EBK COMPUTER SCIENCE ILLUMINATED
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781284174755
Author: Dale
Publisher: JONES+B CO
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 14, Problem 2TQ
Program Plan Intro
Queue:
- This is the abstract data type in which access of data is made at both the ends.
- The data is inserted at one end or removed at the other end.
- So, the first item inserted at one end can be retrieved first at the other end. This
mechanism is referred to as first-in-first-out (FIFO). - Insertion and deletion are the common operations of a queue.
- Inserting an item into the queue is called “Enqueue”.
- Removing an item from the queue is called “Dequeue”.
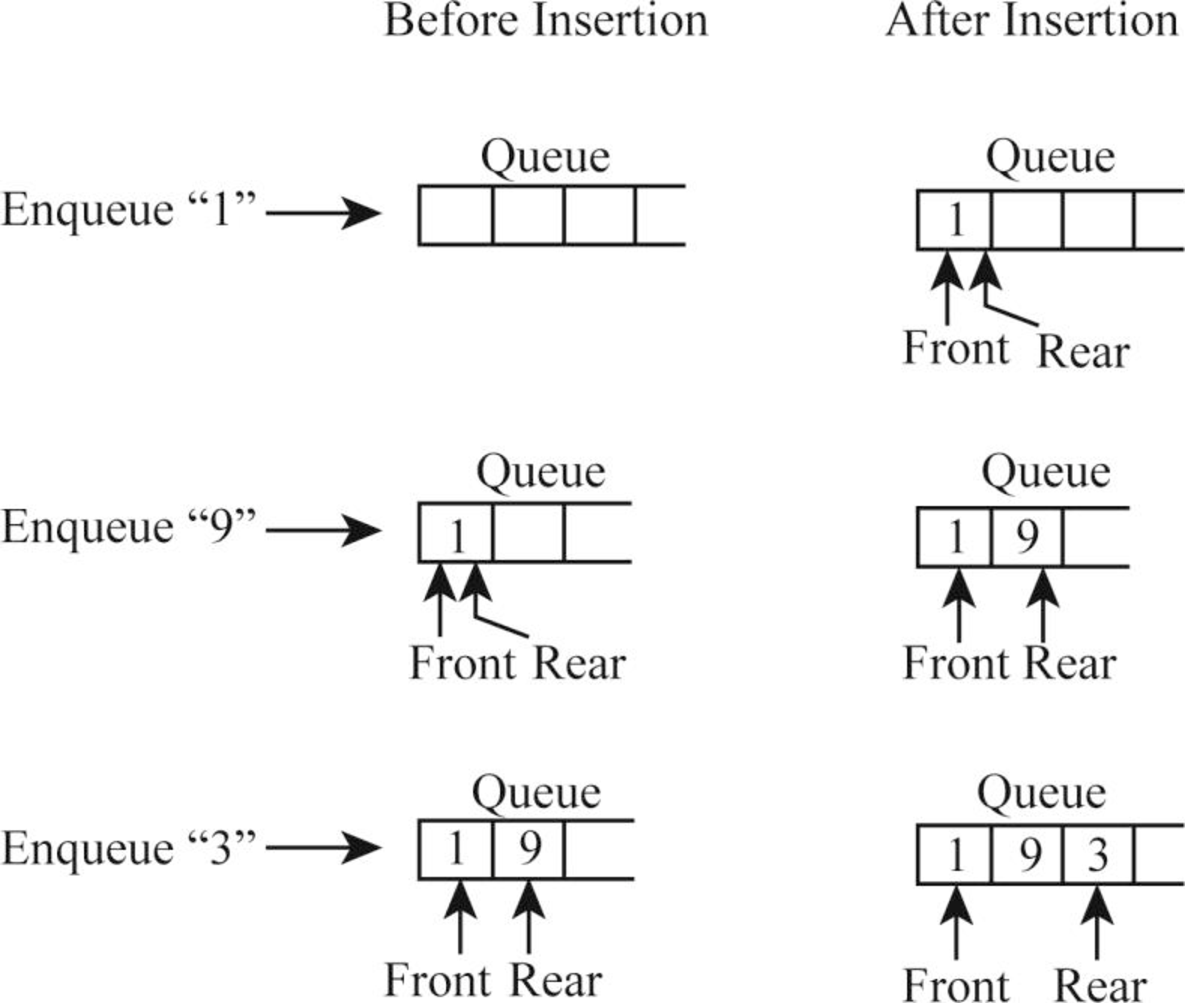
- Diagrammatic representation of enqueue operation:
|
|
In the above diagram,
- After inserting the item “1” to the empty queue, the “front” and the “rear” pointers point to this first item.
