
(a)
Interpretation:
Structural formula has to be written for the given alcohols and correct IUPAC name has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
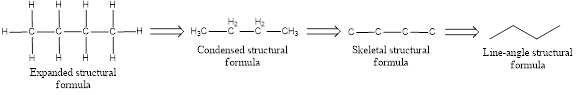
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in
alkane with “-ol”. - The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(a)
Answer to Problem 14.20EP
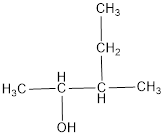
The structural formula is,
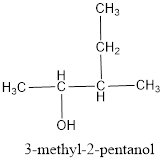
The correct IUPAC name of the given alcohol is 3-methyl-2-pentanol.
Explanation of Solution
Given name of alcohol is 3-ethyl-2-butanol.
From the name it is identified that the parent alkane is butane with a hydroxyl group on second carbon atom and an ethyl group on third carbon atom.

The structural formula for the given alcohol is drawn as shown above.
IUPAC name can be identified by finding the longest continuous carbon chain with the hydroxyl group. In this case it is found to be a five carbon chain and hence the parent is pentane. As the structure has a hydroxyl group in it, the suffix “-ol” has to be added instead of “-e” in the parent alkane. The numbering has to be given in a way that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering. Looking for the substituent, a methyl group is present on the third carbon atom. This gives the IUPAC name of the alcohol as 3-methyl-2-pentanol as hydroxyl group is in the second carbon atom.
The structural formula for the given alcohol is drawn and correct IUPAC name is assigned.
(b)
Interpretation:
Structural formula has to be written for the given alcohols and correct IUPAC name has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
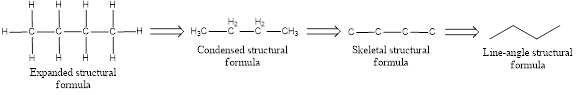
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in alkane with “-ol”.
- The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(b)
Answer to Problem 14.20EP
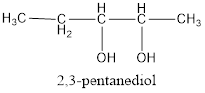
The structural formula is,
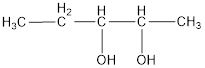
The correct IUPAC name of the given alcohol is 2,3-pentanediol.
Explanation of Solution
Given name of alcohol is 3,4-pentanediol.
From the name it is identified that there are two hydroxyl groups present each on third and fourth carbon atom of the parent alkane, pentane. The structure can be drawn as,

The structural formula for the given alcohol is drawn as shown above.
IUPAC name can be identified by finding the longest continuous carbon chain with the hydroxyl group. In this case it is found to be a five carbon chain and hence the parent is pentane. As the structure has two hydroxyl groups in it, the suffix “-
The structural formula for the given alcohol is drawn and correct IUPAC name is assigned.
(c)
Interpretation:
Structural formula has to be written for the given alcohols and correct IUPAC name has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
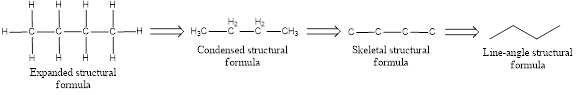
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in alkane with “-ol”.
- The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(c)
Answer to Problem 14.20EP
The structural formula is,
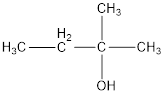
The correct IUPAC name of the given alcohol is 2-methyl-2-butanol.
Explanation of Solution
Given name of alcohol is 3-methyl-3-butanol.
From the name it is identified that the parent alkane is butane with a methyl group substituted in third carbon atom and a hydroxyl functional group on third carbon atom. The structure can be drawn as,
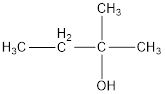
The structural formula for the given alcohol is drawn as shown above.
IUPAC name can be identified by finding the longest continuous carbon chain with the hydroxyl group. In this case it is found to be a four carbon chain and hence the parent is butane. As the structure has a hydroxyl group in it, the suffix “-ol” has to be added instead of “-e” in the parent alkane. The numbering has to be given in a way that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering. Looking for the substituents, a methyl group is present in the second carbon atom. This gives the IUPAC name of the alcohol as 2-methyl-2-butanol as hydroxyl group is in the second carbon atom.
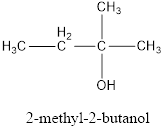
The structural formula for the given alcohol is drawn and correct IUPAC name is assigned.
(d)
Interpretation:
Structural formula has to be written for the given alcohols and correct IUPAC name has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
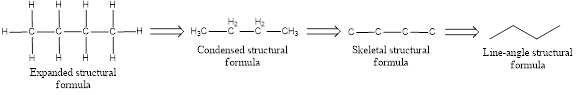
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in alkane with “-ol”.
- The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(d)
Answer to Problem 14.20EP
The structural formula is,
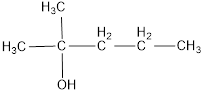
The correct IUPAC name of the given alcohol is 2-methyl-2-pentanol.
Explanation of Solution
Given name of alcohol is 1,1-dimethyl-1-butanol.
From the name it is identified that the parent alkane is butane with a hydroxyl group at first carbon atom and two methyl groups as substituents in first carbon atom. The structure can be drawn as,

The structural formula for the given alcohol is drawn as shown above.
IUPAC name can be identified by finding the longest continuous carbon chain with the hydroxyl group. In this case it is found to be a five carbon chain and hence the parent is pentane. As the structure has a hydroxyl group in it, the suffix “-ol” has to be added. The numbering has to be given in a way that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering. Looking for the substituents it is identified that a methyl group is present on second carbon atom. This gives the IUPAC name of the alcohol as 2-methyl-2-pentanol as hydroxyl group is in the second carbon atom.
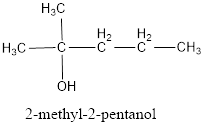
The structural formula for the given alcohol is drawn and correct IUPAC name is assigned.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC,+BIO.CHEM.-MINDTAP
- in the scope of the SCH4U course! please show all steps as im still learning how to format my answers in the format given, thank you!arrow_forwardhelp me solve this HWarrow_forwardMolecules of the form AH2 can exist in two potential geometries: linear or bent. Construct molecular orbital diagrams for linear and bent CH2. Identify the relevant point group, include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Which geometry would you predict to be more stable, and why? (Please draw out the diagram and explain)arrow_forward
- Indicate the variation in conductivity with concentration in solutions of strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes.arrow_forwardThe molar conductivity of a very dilute solution of NaCl has been determined. If it is diluted to one-fourth of the initial concentration, qualitatively explain how the molar conductivity of the new solution will compare with the first.arrow_forwardWhat does the phrase mean, if instead of 1 Faraday of electricity, Q coulombs (Q/F Faradays) pass through?arrow_forward
- What characteristics should an interface that forms an electrode have?arrow_forwardFor a weak acid AcH, calculate the dissociated fraction (alpha), if its concentration is 1.540 mol L-1 and the concentration [H+] is 5.01x10-4 mol L-1.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forward
- If the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardDetermine the distance between the metal and the OHP layer using the Helm- holtz model when the electrode's differential capacitance is 145 μF cm². DATA: dielectric constant of the medium for the interfacial zone &r= lectric constant of the vacuum &0 = 8.85-10-12 F m-1 = 50, die-arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning



