
Concept explainers
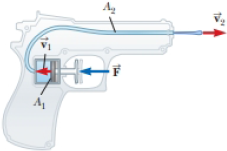
Review. In a water pistol, a piston drives water through a large tube of area A1 into a smaller tube of area A2 as shown in Figure P14.46. The radius of the large tube is 1.00 cm and that of the small tube is 1.00 mm. The smaller tube is 3.00 cm above the larger tube. (a) If the pistol is fired horizontally at a height of 1.50 m, determine the time interval required for the water to travel from the nozzle to the ground. Neglect air resistance and assume atmospheric pressure is 1.00 atm. (b) If the desired range of the stream is 8.00 m, with what speed v2 must the stream leave the nozzle? (c) At what speed v1 must the plunger be moved to achieve the desired range? (d) What is the pressure at the nozzle? (e) Find the pressure needed in the larger tube. (f) Calculate the force that must be exerted on the trigger to achieve the desired range. (The force that must be exerted is due to pressure over and above atmospheric pressure.)
Figure P14.46
(a)
The time required for the water to travel from the nozzle to the ground.
Answer to Problem 14.78AP
The time required for the water to travel from the nozzle to the ground is
Explanation of Solution
The radius of the large tube is
Formula to calculate the time interval is,
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the time required for the water to travel from the nozzle to the ground is
(b)
The speed of the stream to leave the nozzle if the range of the stream is
Answer to Problem 14.78AP
The speed of the stream to leave the nozzle is
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the speed of the stream to leave the nozzle is,
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the speed of the stream to leave the nozzle is
(c)
The speed of the plunger is moved to achieve the range of
Answer to Problem 14.78AP
The speed of the plunger is
Explanation of Solution
By continuity equation at the plunger and exit point of the nozzle is,
Here,
Formula to calculate the area of the large tube is,
Here,
Formula to calculate the area of the small tube is,
Here,
Substitute
`
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the speed of the plunger is
(d)
The pressure at the nozzle.
Answer to Problem 14.78AP
The pressure at the nozzle is
Explanation of Solution
The pressure at the nozzle is equal to the atmospheric pressure.
The atmospheric pressure is equal to the
Conclusion:
Therefore, the pressure at the nozzle is
(e)
The pressure needed in the large tube.
Answer to Problem 14.78AP
The pressure needed in the large tube is
Explanation of Solution
Apply the Bernoulli’s equation at point
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the pressure needed in the large tube is
(f)
The force exerted on the trigger to achieve the range of
Answer to Problem 14.78AP
The force exerted on the trigger to achieve the range of
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the force exerted on the trigger is,
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the force exerted on the trigger to achieve the range of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Organic Chemistry
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardAir temperature of 37 °C increases swimming pool temperature of 2.55 °C. What is the fraction of the water in the pool must evaporate during this time to carry enough energy to keep the temperature of the pool constant? 4186 J/(kg°C) = specific heat of water 2,430,000 (2.43 x 106) J/kg = latent heat of vaporization for the water in the pool.arrow_forwardThe iceberg requires 7.4 x 1020 Joules of energy to melt it completely. It absorbs energy from the Sun at a constant average rate of 88 Watts/m2. The total surface area of iceberg exposed to the sunlight is 12 billion (1.2 x 1010) square meters. How long will it take for sunlight to melt the entire iceberg in yearsarrow_forward
- 1.0 kg block of ice to melt in the kitchen. The temperature in the kitchen is 31 °C. The ice starts out at 0 °C and takes an hour to melt and reach the same temperature as the surrounding room (31 °C). How much heat does the 1.0 kg of ice/water absorb from the room as it melts and heats up to 31 °C in Joules absorbed? Latent heat of fusion for water/ice is 334,000 J/kg Specific heat of water is 4186 J/kg°Carrow_forward5.84 If the coefficient of static friction between a table and a uni- form, massive rope is μ, what fraction of the rope can hang over the edge of the table without the rope sliding? 5.97 Block A, with weight Figure P5.97 3w, slides down an inclined plane S of slope angle 36.9° at a constant speed while plank B, with weight w, rests on top of A. The plank is attached by a cord to the wall (Fig. P5.97). (a) Draw a diagram of all the forces acting on block A. (b) If the coefficient of kinetic friction is the same between A and B and between S and A, determine its value. 36.9° 1arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





