
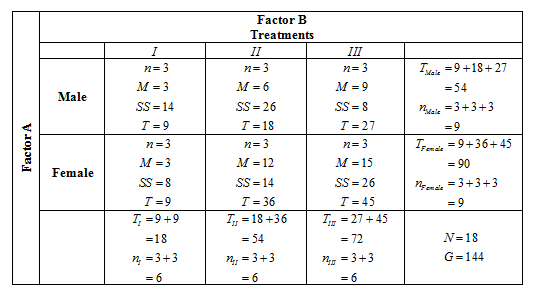
The following data are from a two-factor study examining the effects of three treatment conditions on males and females.
a. Use an ANOVA with
b. Test the simple main effects using
| Treatment | ||||
| I | II | III | ||
| 1 | 7 | 9 | ||
| Male | 2 | 2 | 11 | |
| 6 | 9 | 7 | ||
| Factor A: Gender | ||||
| 3 | 10 | 16 | ||
| 1 | 11 | 18 | ||
| 5 | 15 | 11 | ||
| Female | ||||
- If the mean differences of the treatments are different.
- Test the simple main effects to evaluate the difference between males and females for each treatment.
Answer to Problem 21P
Solution:
- For these data, gender (Factor A) and treatment (Factor B) have significant effect. These data do not produce a significant interaction. This means, that the effect of treatment does not depend on the gender.
- There is a significant difference between males and females in treatments II and III but not in treatment I.
Explanation of Solution
Given Info:
Formula used:
The degrees of freedoms are:
The sums of squares are:
The MS values needed for the F-ratios are:
The F-ratios are:
Calculation:
Part a:
For a two-factor study, there are three separate hypotheses, the two main effects and the interaction.
For Factor A, the null hypothesis states that there is no difference in the scores for male vs. female. In symbols,
For Factor B, the null hypothesis states that there is no difference in the scores at different treatments. In symbols,
For the
The degrees of freedoms are:
The sums of squares are:
The MS values needed for the F-ratios are:
The F-ratios are:
The two factor ANOVA table is shown below:
| Source | SS | df | MS | F |
| Between Treatments | 360 | 5 | ||
| Factor | 72 | 1 | 72 | 9.00 |
| Factor | 252 | 2 | 126 | 15.75 |
| | 36 | 2 | 18 | 2.25 |
| Within Treatments | 96 | 12 | 8 | |
| Total | 456 | 17 |
From F table, at
Part b:
We test the simple main effect of factor A for each level of factor B.
For treatment I:
| Treatments I | ||
| Male | Female | |
| | | |
There is no significant difference between males and females in treatment I.
For treatment II:
| Treatments II | ||
| Male | Female | |
| | | |
There is significant difference between males and females in treatment II.
For treatment III:
| Treatments III | ||
| Male | Female | |
| | | |
There is significant difference between males and females in treatment III.
Conclusion:
- There is a significant main effect for gender (Factor A) and treatment (Factor B) but there is no significant interaction.
- There is a significant difference between males and females in treatments II and III but not in treatment I.
Justification:
Since
Since
Since
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap Course List)
- 1. Define probability: 2. Define statistics:arrow_forwardResults of tossing a coin four times: H, H, H, H How many times is the Coin expected to come up heads? How did you determine this number? Calculate the % deviation. Can these results be used to conclude that a coin is not fair? Why or why not?arrow_forwardCycles to failure Position in ascending order 0.5 f(x)) (x;) Problem 44 Marsha, a renowned cake scientist, is trying to determine how long different cakes can survive intense fork attacks before collapsing into crumbs. To simulate real-world cake consumption, she designs a test where cakes are subjected to repeated fork stabs and bites, mimicking the brutal reality of birthday parties. After rigorous testing, Marsha records 10 observations of how many stabs each cake endured before structural failure. Construct P-P plots for (a.) a normal distribution, (b.) a lognormal distribution, and (c.) a Weibull distribution (using the information included in the table below). Which distribution seems to be the best model for the cycles to failure for this material? Explain your answer in detail. Observation Empirical cumulative Probability distribution Cumulative distribution Inverse of cumulative distribution F-1 (-0.5) F(x)) (S) n 4 3 1 0.05 9 5 2 0.15 7 7 3 0.25 1 10 4 0.35 3 12 5 0.45 Normal…arrow_forward
