
(a)
The natural rate of
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The IS LM framework of the economy deals with the closed economy and does not consider the international trade and Balance of Payments into consideration. This leads to the generation of the new model that incorporated the Balance of Payment into the calculations which is known as the Mundell - Fleming model. The
The natural rate of unemployment is the unemployment rate in the economy at the time when the labor market is in equilibrium. Thus, it consists of the structural and frictional unemployment in the economy when the economy is operating efficiently. This natural rate of unemployment is a case where the inflation in the economy will be equivalent to the expected rate of inflation. Thus, there will be no deviation to the actual level of inflation from the expected.
Thus, the expected inflation in this case will be equal to the last period's inflation in the economy. Thus, setting the inflation to the last period's inflation,
Natural Rate of Unemployment: The natural rate of unemployment is the rate of unemployment that is persisting in the economy when the labor market of the economy is in its equilibrium.
(b)
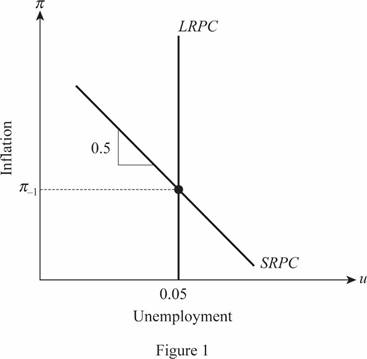
The short run and long run relationship between the inflation and unemployment.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The inflation and the unemployment are the two important aspects that an economy has to handle very carefully. When the measure to tackle and reduce the inflation is taken, it will increase the unemployment and vice versa in the economy. This happens in the short run and thus, they both are inversely related with each other. This short run or single period relation between the inflation and the unemployment is explained using the Phillips curve for the economy. Here, the expected inflation rate is equal to the last period's inflation rate and the slope of the Phillips curve will be 0.5. The short run Phillips curve will pass through the point where the
The long run period or the multi period relation is different from the short run relation. The expected inflation of the economy will be equal to the actual level of inflation in the economy. Thus,
(c)
The cyclical unemployment required to reduce the inflation by 4 percentage points.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The Phillips curve of the economy is given to be
When the inflation has to be reduced, the unemployment in the economy should be above its natural level of unemployment according to the Phillips curve. Thus, the required fall in the inflation rate should be plugged into the left side of the Phillips curve equation as follows:
Thus, it indicates that there should be 8 percent more cyclical unemployment in the economy in order to bring the inflation by 4 percentage. The Okun's law states that an increase in the unemployment by 1 percent will correspond to the 2 percent fall in the total
The sacrifice ratio is the ratio of the percentage of GDP that the economy must foregoin order to reduce the inflation by 1 percentage point. Here, the total GDP foregone is 16 percentage points and the total inflation reduced is 4 percentage points. Thus, the sacrifice ratio can be calculated by dividing the total GDP foregone with the inflation reduced as follows:
Thus, the sacrifice ratio of the economy is 4.
(d)
The scenarios to reduce the inflation by 4 percentage points.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The Phillips curve of the economy is given to be
In order to reduce the inflation by 4 percentage points, the economy should have to face the higher unemployment rate of 13 percent for the short run as calculated above. Thus, the first measure that the government can relay is to make the unemployment rate very high at 13 percent in order to reduce the inflation by 4 percentage points.
The second measure that the government can relay is to fix the level of unemployment at 7 percent for 4 years which would slowly reduce the level of inflation in the economy by 4 percentage points. These are the two different measures that the government can relay up on in order to reduce the inflation by 4 percentage points.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- In the graph at the right, the average variable cost is curve ☐. The average total cost is curve marginal cost is curve The C Cost per Unit ($) Per Unit Costs A 0 Output Quantity Barrow_forwardWhat are some of the question s that I can ask my economic teacher?arrow_forwardAnswer question 2 only.arrow_forward
- 1. A pension fund manager is considering three mutual funds. The first is a stock fund, the second is a long-term government and corporate fund, and the third is a (riskless) T-bill money market fund that yields a rate of 8%. The probability distributions of the risky funds have the following characteristics: Standard Deviation (%) Expected return (%) Stock fund (Rs) 20 30 Bond fund (RB) 12 15 The correlation between the fund returns is .10.arrow_forwardFrederick Jones operates a sole proprietorship business in Trinidad and Tobago. His gross annual revenue in 2023 was $2,000,000. He wants to register for VAT, but he is unsure of what VAT entails, the requirements for registration and what he needs to do to ensure that he is fully compliant with VAT regulations. Make reference to the Vat Act of Trinidad and Tobago and explain to Mr. Jones what VAT entails, the requirements for registration and the requirements to be fully compliant with VAT regulations.arrow_forwardCan you show me the answers for parts a and b? Thanks.arrow_forward
- What are the answers for parts a and b? Thanksarrow_forwardWhat are the answers for a,b,c,d? Are they supposed to be numerical answers or in terms of a variable?arrow_forwardSue is a sole proprietor of her own sewing business. Revenues are $150,000 per year and raw material (cloth, thread) costs are $130,000 per year. Sue pays herself a salary of $60,000 per year but gave up a job with a salary of $80,000 to run the business. ○ A. Her accounting profits are $0. Her economic profits are - $60,000. ○ B. Her accounting profits are $0. Her economic profits are - $40,000. ○ C. Her accounting profits are - $40,000. Her economic profits are - $60,000. ○ D. Her accounting profits are - $60,000. Her economic profits are -$40,000.arrow_forward
- Select a number that describes the type of firm organization indicated. Descriptions of Firm Organizations: 1. has one owner-manager who is personally responsible for all aspects of the business, including its debts 2. one type of partner takes part in managing the firm and is personally liable for the firm's actions and debts, and the other type of partner takes no part in the management of the firm and risks only the money that they have invested 3. owners are not personally responsible for anything that is done in the name of the firm 4. owned by the government but is usually under the direction of a more or less independent, state-appointed board 5. established with the explicit objective of providing goods or services but only in a manner that just covers its costs 6. has two or more joint owners, each of whom is personally responsible for all of the partnership's debts Type of Firm Organization a. limited partnership b. single proprietorship c. corporation Correct Numberarrow_forwardThe table below provides the total revenues and costs for a small landscaping company in a recent year. Total Revenues ($) 250,000 Total Costs ($) - wages and salaries 100,000 -risk-free return of 2% on owner's capital of $25,000 500 -interest on bank loan 1,000 - cost of supplies 27,000 - depreciation of capital equipment 8,000 - additional wages the owner could have earned in next best alternative 30,000 -risk premium of 4% on owner's capital of $25,000 1,000 The economic profits for this firm are ○ A. $83,000. B. $82,500. OC. $114,000. OD. $83,500. ○ E. $112,500.arrow_forwardOutput TFC ($) TVC ($) TC ($) (Q) 2 100 104 204 3 100 203 303 4 100 300 400 5 100 405 505 6 100 512 612 7 100 621 721 Given the information about short-run costs in the table above, we can conclude that the firm will minimize the average total cost of production when Q = (Round your response to the nearest whole number.)arrow_forward
 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning


 Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning





