
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bromination:

2-methyl propane undergoes radical bromination which yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.because bromination will occur where the tertiary radical is present.(Bromination reactions are more selective reaction).
The mechanism of monobromination of ethane (as an example) includes three steps,
- (i) Initiation
- (ii) Propagation
- (iii) Termination
Thus the mechanism of monobromination of ethane is shown below,
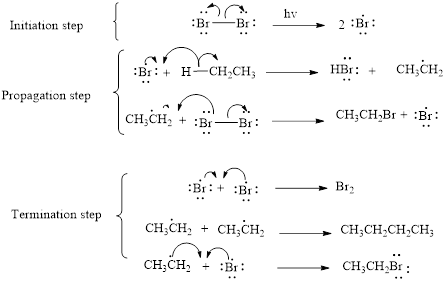
In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
Bromination will occur on tertiary radical than the secondary than primary radical, tertiary radical is more stable radical than the other radicals.
(a)
Answer to Problem 12P
3-methyl hexane undergoes radical bromination and yields the 3-bromo-3-methylhexane which is shown below
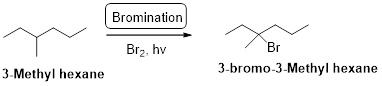
Explanation of Solution
3-methyl hexane undergoes radical bromination and yields the 3-bromo-3-methylhexane according to the above mentioned mechanism steps. The reaction is shown below,
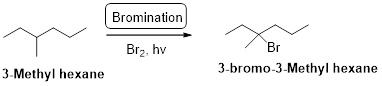
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Chlorination:
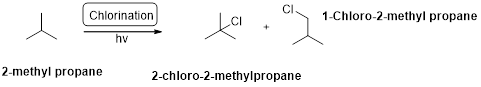
2-methyl propane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and 1-bromo-2-methyl propane.
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane includes three steps,
- (i) Initiation
- (ii) Propagation
- (iii) Termination
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane is shown below,
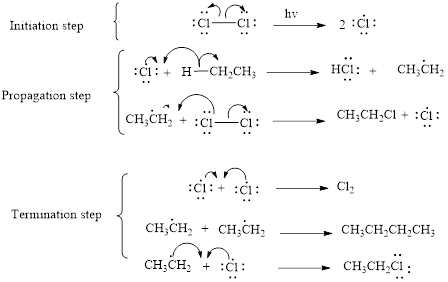
In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
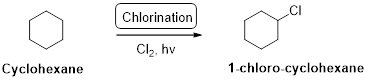
Cyclohexane undergoes radical chlorination; all the carbons in cyclohexane are secondary. Therefore, it yields the 1-chloro cyclohexane according to the above mentioned mechanism steps. And the reaction is shown above.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Chlorination:
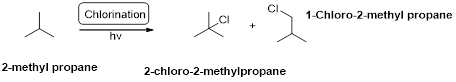
2-methyl propane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and 1-bromo-2-methyl propane.
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane includes three steps,
- (i) Initiation
- (ii) Propagation
- (iii) Termination
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane is shown below,

In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
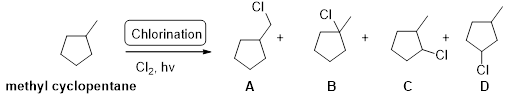
Methyl cyclopentane undergoes radical chlorination; the carbons in cyclopentane are secondary and primary. Therefore, it yields the four types of chlorocyclopentane according to the above mentioned mechanism steps. And the reaction is shown below
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry Study Guide & Solution Manual, Books a la Carte Edition
- 4. For the reactions below, draw the expected product. Be sure to indicate relevant stereochemistry or formal charges in the product structure. a) CI, H e b) H lux ligh Br 'Harrow_forwardArrange the solutions in order of increasing acidity. (Note that K (HF) = 6.8 x 10 and K (NH3) = 1.8 × 10-5) Rank solutions from least acidity to greatest acidity. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. ▸ View Available Hint(s) Least acidity NH&F NaBr NaOH NH,Br NaCIO Reset Greatest acidityarrow_forward1. Consider the following molecular-level diagrams of a titration. O-HA molecule -Aion °° о ° (a) о (b) (c) (d) a. Which diagram best illustrates the microscopic representation for the EQUIVALENCE POINT in a titration of a weak acid (HA) with sodium. hydroxide? (e)arrow_forward
- Answers to the remaining 6 questions will be hand-drawn on paper and submitted as a single file upload below: Review of this week's reaction: H₂NCN (cyanamide) + CH3NHCH2COOH (sarcosine) + NaCl, NH4OH, H₂O ---> H₂NC(=NH)N(CH3)CH2COOH (creatine) Q7. Draw by hand the reaction of creatine synthesis listed above using line structures without showing the Cs and some of the Hs, but include the lone pairs of electrons wherever they apply. (4 pts) Q8. Considering the Zwitterion form of an amino acid, draw the Zwitterion form of Creatine. (2 pts) Q9. Explain with drawing why the C-N bond shown in creatine structure below can or cannot rotate. (3 pts) NH2(C=NH)-N(CH)CH2COOH This bond Q10. Draw two tautomers of creatine using line structures. (Note: this question is valid because problem Q9 is valid). (4 pts) Q11. Mechanism. After seeing and understanding the mechanism of creatine synthesis, students should be ready to understand the first half of one of the Grignard reactions presented in a past…arrow_forwardPropose a synthesis pathway for the following transformations. b) c) d)arrow_forwardThe rate coefficient of the gas-phase reaction 2 NO2 + O3 → N2O5 + O2 is 2.0x104 mol–1 dm3 s–1 at 300 K. Indicate whether the order of the reaction is 0, 1, or 2.arrow_forward
- 8. Draw all the resonance forms for each of the following molecules or ions, and indicate the major contributor in each case, or if they are equivalent. (4.5 pts) (a) PH2 سمةarrow_forward3. Assign absolute configuration (Rors) to each chirality center. a. H Nitz C. он b. 0 H-C. C H 7 C. ་-4 917-417 refs H 1つ ८ ડુ d. Но f. -2- 01 Ho -OH 2HNarrow_forwardHow many signals do you expect in the H NMR spectrum for this molecule? Br Br Write the answer below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with Hs shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is colored red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red. Note for advanced students: In this question, any multiplet is counted as one signal. Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. No additional Hs to color in top molecule For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. No additional Hs to color in bottom moleculearrow_forward
- In the drawing area below, draw the major products of this organic reaction: 1. NaOH ? 2. CH3Br If there are no major products, because nothing much will happen to the reactant under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☐ : A คarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: NC Δ ? Some important Notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to draw bonds carefully to show important geometric relationships between substituents. Note: if your answer contains a complicated ring structure, you must use one of the molecular fragment stamps (available in the menu at right) to enter the ring structure. You can add any substituents using the pencil tool in the usual way. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х аarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction. Be sure you use dash and wedge bonds to show stereochemistry where it's important. + ☑ OH 1. TsCl, py .... 文 P 2. t-BuO K Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

