
Concept explainers
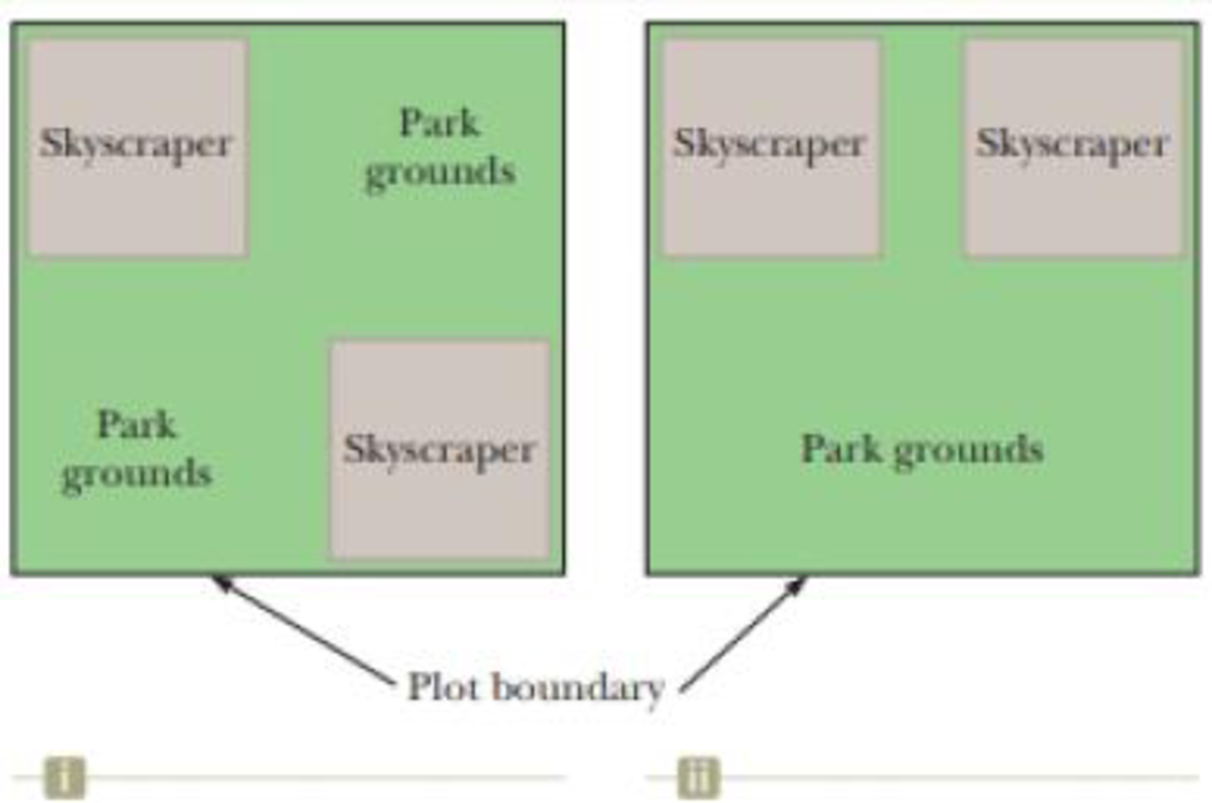
You are working as an expert witness for the owner of a skyscraper complex in a downtown area. The owner is being sued by pedestrians on the streets below his buildings who were injured by falling glass when windows popped outward from the sides of the building. The Bernoulli effect can have important consequences for window’s in such buildings. For example, wind can blow around a skyscraper at remarkably high speed, creating low pressure on the outside surface of the windows. The higher atmospheric pressure in the still air inside the buildings can cause windows to pop out. (a) In your research into the case, you find some overhead views of your client’s project, as shown below. The project includes two tall skyscrapers and some park area on a square plot. Plan (i) (Fig. P14.26(i), page 382) was submitted by the original architects and planners. At the last minute, the owner decided he didn’t want the park grounds to be divided into two areas and submitted Plan (ii) (Fig. P14.26(ii), which is the way the project was built. Explain to your client why Plan (ii) is a much more dangerous situation in terms of windows popping out than Plan (i). (b) Your client is not convinced by your conceptual argument in part (a), so you provide a numerical argument. Suppose a horizontal wind blows with a speed of 11.2 m/s outside a large pane of plate glass with dimensions 4.00 m × 1.50 m. Assume the density of the air to be constant at 1.20 kg/ m3. The air inside the building is at atmospheric pressure. Calculate the total force exerted by air on the windowpane for your client. (c) What If? To further convince your client of the problems with the building design, calculate the total force exerted by air on the windowpane if the wind speed between the buildings is 22.4 m/s, twice as high as in part (b).
Figure P14.26
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Bundle: Physics For Scientists And Engineers With Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 10th + Webassign Printed Access Card For Serway/jewett's Physics For Scientists And Engineers, 10th, Single-term
- A block of mass m = 3.00 kg situated on a rough incline at an angle of 0 = 37.0° is connected to a spring of negligible mass having a spring constant of 100 N/m (see the figure below). The pulley is frictionelss. The block is released from rest when the spring is unstretched. The block moves 11.0 cm down the incline before coming to rest. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between block and incline. k=100 N/m Ө marrow_forward23. What is the velocity of a beam of electrons that goes undeflected when passing through perpendicular electric and magnetic fields of magnitude 8.8 X 103 V/m and 7.5 X 10-3 T. respectively? What is the radius of the electron orbit if the electric field is turned off?arrow_forward10. A light bulb emits 25.00 W of power as visible light. What are the average electric and magnetic fields from the light at a distance of 2.0 m?arrow_forward
- 9. Some 1800 years ago Roman soldiers effectively used slings as deadly weapons. The length of these slings averaged about 81 cm and the lead shot that they used weighed about 30 grams. If in the wind up to a release, the shot rotated around the Roman slinger with a period of .15 seconds. Find the maximum acceleration of the shot before being released in m/s^2 and report it to two significant figures.arrow_forwardIn the movie Fast X, a 10100 kg round bomb is set rolling in Rome. The bomb gets up to 17.6 m/s. To try to stop the bomb, the protagonist Dom swings the counterweight of a crane, which has a mass of 354000 kg into the bomb at 3.61 m/s in the opposite direction. Directly after the collision the crane counterweight continues in the same direction it was going at 2.13 m/s. What is the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the bomb right after the collision?arrow_forwardDon't use aiarrow_forward
- Make sure to draw a sketch with scale as wellarrow_forwardMake sure to draw a sketch with scalearrow_forwardUltimate Byleth and Little Mac fight. Little Mac, who is a boxer, dashes forward at 26.6 m/s, fist first. Byleth moves in the opposite direction at 3.79 m/s, where they collide with Little Mac’s fist. After the punch Byleth flies backwards at 11.1 m/s. How fast, and in what direction, is Little Mac now moving? Little Mac has a mass of 48.5 kg and Byleth has a mass of 72.0 kg.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





