
Concept explainers
14-8 Answer true or false.
- The
functional group of an alcohol is the —OH (hydroxyl) group.
(h, The solubility of alcohols in water increases with increasing molecular weight.
(a)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: The functional group of an alcohol is the −OH (hydroxyl) group, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
The functional group of an alcohol is the −OH (hydroxyl) group. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The functional group of any alcohol is the —OH group. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(b)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: The parent name of an alcohol is the name of the longest carbon chain that contains the −OH group, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
The parent name of an alcohol is the name of the longest carbon chain that contains the −OH group.Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
According to IUPAC nomenclature, the parent name of an alcohol is the name of the longest.
carbon chain that contains the —OH group. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(c)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: A primary alcohol contains one −OH group, and a tertiary alcohol contains three-OH groups, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
A primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohol contains only one -OH groups but the connectivity of carbon atoms bearing −OH group is different. Thus, the statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Primary alcohol is alcohol in which the -OH group is linked to carbon that is connected to only one carbon atom. It has like -CH2 OH group in molecule. Secondary alcohol is alcohol in which the -OH group is linked to carbon that is connected to two other carbon atoms. Tertiary alcohol is alcohol in which the -OH group is linked to carbon that is connected to three other carbon atoms. Primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols have only one -OH group in their molecule but the connectivity of carbon atom bearing -OH group is different. Therefore, the given statement is false.
(d)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: In the IUPAC system, the presence of three −OH groups is shown by the ending −triol, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
In the IUPAC system, the presence of three −OH groups is shown by the ending −triol. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
In IUPAC nomenclature, the presence of three -OH groups is shown by the ending triol Therefore, the given statement is true.
(e)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: A glycol is a compound that contains two-OH groups. The simplest glycol is ethylene glycol,
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
A glycol is a compound that contains two-OH groups. The simplest glycol is ethylene glycol,
Explanation of Solution
Glycol is a compound that has two -OH groups attached to carbon atoms. Ethyl glycol is the simplest form of glycol. Its structural formula is:
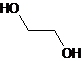
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(f)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: Because of the presence of an-OH group, all alcohols are polar compounds, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
Because of the presence of an -OH group, all alcohols are polar compounds. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Polar molecules have polar covalent bonds connected between the atoms. Methanol is an example of alcohol. Here, the O-C bond and O-H bond are polar covalent bonds. In methanol, there is a difference in electronegativity between the O-C bond (3.5-2.5 = 1.0) and O-H bond (3.5-2.1 = 1.4) Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself. Due to the presence of the O-H bond, all alcohols are polar molecules.
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(g)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: The boiling point of alcohols increases with increasing molecular weight, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
The boiling point of alcohols increases with increasing molecular weight. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The temperature at which the atmospheric pressure is equal to the vapor pressure is known as boiling point. As the molecular weight increases, more atoms are involved in the non-covalent interaction. Due to this tact, more energy (more temperature) is required to break this non-covalent interactions.Therefore, the given statement is true.
(h)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: The solubility of alcohols in water increases with increasing molecular weight, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
The solubility of alcohols in water decreases with increasing molecular weight. Thus, the statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Alcohols are more soluble in water than hydrocarbons. This is due to the presence of the O-H group in alcohol. The O-H group undergoes hydrogen bonding with a hydrogen atom in the water molecule.
As the molecular weight increases, simultaneously the hydrocarbon chain in alcohol will also increase. Now the alcohol stars behaving more like hydrocarbons. Therefore, the solubility decreases with the increase in molecular weight.
Therefore, the given statement is false.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Bundle: Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry, 11th + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Please draw the inverted chair forms of the products for the two equilibrium reactions shown below. Circle the equilibrium reaction that would have a AG = 0, i.e., the relative energy of the reactant (to the left of the equilibrium arrows) equals the relative energy of the product? [No requirement to show or do calculations.] CH3 CH3 HH CH3 1 -CH3arrow_forward5. Please consider the Newman projection of tartaric acid drawn below as an eclipsed conformer (1). Please draw the most stable conformer and two intermediate energy conformers noting that staggered conformers are lower in energy than eclipsed forms even if the staggered conformers have gauche relationships between groups. [Draw the substituents H and OH on the front carbons and H, OH and CO₂H on the back carbons based on staggered forms. -CO₂H is larger than -OH.] OH COH ICOOH COOH COOH 1 2 COOH COOH 3 4 Staggered Staggered Staggered (most stable) Indicate the number of each conformer above (1, 2, 3 and 4) that corresponds to the relative energies below. Ref=0 Rotation 6. (60 points) a. Are compounds 1 and 2 below enantiomers, diastereomers or identical? OH OH HO HO LOH HO HO OH 2 OH OH b. Please complete the zig-zag conformation of the compound (3R,4S)-3,4-dichloro-2,5-dimethylhexane by writing the respective atoms in the boxes. 3.arrow_forwardThe plutonium isotope with 144 neutrons Enter the chemical symbol of the isotope.arrow_forward
- The mass ratio of sodium to fluorine in sodium fluoride is 1.21:1. A sample of sodium fluoride produced 26.1 gg of sodium upon decomposition. How much fluorine was formed?arrow_forward32S 16 Enter your answers numerically separated by a comma. Np. Nn = 跖 ΟΙ ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer ? protons, neutronsarrow_forward2. Which dimethylcyclohexane compounds shown below exhibit symmetry and therefore are not chiral and would not rotate plane polarized light. 1 CH3 CH CH3 CH3 2 3 CH3arrow_forward
- Can you please explain why the correct answer for this question is letter B? I chose letter A because I thought that a kinetic product was a 1,2-addition. Please give a detailed explanation.arrow_forwardCan you please explain why the answer is structures 2 and 3? Please include a detailed explanation and show how the synthesis can be done with those two structures.arrow_forwardCan you please explain why the correct answer to this question is option 2? I am having trouble understanding how and why. Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing of how the diene and dienophile would create the product in the question.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

