
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The model of cyclohexyne is to be built. An explanation for the instability of cyclohexyne structure is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 14.1P
The model of cyclohexyne is shown below.
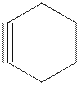
Cyclohexyne is unstable because of the ring strain due to the reduced bond angle in six carbon cyclic structure.
Explanation of Solution
Alkynes are hydrocarbons containing at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. The triple bonded carbons are sp hybridized. Alkynes have a linear geometry with bond angle of

Figure 1
In cyclohexyne, the six carbon atoms ring contains one carbon-carbon triple bond. The bond angle from
Cycloalkynes with carbon ring less than
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of cyclodecyne is to be built. The stability of cyclodecyne and cyclohexyne is to be compared.
Concept introduction:
Alkynes are hydrocarbons containing at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. The triple bonded carbons are sp hybridized. Alkynes due to triple bonds do not rotate and have linear geometry with bond angle
Answer to Problem 14.1P
The model of cyclodecyne is shown below.
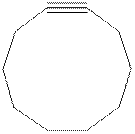
Cyclodecyne is more stable than cyclohexyne due to less bond angle strain.
Explanation of Solution
Alkynes are hydrocarbons containing at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. The triple bonded carbons are sp hybridized. Alkynes have a linear geometry with bond angle of

Figure 2
Cyclodecyne is comparatively stable than cyclohexyne because of the reduced ring strain. In cyclodecyne, the ten membered carbon ring of is large enough to accommodate a triple bond due to its floppiness arised by carbon-carbon bond rotations.
In cyclohexyne, the six carbon atoms ring contains one carbon-carbon triple bond. The bond angle from
The structure of cyclodecyne is shown in Figure 2.
Cyclodecyne is more stable than cyclohexyne due to less bond angle strain and large ring size of cyclodecyne.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- Feedback (7/10) Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining Ο (CH3CH2)2NH, TSOH Select to Draw V N. 87% Retryarrow_forwardIf I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene from 1-bromopropene, indicate the product that I have to add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when fluorobenzene reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained when chlorobenzene acid reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting benzenesulfonic acid with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting ethylbenzene with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained when tert-butylbenzene reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when acetophenone reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained from the reaction of N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained from the reaction of 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile with a sulfonitric mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained in the reaction of p-Toluidine with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained from the reaction of 4-methylbenzonitrile with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