- After inserting the item “9”, the “rear” pointer moves from the item “1” to the item “9”.
- After inserting the item “3”, the “rear” pointer moves from the item “9” to the item “3” and during insertion, the “front” pointer points only to the first item.
Priority queue:
- If the items in the queue are assigned with a priority, then it is called priority queue.
- When inserting an item into the priority queue, the item is added with the priority.
- When removing an item from the priority queue, the item with higher priority is first removed. Then, based on the priority, the other items are removed.
- The maximum number or the minimum number can be deleted by using deletemaximum() or deleteminimum() function.
- Deletemaximum() is a function which deletes the number which is having the highest priority.
- Deleteminimum() is a function which deletes the number which is having the lowest priority.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I need help creating the network diagram and then revising it for the modified activity times.
Activity No.
Activity
Time (weeks)
Immediate Predecessors
1
Requirements collection
3
2
Requirements structuring
4
1
3
Process analysis
3
2
4
Data analysis
3
2
5
Logical design
50
3,4
6
Physical design
5
5
7
Implementation
6
6
c. Using the information from part b, prepare a network diagram. Identify the critical path.
Given the following Extended-BNF grammar of the basic mathematical expressions:
Show the derivation steps for the expression: ( 2 + 3 ) * 6 – 20 / ( 3 + 1 )
Draw the parsing tree of this expression.
SEE IMAGE
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK COMPUTER SCIENCE ILLUMINATED
Ch. 14 - Prob. 1ECh. 14 - Prob. 2ECh. 14 - Prob. 3ECh. 14 - Prob. 4ECh. 14 - Prob. 5ECh. 14 - Prob. 6ECh. 14 - Prob. 7ECh. 14 - Prob. 8ECh. 14 - Prob. 9ECh. 14 - Prob. 10E
Ch. 14 - Prob. 11ECh. 14 - Prob. 12ECh. 14 - Prob. 13ECh. 14 - Prob. 14ECh. 14 - Prob. 15ECh. 14 - Prob. 16ECh. 14 - Prob. 17ECh. 14 - Prob. 18ECh. 14 - Prob. 19ECh. 14 - Prob. 20ECh. 14 - Prob. 21ECh. 14 - Prob. 22ECh. 14 - Prob. 23ECh. 14 - Prob. 24ECh. 14 - Prob. 25ECh. 14 - Prob. 26ECh. 14 - Prob. 27ECh. 14 - Prob. 28ECh. 14 - Prob. 29ECh. 14 - Prob. 30ECh. 14 - Prob. 31ECh. 14 - Prob. 32ECh. 14 - Prob. 33ECh. 14 - Prob. 34ECh. 14 - Prob. 35ECh. 14 - Prob. 36ECh. 14 - Prob. 37ECh. 14 - Prob. 38ECh. 14 - Prob. 39ECh. 14 - Prob. 40ECh. 14 - Prob. 41ECh. 14 - Prob. 42ECh. 14 - Prob. 43ECh. 14 - Prob. 44ECh. 14 - Prob. 45ECh. 14 - Prob. 46ECh. 14 - Prob. 47ECh. 14 - Prob. 48ECh. 14 - Prob. 49ECh. 14 - Prob. 50ECh. 14 - Prob. 51ECh. 14 - Prob. 52ECh. 14 - Prob. 1TQCh. 14 - Prob. 2TQCh. 14 - Prob. 3TQCh. 14 - Prob. 4TQCh. 14 - Prob. 5TQCh. 14 - Prob. 6TQCh. 14 - Prob. 7TQCh. 14 - Prob. 8TQ
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Whentheuserenters!!,themostrecentcommandinthehistoryisexecuted.In the example above, if the user entered the command: Osh> !! The ‘ls -l’ command should be executed and echoed on user’s screen. The command should also be placed in the history buffer as the next command. Whentheuserentersasingle!followedbyanintegerN,theNthcommandin the history is executed. In the example above, if the user entered the command: Osh> ! 3 The ‘ps’ command should be executed and echoed on the user’s screen. The command should also be placed in the history buffer as the next command. Error handling: The program should also manage basic error handling. For example, if there are no commands in the history, entering !! should result in a message “No commands in history.” Also, if there is no command corresponding to the number entered with the single !, the program should output "No such command in history."arrow_forwardActivity No. Activity Time (weeks) Immediate Predecessors 1 Requirements collection 3 2 Requirements structuring 4 1 3 Process analysis 3 2 4 Data