- Problem 3 In their lab, engineer Daniel and Paulina are desperately trying to perfect time travel. But the problem is that their machine still struggles with power inconsistencies-sometimes generating too little energy, other times too much, causing unstable time jumps. To prevent catastrophic misjumps into the Jurassic era or the far future, they must calibrate the machine's power output. After extensive testing, they found that the time machine's power output follows a normal distribution, with an average energy level of 8.7 gigawatts and a standard deviation of 1.2 gigawatts. The Time Travel Safety Board has set strict guidelines: For a successful time jump, the machine's power must be between 8.5 and 9.5 gigawatts. What is the probability that a randomly selected time jump meets this precision requirement? Daniel suggests that adjusting the mean power output could improve time-travel accuracy. Can adjusting the mean reduce the number of dangerous misjumps? If yes, what should the…arrow_forwardProblem 5 ( Marybeth is also interested in the experiment from Problem 2 (associated with the enhancements for Captain America's shield), so she decides to start a detailed literature review on the subject. Among others, she found a paper where they used a 2"(4-1) fractional factorial design in the factors: (A) shield material, (B) throwing mechanism, (C) edge modification, and (D) handle adjustment. The experimental design used in the paper is shown in the table below. a. Run A B с D 1 (1) -1 -1 -1 1 2 a 1 -1 -1 1 3 bd -1 1 -1 1 4 abd 1 1 -1 1 5 cd -1 -1 1 -1 6 acd 1 -1 1 -1 7 bc -1 1 1 -1 abc 1 1 1 -1 paper? s) What was the generator used in the 2"(4-1) fractional factorial design described in the b. Based on the resolution of this design, what do you think about the generator used in the paper? Do you think it was a good choice, or would you have selected a different one? Explain your answer in detail.arrow_forwardSuppose we wish to test the hypothesis that women with a sister’s history of breast cancer are at higher risk of developing breast cancer themselves. Suppose we assume that the prevalence rate of breast cancer is 3% among 60- to 64-year-old U.S. women, whereas it is 5% among women with a sister history. We propose to interview 400 women 40 to 64 years of age with a sister history of the disease. What is the power of such a study assuming that the level of significance is 10%? I only need help writing the null and alternative hypotheses.arrow_forward
- 4.96 The breaking strengths for 1-foot-square samples of a particular synthetic fabric are approximately normally distributed with a mean of 2,250 pounds per square inch (psi) and a standard deviation of 10.2 psi. Find the probability of selecting a 1-foot-square sample of material at random that on testing would have a breaking strength in excess of 2,265 psi.4.97 Refer to Exercise 4.96. Suppose that a new synthetic fabric has been developed that may have a different mean breaking strength. A random sample of 15 1-foot sections is obtained, and each section is tested for breaking strength. If we assume that the population standard deviation for the new fabric is identical to that for the old fabric, describe the sampling distribution forybased on random samples of 15 1-foot sections of new fabricarrow_forwardUne Entreprise œuvrant dans le domaine du multividéo donne l'opportunité à ses programmeurs-analystes d'évaluer la performance des cadres supérieurs. Voici les résultats obtenues (sur une échelle de 10 à 50) où 50 représentent une excellente performance. 10 programmeurs furent sélectionnés au hazard pour évaluer deux cadres. Un rapport Excel est également fourni. Programmeurs Cadre A Cadre B 1 34 36 2 32 34 3 18 19 33 38 19 21 21 23 7 35 34 8 20 20 9 34 34 10 36 34 Test d'égalité des espérances: observations pairéesarrow_forwardA television news channel samples 25 gas stations from its local area and uses the results to estimate the average gas price for the state. What’s wrong with its margin of error?arrow_forward
- You’re fed up with keeping Fido locked inside, so you conduct a mail survey to find out people’s opinions on the new dog barking ordinance in a certain city. Of the 10,000 people who receive surveys, 1,000 respond, and only 80 are in favor of it. You calculate the margin of error to be 1.2 percent. Explain why this reported margin of error is misleading.arrow_forwardYou find out that the dietary scale you use each day is off by a factor of 2 ounces (over — at least that’s what you say!). The margin of error for your scale was plus or minus 0.5 ounces before you found this out. What’s the margin of error now?arrow_forwardSuppose that Sue and Bill each make a confidence interval out of the same data set, but Sue wants a confidence level of 80 percent compared to Bill’s 90 percent. How do their margins of error compare?arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

