
Sketch the magnitude Bode plot for
Sketch the Bode magnitude plots for given transfer function.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The transfer function is,
Calculation:
Compare the denominator factor of equation (1) with the standard quadratic equation
For the quadratic factor, the corner frequency is
Substitute
Simplify the above equation as follows:
From the above equation, the corner frequencies
Re-write the transfer function
From equation (2), the magnitude function of
Write the above equation in decibel (dB).
From equation (2), the phase angle is expressed as follows:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Similarly, by substituting various values for
Table 1:
| 0.1 | 1 | 2 | 10 | 20 | 50 | |
| –26.063 | –9.0092 | –6.903 | –4.192 | –3.021 | –12.709 |
The Figure 1 is the magnitude plot of the given transfer function obtained using Table 1.
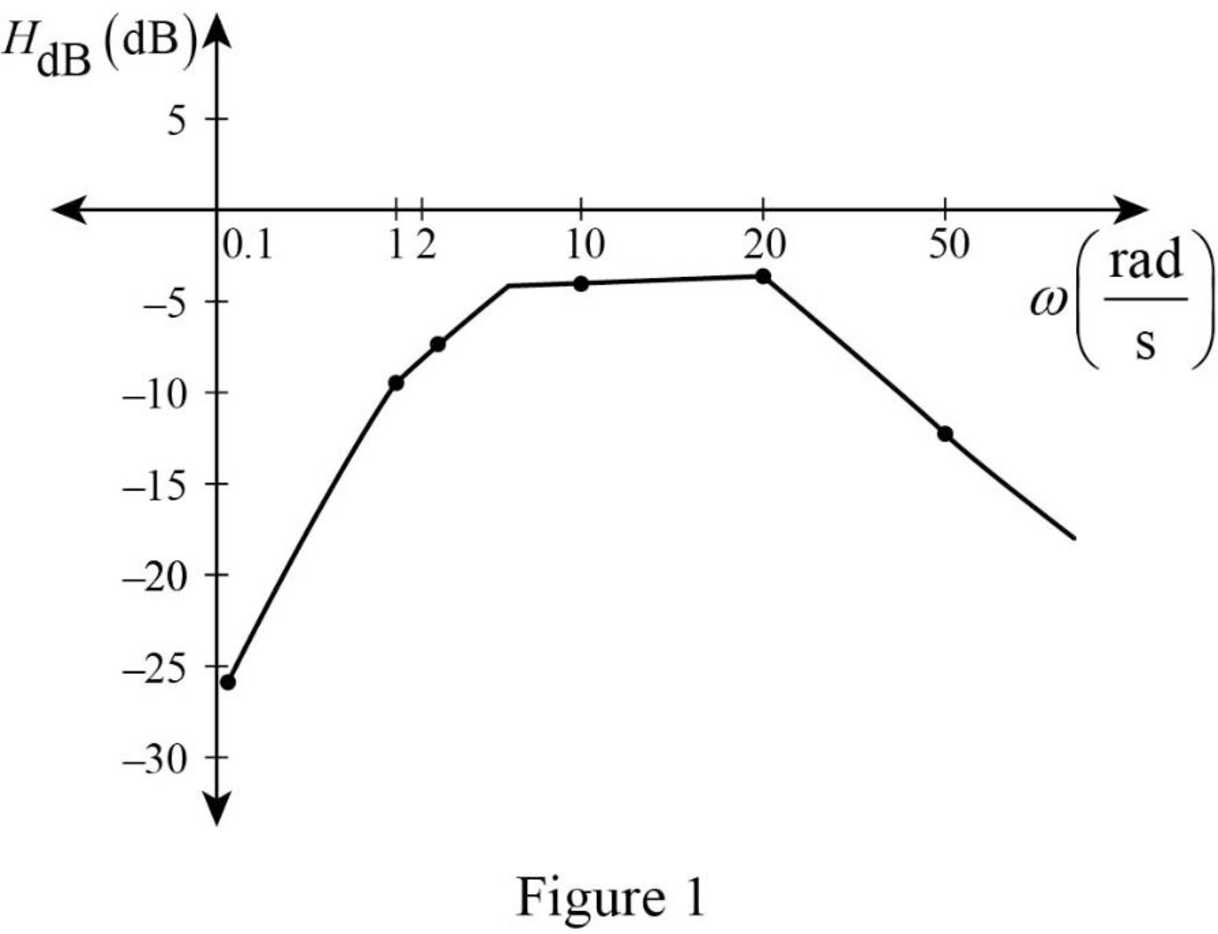
Conclusion:
Thus, the Bode magnitude plot for given transfer function is sketched.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
- The circuit is in the DC steady state, So all transients are passed. What are the values of 1 and V, under those conditions. P 24v + + √2 АЛАД 42 4F 3.H ww 22 eee + 203 Varrow_forwardFind the value of Vc (t) for all I That is, the complete response including natural and forced responses.) АДДА 422 OV ДААД t = 0 3F + V(t) -arrow_forward1.0 Half-power point (left) 0.5 Minor lobes Main lobe maximum direction Main lobe Half-power point (right) Half-power beamwidth (HP) Beamwidth between first nulls (BWFN) *Which of the following Lobes of an antenna Pattern 180 out of Phase the main Lobe ? And where are the ch other gems ?arrow_forward
- The normalized radiation intensity of an antenna is represented by U(0) = cos² (0) cos² (30), w/sr Find the a. half-power beamwidth HPBW (in radians and degrees) b. first-null beamwidth FNBW (in radians and degrees)arrow_forwardQ1/ Route the following flood hydrograph through a river reach for which storage duration constant = 10 hr and weighted factor = 0.25. At the start of the inflow flood, the outflow discharge is 60m³/s. Inflow (m/s) Time (hr) 140 60 100 0 4 8 12 16 120 80 40 20 Q2/ Answer the following: 1. Define water requirements and list the losses of irrigation. Q3/ Irrigation project with the following data: = 150 mm/m Root Zone Depth (RZD) = 1.1 m 15% of the net depth - Available Water PAD = 50%, Leaching Requirement Rainfall = 12 mm, = water Losses = 10% of the net depth. If the net water depth added after depletion of already available water, Calculate: gross irrigation water, and application efficiency. C= Carrow_forwardA3 m long cantilever ABC is built-in at A, partially supported at B, 2 m from A, with a force of 10 kN and carries a vertical load of 20 kN at C. A uniformly distributed bad of 5 kN/m is also applied between A and B. Determine (a) the values of the vertical reaction and built-in moment at A and (b) the deflection of the free end C of the cantilever, Develop an expression for the slope of the beam at any position and hence plot a slope diagram. E = 208GN / (m ^ 2) and 1 = 24 * 10 ^ - 6 * m ^ 4arrow_forward