analysis 3 2 5 Logical design 50 3,4 6 Physical design 5 5 7 Implementation 6 6 c. Using the information from part b, prepare a network diagram. Identify the critical path.arrow_forward2. UNIX Shell and History Feature [20 points] This question consists of designing a C program to serve as a shell interface that accepts user commands and then executes each command in a separate process. A shell interface gives the user a prompt, after which the next command is entered. The example below illustrates the prompt osh> and the user's next command: cat prog.c. The UNIX/Linux cat command displays the contents of the file prog.c on the terminal using the UNIX/Linux cat command and your program needs to do the same. osh> cat prog.c The above can be achieved by running your shell interface as a parent process. Every time a command is entered, you create a child process by using fork(), which then executes the user's command using one of the system calls in the exec() family (as described in Chapter 3). A C program that provides the general operations of a command-line shell can be seen below. #include #include #define MAX LINE 80 /* The maximum length command */ { int…arrow_forward
- Question#2: Design and implement a Java program using Abstract Factory and Singleton design patterns. The program displays date and time in one of the following two formats: Format 1: Date: MM/DD/YYYY Time: HH:MM:SS Format 2: Date: DD-MM-YYYY Time: SS,MM,HH The following is how the program works. In the beginning, the program asks the user what display format that she wants. Then the program continuously asks the user to give one of the following commands, and performs the corresponding task. Note that the program gets the current date and time from the system clock (use the appropriate Java date and time operations for this). 'd' display current date 't': display current time 'q': quit the program. • In the program, there should be 2 product hierarchies: "DateObject” and “TimeObject”. Each hierarchy should have format and format2 described above. • Implement the factories as singletons. • Run your code and attach screenshots of the results. • Draw a UML class diagram for the program.arrow_forward#include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> // part 2 #include <linux/sched.h> // part 2 extra #include <linux/hash.h> #include <linux/gcd.h> #include <asm/param.h> #include <linux/jiffies.h> void print_init_PCB(void) { printk(KERN_INFO "init_task pid:%d\n", init_task.pid); printk(KERN_INFO "init_task state:%lu\n", init_task.state); printk(KERN_INFO "init_task flags:%d\n", init_task.flags); printk(KERN_INFO "init_task runtime priority:%d\n", init_task.rt_priority); printk(KERN_INFO "init_task process policy:%d\n", init_task.policy); printk(KERN_INFO "init_task task group id:%d\n", init_task.tgid); } /* This function is called when the module is loaded. */ int simple_init(void) { printk(KERN_INFO "Loading Module\n"); print_init_PCB(); printk(KERN_INFO "Golden Ration Prime = %lu\n", GOLDEN_RATIO_PRIME); printk(KERN_INFO "HZ = %d\n", HZ); printk(KERN_INFO "enter jiffies = %lu\n", jiffies); return 0; } /* This function is called when the…arrow_forwardList at least five Operating Systems you know. What is the difference between the kernel mode and the user mode for the Linux? What is the system-call? Give an example of API in OS that use the system-call. What is cache? Why the CPU has cache? What is the difference between the Static Linking and Dynamic Linking when compiling the code.arrow_forward
