
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of
Concept-Introduction:
Lewis structure:
Electron dot structure also known as Lewis dot structure represents the number of valence electrons of an atom or constituent atoms bonded in a molecule. Each dot corresponds to one electron.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecules are determined by first drawing the skeletal structure for the given molecules, then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecules are determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Draw Lewis structure of
Outer valence electrons of Carbon and Oxygen are four and six respectively.
Here, one triple bond is required to complete the complete the octets of all the atoms.
After the distribution of electrons, both Carbon and Oxygen atoms gets a lone pair of electrons.
The Lewis structure of

Draw Lewis structure of
Outer valence electrons of Carbon and Nitrogen are four and five respectively.
Here, one triple bond is required to complete the complete the octets of all the atoms.
After the distribution of electrons, both Carbon and Nitrogen atoms gets a lone pair of electrons.
The Lewis structure of

Draw Lewis structure of
Outer valence electrons of Carbon are four.
Here, one triple bond is required to complete the complete the octets of all the atoms.
After the distribution of electrons, both Carbon and Carbon atoms gets a lone pair of electrons.
The Lewis structure of
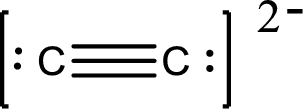
(b)
Interpretation:
MO diagrams of
Concept-Introduction:
Molecular orbital (MO) theory: It is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule.
According to this theory there are two types of orbitals,
- (1) Bonding orbitals
- (2) Antibonding orbitals
Electrons in molecules are filled in accordance with the energy; the anti-bonding orbital has more energy than the bonding orbitals.
The electronic configuration of oxygen molecule
The * represent the antibonding orbital
Orbital diagram represents each orbital with a box, with orbital’s in the same subshell in connected boxes, electrons are shown as arrows in the boxes, pointing up or down to indicate their spins.
Bond order: It is the measure of number of electron pairs shared between two atoms.
Bond length is inversely proportional to the bond order.