- 7. Consider the following feedback system with a proportional controller. K G(s) The plant transfer function is given by G(s) = 10 (s + 2)(s + 10) You want the system to have a damping ratio of 0.3 for unit step response. What is the value of K you need to choose to achieve the desired damping ratio? For that value of K, find the steady-state error for ramp input and settling time for step input. Hint: Sketch the root locus and find the point in the root locus that intersects with z = 0.3 line.arrow_forwardCreate the PLC ladder logic diagram for the logic gate circuit displayed in Figure 7-35. The pilot light red (PLTR) output section has three inputs: PBR, PBG, and SW. Pushbutton red (PBR) and pushbutton green (PBG) are inputs to an XOR logic gate. The output of the XOR logic gate and the inverted switch SW) are inputs to a two-input AND logic gate. These inputs generate the pilot light red (PLTR) output. The two-input AND logic gate output is also fed into a two-input NAND logic PBR PBG SW TSW PLTR Figure 7-35. Logic gate circuit for Example 7-3. PLTW Goodheart-Willcox Publisher gate. The temperature switch (TSW) is the other input to the NAND logic gate. The output generated from the NAND logic gate is labeled pilot light white (PLTW).arrow_forwardImaginary Axis (seconds) 1 6. Root locus for a closed-loop system with L(s) = is shown below. s(s+4)(s+6) 15 10- 0.89 0.95 0.988 0.988 -10 0.95 -15 -25 0.89 20 Root Locus 0.81 0.7 0.56 0.38 0.2 5 10 15 System: sys Gain: 239 Pole: -0.00417 +4.89 Damping: 0.000854 Overshoot (%): 99.7 Frequency (rad/s): 4.89 System: sys Gain: 16.9 Pole: -1.57 Damping: 1 Overshoot (%): 0 Frequency (rad/s): 1.57 0.81 0.7 0.56 0.38 0.2 -20 -15 -10 -5 5 10 Real Axis (seconds) From the values shown in the figure, compute the following. a) Range of K for which the closed-loop system is stable. b) Range of K for which the closed-loop step response will not have any overshoot. Note that when all poles are real, the step response has no overshoot. c) Smallest possible peak time of the system. Note that peak time is the smallest when wa is the largest for the dominant pole. d) Smallest possible settling time of the system. Note that peak time is the smallest when σ is the largest for the dominant pole.arrow_forward
- For a band-rejection filter, the response drops below this half power point at two locations as visualised in Figure 7, we need to find these frequencies. Let's call the lower frequency-3dB point as fr and the higher frequency -3dB point fH. We can then find out the bandwidth as f=fHfL, as illustrated in Figure 7. 0dB Af -3 dB Figure 7. Band reject filter response diagram Considering your AC simulation frequency response and referring to Figure 7, measure the following from your AC simulation. 1% accuracy: (a) Upper-3db Frequency (fH) = Hz (b) Lower-3db Frequency (fL) = Hz (c) Bandwidth (Aƒ) = Hz (d) Quality Factor (Q) =arrow_forwardP 4.4-21 Determine the values of the node voltages V1, V2, and v3 for the circuit shown in Figure P 4.4-21. 29 ww 12 V +51 Aia ww 22. +21 ΖΩ www ΖΩ w +371 ①1 1 Aarrow_forward1. What is the theoretical attenuation of the output voltage at the resonant frequency? Answer to within 1%, or enter 0, or infinity (as “inf”) Attenuation =arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





