
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bromination:

2-methyl propane undergoes radical bromination which yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.because bromination will occur where the tertiary radical is present.(Bromination reactions are more selective reaction).
The mechanism of monobromination of ethane (as an example) includes three steps,
- (i) Initiation
- (ii) Propagation
- (iii) Termination
Thus the mechanism of monobromination of ethane is shown below,
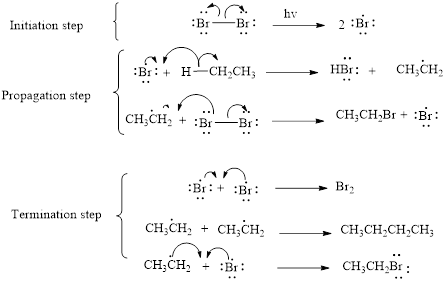
In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
Bromination will occur on tertiary radical than the secondary than primary radical, tertiary radical is more stable radical than the other radicals.
(a)
Answer to Problem 12P
3-methyl hexane undergoes radical bromination and yields the 3-bromo-3-methylhexane which is shown below
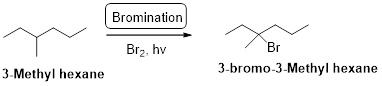
Explanation of Solution
3-methyl hexane undergoes radical bromination and yields the 3-bromo-3-methylhexane according to the above mentioned mechanism steps. The reaction is shown below,
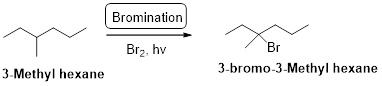
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Chlorination:
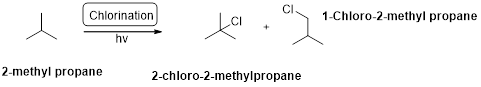
2-methyl propane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and 1-bromo-2-methyl propane.
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane includes three steps,
- (i) Initiation
- (ii) Propagation
- (iii) Termination
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane is shown below,
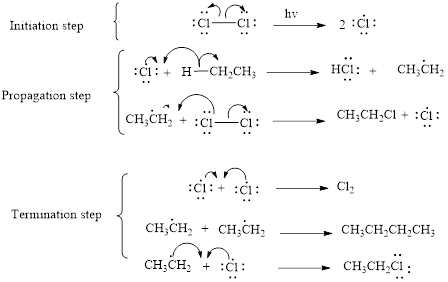
In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
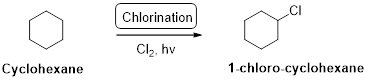
Cyclohexane undergoes radical chlorination; all the carbons in cyclohexane are secondary. Therefore, it yields the 1-chloro cyclohexane according to the above mentioned mechanism steps. And the reaction is shown above.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Chlorination:
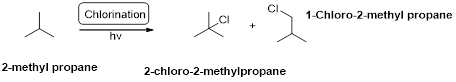
2-methyl propane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and 1-bromo-2-methyl propane.
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane includes three steps,
- (i) Initiation
- (ii) Propagation
- (iii) Termination
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane is shown below,

In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
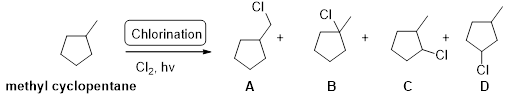
Methyl cyclopentane undergoes radical chlorination; the carbons in cyclopentane are secondary and primary. Therefore, it yields the four types of chlorocyclopentane according to the above mentioned mechanism steps. And the reaction is shown below
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EP ESSENTIAL ORG.CHEM.-MOD.MASTERING
- pls helparrow_forwardState the reason why compound A (m.p. 99-100°C) is heated under vacuum.1. So that the sample heating temperature is not too high when heated under vacuum.2. So that the temperature is higher than the melting point of compound A.3. So that cold water is not required in the sublimator.arrow_forwardTo find the theoretical % yield of a given reaction:1. actual amount obtained once crystallized2. (actual amount obtained / theoretical amount) x 1003. maximum amount of product that can be obtained / amount of initial reactantarrow_forward
- The reason activated carbon decolorizes and purifies a product is:1. It helps dissolve the product and then recrystallize it.2. It reacts with impurities in the product and removes them.3. It retains impurities by adsorption, purifying the product.arrow_forwardThe principle of a rotary evaporator is the same as that of:1. vacuum distillation2. reflux3. fractional distillationarrow_forwardAnhydrous MgSO4 is used to:1. Form a salt with the compound dissolved in the solution2. Remove water from a solution3. Neutralize a solutionarrow_forward
- Distillation under reduced pressure or vacuum consists of:1. Achieving distillation under anhydrous conditions.2. Causing a decrease in the distillation rate.3. Decreasing the pressure to lower the boiling point of the compound to be distilled.arrow_forwardAt the end of the silica gel production process, color changes occur during drying. Explain these color changes.arrow_forwardIf CoCl2/H2O is dissolved in a mixture of H2O and concentrated HCl in a test tube, the tube is gently heated over a flame to approximately 80°C and then cooled externally. Explain the color changes that occur.arrow_forward
- When producing silica gel, color changes occur at the end of the drying process. Explain these color changes.arrow_forwardDesign experiments in UV-Vis to figure the optimal mole ratio of copper (1:1, 2:1, 3:1 and etc)versus ethambutol using all necessary chemicals including dihydrochloride and copper nitrate hemipentahydrate and sodium hydroxide. Show how UV-Vis absorbance and maximum wavelength would change in responsearrow_forwardCorrect each molecule in the drawing area below so that it has the condensed structure it would have if it were dissolv a 0.1 M aqueous solution of HCI. If there are no changes to be made, check the No changes box under the drawing area. No changes. HO—CH,—C—CH,—OH X 5 2 2 2 HO–CH,—CH,—C—CH,—OH Explanation Check Center Accessi ©2025 on 5 Carrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

