
Concept explainers
Name the two types of
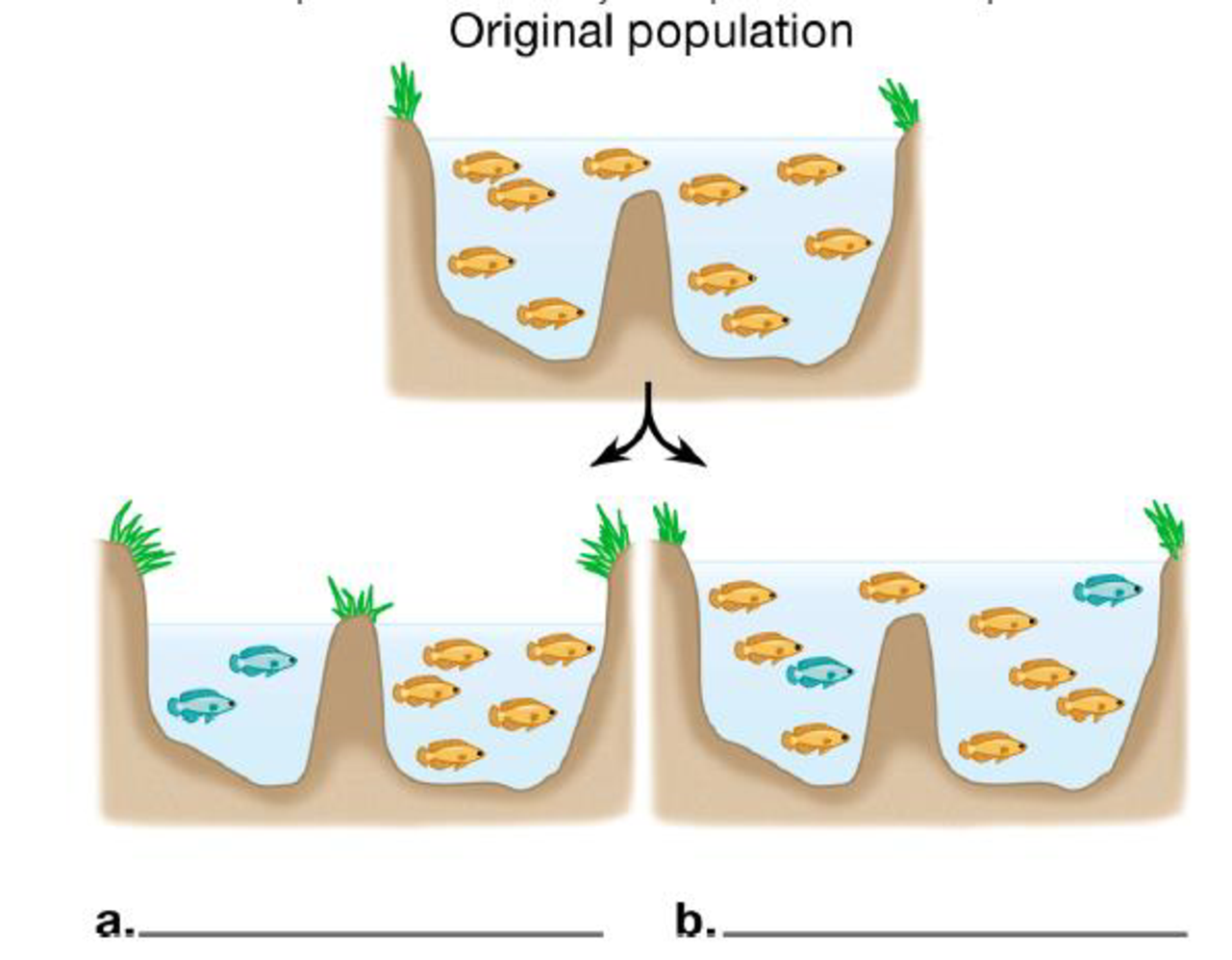
To name: Two types of speciation represented in the diagram and also to describe for each type in what way the reproductive barriers might have developed between the new species.
Concept introduction:
The speciation is an evolutionary process by which new species are formed. It can occur due to geographic, behavioral, anatomical and physiological factors.
