due to these forces.
Write the equation to find the torque produced by the tension on the rope.
Here,
Write the equation to find the torque acting on the arm due to earth’s gravity.
Here,
Write the equation to find the gravitational force.
Substitute the above equation in (II) to get
The force of gravity is in down ward direction, therefore the torque due to gravitational force has a negative sign.
Add equations (III) and (I) to find the sum of torques at the arm.
Since the sum of torque is zero in equilibrium condition, equate equation (IV) to zero and solve for
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the tension in the support rope is
(b)
The magnitude and direction of force exerted by hinge
Answer to Problem 32PQ
The magnitude of the force exerted by hinge
Explanation of Solution
At equilibrium the sum of both x and y components of all the force is equal to zero.
The forces in the y direction are the force exerted by the hinge, force due to the tension on rope, and the force due to gravity.
Write the equation to find the y component of force due tension on the rope.
Here,
Write the equation to find the force due to gravity.
Add equation (VI) and (VII) to get the sum of forces.
In addition to these two forces there is the force exerted by the hinge on the arm of the robot. Let this force be
Add
Here,
At equilibrium, the sum of y component of forces is equal to zero. Equate equation (VIII) to zero and solve for
Substitute equation (V) in (IX) and solve for
The forces acting in the x direction are the force due to tension on rope and the horizontal component of force exerted by the hinge.
Write the equation to find the x component of the tension force on the rope.
Here,
Substitute equation (V) in (XI).
Write the equation to find the sum of forces in the x direction.
Here,
Substitute equation (XII) to the above equation to get
In equilibrium, sum of forces in the x direction is zero. Equate equation (XIII) to zero.
Solve equation (XIV) to get
Write the equation to find the resultant force exerted by hinge.
Here,
Write the equation to find the angle made by the resultant force with the horizontal.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the magnitude of the force exerted by hinge on arm is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK WEBASSIGN FOR KATZ'S PHYSICS FOR SC
- 1. Two pendula of slightly different length oscillate next to each other. The short one oscillates with frequency 0.52 Hz and the longer one with frequency 0.50 Hz. If they start of in phase determine their phase difference after 75 s.arrow_forwardA mass is connect to a vertical revolving axle by two strings of length L, each making an angle of 45 degrees with the axle, as shown. Both the axle and mass are revolving with angular velocity w, Gravity is directed downward. The tension in the upper string is T_upper and the tension in the lower string is T_lower.Draw a clear free body diagram for mass m. Please include real forces only.Find the tensions in the upper and lower strings, T_upper and T_lowerarrow_forward2. A stone is dropped into a pool of water causing ripple to spread out. After 10 s the circumference of the ripple is 20 m. Calculate the velocity of the wave.arrow_forward
- 10. Imagine you have a system in which you have 54 grams of ice. You can melt this ice and then vaporize it all at 0 C. The melting and vaporization are done reversibly into a balloon held at a pressure of 0.250 bar. Here are some facts about water you may wish to know. The density of liquid water at 0 C is 1 g/cm³. The density of ice at 0 C is 0.917 g/cm³. The enthalpy of vaporization of liquid water is 2.496 kJ/gram and the enthalpy of fusion of solid water is 333.55 J/gram. A. How much energy does the ice absorb as heat when it melts? B. How much work is involved in melting the ice? C. What is the total change in energy for melting the ice? D. What is the enthalpy change for melting the ice? E. What is the entropy change for melting the ice? F. What is the change in Helmholtz energy for melting the ice? G. What is the change in Gibbs energy for melting the ice?arrow_forwardIn the figure Q = 5.7 nC and all other quantities are accurate to 2 significant figures. What is the magnitude of the force on the charge Q? (k = 1/4πε 0 = 8.99 × 109 N · m2/C2)arrow_forwardNow add a fourth charged particle, particle 3, with positive charge q3, fixed in the yz-plane at (0,d2,d2). What is the net force F→ on particle 0 due solely to this charge? Express your answer (a vector) using k, q0, q3, d2, i^, j^, and k^. Include only the force caused by particle 3.arrow_forward
- For a tornadoes and hurricanes, which of the following is most critical? an alert a watch a warning a predictionarrow_forwardWhen a warm front advances up and over a cold front, what is it called? front inversion stationary front cold front occlusion warm front occlusionarrow_forward1) Consider two positively charged particles, one of charge q0 (particle 0) fixed at the origin, and another of charge q1 (particle 1) fixed on the y-axis at (0,d1,0). What is the net force F→ on particle 0 due to particle 1? Express your answer (a vector) using any or all of k, q0, q1, d1, i^, j^, and k^. 2) Now add a third, negatively charged, particle, whose charge is −q2− (particle 2). Particle 2 fixed on the y-axis at position (0,d2,0). What is the new net force on particle 0, from particle 1 and particle 2? Express your answer (a vector) using any or all of k, q0, q1, q2, d1, d2, i^, j^, and k^. 3) Particle 0 experiences a repulsion from particle 1 and an attraction toward particle 2. For certain values of d1 and d2, the repulsion and attraction should balance each other, resulting in no net force. For what ratio d1/d2 is there no net force on particle 0? Express your answer in terms of any or all of the following variables: k, q0, q1, q2.arrow_forward
- A 85 turn, 10.0 cm diameter coil rotates at an angular velocity of 8.00 rad/s in a 1.35 T field, starting with the normal of the plane of the coil perpendicular to the field. Assume that the positive max emf is reached first. (a) What (in V) is the peak emf? 7.17 V (b) At what time (in s) is the peak emf first reached? 0.196 S (c) At what time (in s) is the emf first at its most negative? 0.589 x s (d) What is the period (in s) of the AC voltage output? 0.785 Sarrow_forwardA bobsled starts at the top of a track as human runners sprint from rest and then jump into the sled. Assume they reach 40 km/h from rest after covering a distance of 50 m over flat ice. a. How much work do they do on themselves and the sled which they are pushing given the fact that there are two men of combined mass 185 kg and the sled with a mass of 200 kg? (If you haven't seen bobsledding, watch youtube to understand better what's going on.) b. After this start, the team races down the track and descends vertically by 200 m. At the finish line the sled crosses with a speed of 55 m/s. How much energy was lost to drag and friction along the way down after the men were in the sled?arrow_forwardFor what type of force is it not possible to define a potential energy expression?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University