- In the GoF book, List interface is defined as follows: interface List { int count(); //return the current number of elements in the list Object get(int index); //return the object at the index in the list Object first(); //return the first object in the list Object last(); //return the last object in the list boolean include(Object obj); //return true is the object in the list void append(Object obj); //append the object to the end of the list void prepend(Object obj); //insert the object to the front of the list void delete(Object obj); //remove the object from the list void deleteLast(); //remove the last element of the list void deleteFirst(); //remove the first element of the list void deleteAll(); //remove all elements of the list (a) Write a class adapter to adapt Java ArrayList to GoF List interface. (b) Write a main program to test your adapters through List interface. (c) Same requirement as (a) and (b), but write an object adapter to adapt Java ArrayList to GoF List…arrow_forwardIn modern packet-switched networks, including the Internet, the source host segments long, application-layer messages (for example, an image or a music file) into smaller packets and sends the packets into the network. The receiver then reassembles the packets back into the original message. We refer to this process as message segmentation. Figure 1.27 (attached) illustrates the end-to-end transport of a message with and without message segmentation. Consider a message that is 106 bits long that is to be sent from source to destination in Figure 1.27. Suppose each link in the figure is 5 Mbps. Ignore propagation, queuing, and processing delays. a. Consider sending the message from source to destination without message segmentation. How long does it take to move the message from the source host to the first packet switch? Keeping in mind that each switch uses store-and-forward packet switching, what is the total time to move the message from source host to destination host? b. Now…arrow_forwardConsider a packet of length L that begins at end system A and travels over three links to a destination end system. These three links are connected by two packet switches. Let di, si, and Ri denote the length, propagation speed, and the transmission rate of link i, for i = 1, 2, 3. The packet switch delays each packet by dproc. Assuming no queuing delays, in terms of di, si, Ri, (i = 1, 2, 3), and L, what is the total end-to-end delay for the packet? Suppose now the packet is 1,500 bytes, the propagation speed on all three links is 2.5 * 10^8 m/s, the transmission rates of all three links are 2.5 Mbps, the packet switch processing delay is 3 msec, the length of the first link is 5,000 km, the length of the second link is 4,000 km, and the length of the last link is 1,000 km. For these values, what is the end-to-end delay?arrow_forward
- how to know the weight to data and data to weight also weight by infomraion gain in rapid miner , between this flow diagram retrieve then selecte attrbuite then set role and split data and decision tree and apply model and peformance ,please show how the operators should be connected:arrow_forwardusing rapid miner how to creat decison trea for all attribute and another one with delete one or more of them also how i know the weight of each attribute and what that mean in impact the resultarrow_forwardQ.1. Architecture performance [10 marks] Answer A certain microprocessor requires either 2, 4, or 6 machine cycles to perform various operations. ⚫ (40+g+f)% require 2 machine cycles, ⚫ (30-g) % require 4 machine cycles, and ⚫ (30-f)% require 6 machine cycles. (a) What is the average number of machine cycles per instruction for this microprocessor? Answer (b) What is the clock rate (machine cycles per second) required for this microprocessor to be a "1000 MIPS" processor? Answer (c) Suppose that 35% of the instructions require retrieving an operand from memory which needs an extra 8 machine cycles. What is the average number of machine cycles per instruction, including the instructions that fetch operands from memory?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education