The new species formed differ from their ancestors and cannot interbreed with their ancestral species to produce viable offspring.
Explanation of Solution
The type of speciation represented in the diagram (a) is allopatric speciation and in (b) is sympatric speciation.
The allopatric speciation occurs when two populations of a species are separated by a physical barrier such as a mountain or a hill. The gene flow between the two populations is stopped and over the time they become reproductively isolated due to natural selection, mutation or genetic drift.
In sympatric speciation, a new species arise from an ancestral species, while occupying the same geographical region. The two populations become reproductively isolated due to polyploidy, habitat differentiation and sexual selection.
Pictorial representation: Fig. 1 shows two types of speciation: (a) Allopatric speciation (b) Sympatric speciation.
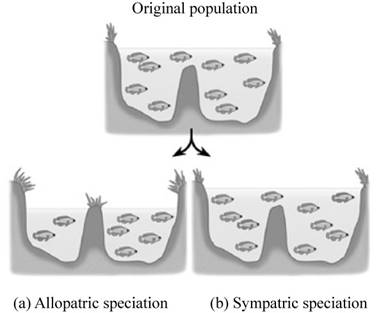
Fig.1: (a) Allopatric speciation (b) Sympatric speciation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
BSC 1005 PKG-W/MOD. MAST. ACCESS >CI<
- View History Bookmarks Window Help Quarter cements ents ons (17) YouTube Which amino acids would you expect to find marked on the alpha helix? canvas.ucsc.edu ucsc Complaint and Grievance Process - Academic Personnel pach orations | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 000000 000000000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 00000000 scope vious De 48 12.415 KATPM FEB 3 F1 F2 80 F3 a F4 F5 2 # 3 $ 85 % tv N A の Mon Feb 3 10:24 PM Lipid bilayer Submit Assignment Next > ZOOM < Å DII 8 བ བ F6 16 F7 F8 F9 F10 34 F11 F12 & * ( 6 7 8 9 0 + 11 WERTY U { 0 } P deletearrow_forwardDifferent species or organisms research for ecologyarrow_forwardWhat is the result of the following gram stain: positive ○ capsulated ○ acid-fast ○ negativearrow_forward
- What type of stain is the image below: capsule stain endospore stain gram stain negative stain ASM MicrobeLibrary.org Keplingerarrow_forwardWhat is the result of the acid-fast stain below: Stock Images by Getty Images by Getty Images by Getty Images by Getty Image Getty Images St Soy Getty Images by Getty Images by Getty Images Joy Getty encapsulated O endosporulating negative ○ positivearrow_forwardYou have a stock vial of diligence 75mg in 3ml and need to draw up a dose of 50mg for your patient.how many mls should you draw up to give this dosearrow_forward
- You are recquired to administer 150mg hydrocortisone intravenously,how many mls should you give?(stock =hydrocortisone 100mg in 2mls)arrow_forwardIf someone was working with a 50 MBq F-18 source, what would be the internal and external dose consequences?arrow_forwardWe will be starting a group project next week where you and your group will research and ultimately present on a current research article related to the biology of a pathogen that infects humans. The article could be about the pathogen itself, the disease process related to the pathogen, the immune response to the pathogen, vaccines or treatments that affect the pathogen, or other biology-related study about the pathogen. I recommend that you choose a pathogen that is currently interesting to researchers, so that you will be able to find plenty of articles about it. Avoid choosing a historical disease that no longer circulates. List 3 possible pathogens or diseases that you might want to do for your group project.arrow_forward
- not use ai pleasearrow_forwardDNK dagi nukleotidlar va undan sintezlangan oqsildagi peptid boglar farqi 901 taga teng bo'lib undagi A jami H boglardan 6,5 marta kam bo'lsa DNK dagi jami H bog‘lar sonini topingarrow_forwardOne of the ways for a cell to generate ATP is through the oxidative phosphorylation. In oxidative phosphorylation 3 ATP are produced from every one NADH molecule. In respiration, every glucose molecule produces 10 NADH molecules. If a cell is growing on 5 glucose molecules, how much ATP can be produced using oxidative phosphorylation/aerobic respiration?arrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College





