
Customer profitability in a manufacturing firm. Mississippi Manufacturing makes a component called B2040. This component is manufactured only when ordered by a customer, so Mississippi keeps no inventory of B2040. The list price is $112 per unit, but customers who place “large” orders receive a 10% discount on price. The customers are manufacturing firms. Currently, the salespeople decide whether an order is large enough to qualify for the discount. When the product is finished, it is packed in cases of 10. If the component needs to be exchanged or repaired, customers can come back within 14 days for free exchange or repair.
The full cost of manufacturing a unit of B2040 is $95. In addition, Mississippi incurs customer-level costs. Customer-level cost-driver rates are:
| Order taking | $360 per order |
| Product handling | $15 per case |
| Rush-order processing | $560 per rush order |
| Exchange and repair costs | $50 per unit |
Information about Mississippi’s five biggest customers follows:
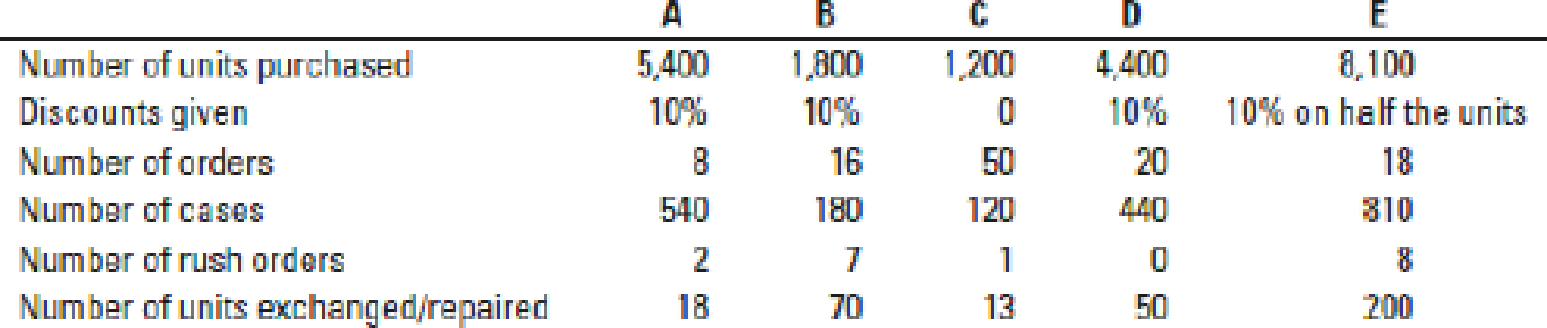
All customers except E ordered units in the same order size. Customer E’s order quantity varied, so E got a discount part of the time but not all the time.
- 1. Calculate the customer-level operating income for these five customers. Use the format in Figure 14-3. Prepare a customer-profitability analysis by ranking the customers from most to least profitable, as in Figure 14-4.
Required
Required
- 2. Discuss the results of your customer-profitability analysis. Does Mississippi have unprofitable customers? Is there anything Mississippi should do differently with its five customers?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting, Student Value Edition Plus MyLab Accounting with Pearson eText - Access Card Package (16th Edition)
- Calculate the costarrow_forwardThe cost to manufacture an unfinished unit is $140 ($95 variable, $45 fixed). The selling price per unit is $155. The company has the unused productive capacity and has determined that units could be finished and sold for $198 with an increase in variable costs of 40%. What is the additional net income per unit to be gained by finishing the unit?arrow_forwardFinancial accounting questionarrow_forward
- If sales revenue is $110 million and accounts receivable increased by $18 million, the amount of cash received from customers: a. was $110 million. b. was $73 million. c. depends on the mix of cash sales and credit sales. d. was $92 million.arrow_forwardPlease solve this question general Accountingarrow_forwardCost accountingarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