If two or more different chemical species having same number of valence electrons are known as isoelectronic species.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
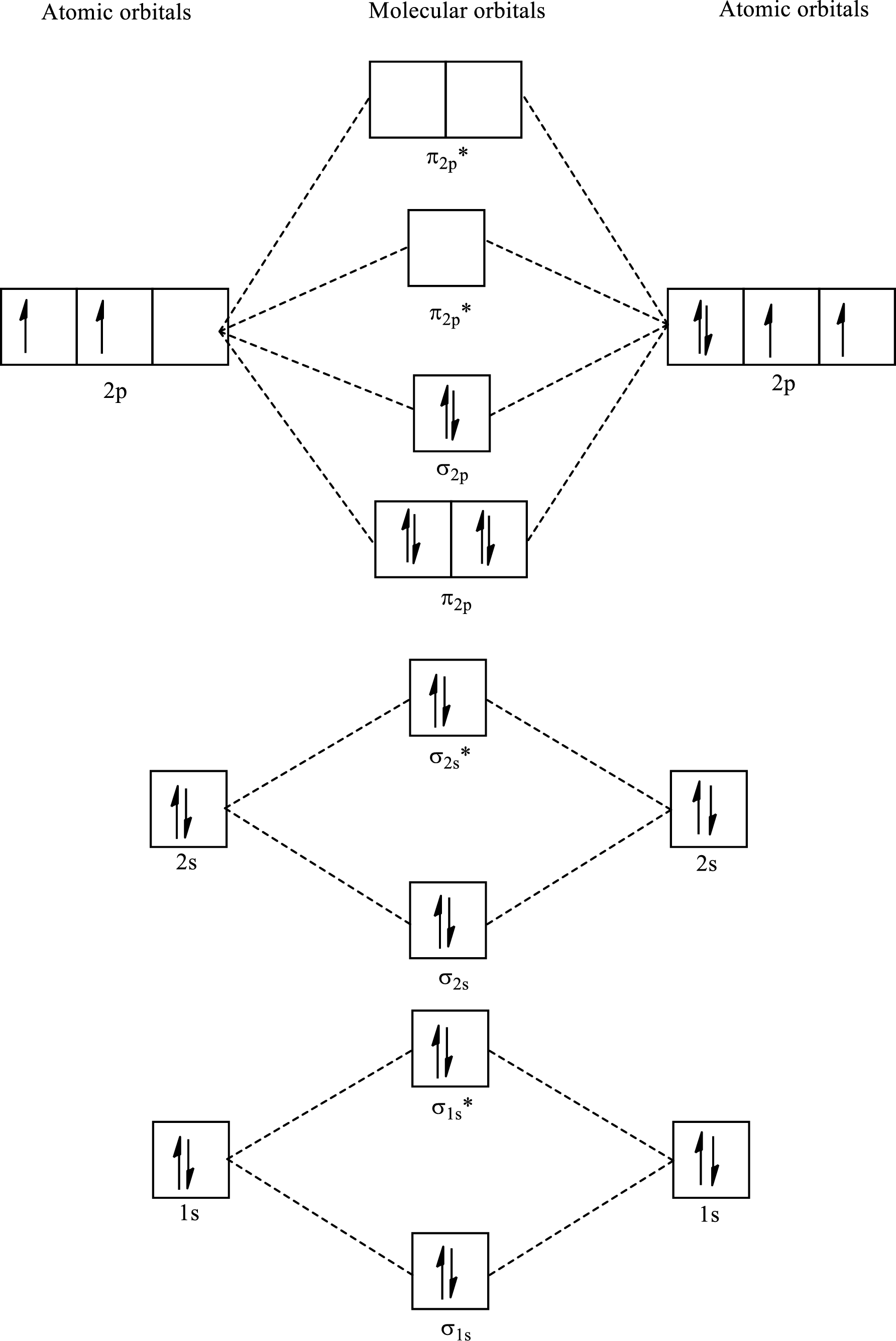
Determine the electron configuration:
Determine the bond order:
Here, number of bonding orbitals is
The number of electrons present in bonding and antibonding orbitals is same for these compounds. Hence,
The bond order for
The bond order for
Draw the MO diagram:
Molecular Orbital diagram for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change - Standalone book
- Briefly indicate the structure and bonding of silicates.arrow_forward4 Part C Give the IUPAC name and a common name for the following ether: Spell out the full names of the compound in the indicated order separated by a comma.arrow_forwardTry: Draw possible resonance contributing structures for the following organic species: CH3CH2NO2 [CH2CHCH2] [CH2CHCHO] [CH2CHCH2] [CH2CHNH2]arrow_forward
- Complete the following synthesis. (d). H+ ง сarrow_forwardCan the target compound be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the substituted benzene of the starting material? If yes, draw the synthesis. Include all steps and all reactants.arrow_forwardThis is a synthesis question. Why is this method wrong or worse than the "correct" method? You could do it thiss way, couldn't you?arrow_forward
- Try: Draw the best Lewis structure showing all non-bonding electrons and all formal charges if any: (CH3)3CCNO NCO- HN3 [CH3OH2]*arrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following reaction? Draw all the major products. If there are no major products, then there is no reaction that will take place. Use wedge and dash bonds when necessary.arrow_forwardZeolites. State their composition and structure. Give an example.arrow_forward
- Don't used hand raiting and show all reactionsarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardIX) By writing the appropriate electron configurations and orbital box diagrams briefly EXPLAIN in your own words each one of the following questions: a) The bond length of the Br2 molecule is 2.28 Å, while the bond length of the compound KBr is 3.34 Å. The radius of K✶ is 1.52 Å. Determine the atomic radius in Å of the bromine atom and of the bromide ion. Br = Br b) Explain why there is a large difference in the atomic sizes or radius of the two (Br and Br). Tarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





