
Concept explainers
When Mendel did crosses of true-breeding purple- and white-flowered pea plants, the white-flowered trait disappeared from the F1. generation but reappeared in the F2 generation. Use genetic terms to explain why that happened.
To explain: Why the white color trait disappeared in the F1 generation and was again observed in the F2 generation in Mendel’s cross between purple- and white- flowered pea plants.
Introduction: Genes have alternate forms known as alleles, which are transmitted to offspring. If the two alleles are different, then there is a hybrid in the F1 generation. The dominant allele out of the two expresses itself and determines the phenotype. In F1 individuals, two different alleles segregate into gametes. During self-pollination, the gametes unite randomly, thereby giving a chance to recessive alleles to be expressed in a homozygous state at the F2 generation.
Explanation of Solution
The cross between the individuals that are true breeding homozygous for one allele gives different traits in F1 progeny. This is called as monohybrid cross. Several traits of pea plants were studied in which Mendel used the purple- and white-colored flower traits to perform monohybrid experiment. When Mendel crossed these plants, the F1 hybrids or first true breeding generation received was both dominant and recessive alleles equally but showed a purple pigment. This is because the purple-colored trait was dominant over white. That is, white-colored trait is and was not expressed recessive in the F1 generation. However, the white trait was expressed in F2 generation of the experiment. This was because it is only possible for a white allele to exist in a homozygous state, which causes the white trait to be expressed in F2 generation.
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows Mendel’s cross between purple- and white-flowered pea plants.
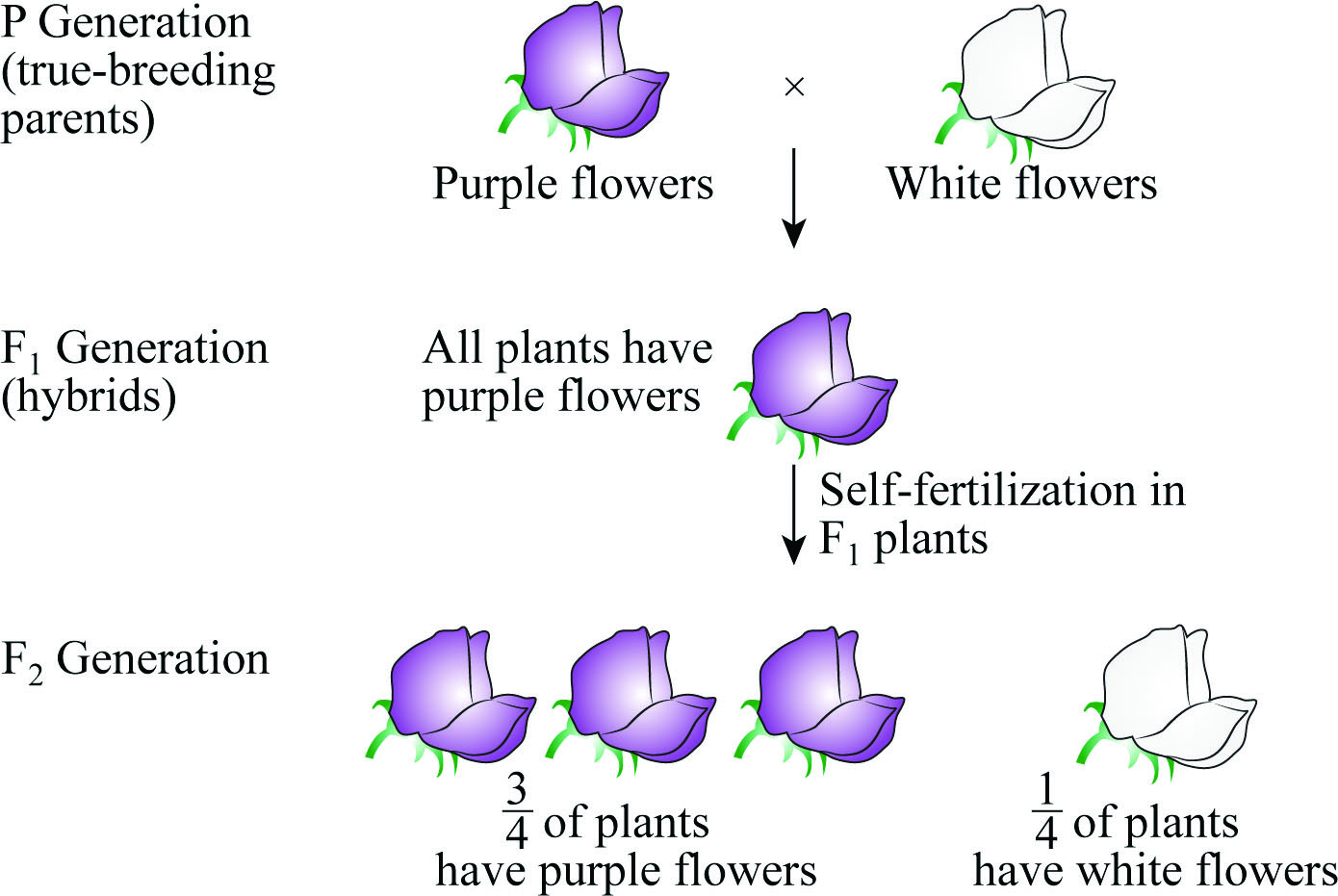
Fig.1: Mendel’s cross between purple- and white-flowered pea plants
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
- What did the Cre-lox system used in the Kikuchi et al. 2010 heart regeneration experiment allow researchers to investigate? What was the purpose of the cmlc2 promoter? What is CreER and why was it used in this experiment? If constitutively active Cre was driven by the cmlc2 promoter, rather than an inducible CreER system, what color would you expect new cardiomyocytes in the regenerated area to be no matter what? Why?arrow_forwardWhat kind of organ size regulation is occurring when you graft multiple organs into a mouse and the graft weight stays the same?arrow_forwardWhat is the concept "calories consumed must equal calories burned" in regrads to nutrition?arrow_forward
- You intend to insert patched dominant negative DNA into the left half of the neural tube of a chick. 1) Which side of the neural tube would you put the positive electrode to ensure that the DNA ends up on the left side? 2) What would be the internal (within the embryo) control for this experiment? 3) How can you be sure that the electroporation method itself is not impacting the embryo? 4) What would you do to ensure that the electroporation is working? How can you tell?arrow_forwardDescribe a method to document the diffusion path and gradient of Sonic Hedgehog through the chicken embryo. If modifying the protein, what is one thing you have to consider in regards to maintaining the protein’s function?arrow_forwardThe following table is from Kumar et. al. Highly Selective Dopamine D3 Receptor (DR) Antagonists and Partial Agonists Based on Eticlopride and the D3R Crystal Structure: New Leads for Opioid Dependence Treatment. J. Med Chem 2016.arrow_forward
- The following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. You are a chef in a fancy new science-themed restaurant. You have a recipe that calls for 1 teaspoon of resinferatoxin, but you feel uncomfortable serving foods with "toxins" in them. How much capsaicin could you substitute instead?arrow_forwardWhat protein is necessary for packaging acetylcholine into synaptic vesicles?arrow_forward1. Match each vocabulary term to its best descriptor A. affinity B. efficacy C. inert D. mimic E. how drugs move through body F. how drugs bind Kd Bmax Agonist Antagonist Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamicsarrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





