
Concept explainers
When a diprotic acid, H2A, is titrated with NaOH, the protons on the diprotic acid are generally removed one at a time, resulting in a pH curve that has the following generic shape:
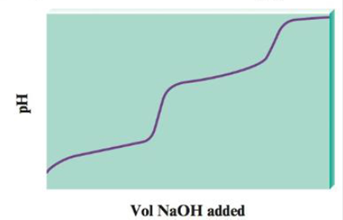
a. Notice that the plot has essentially two titration curves. If the first equivalence point occurs at 100.0 mL NaOH added, what volume of NaOH added corresponds to the second equivalence point?
b. For the following volumes of NaOH added, list the major species present after the OH− reacts completely.
i. 0 mL NaOH added
ii. between 0 and 100.0 mL NaOH added
iii. 100.0 mL NaOH added
iv. between 100.0 and 200.0 mL NaOH added
v. 200.0 mL NaOH added
vi. after 200.0 mL NaOH added
c. If the pH at 50.0 mL NaOH added is 4.0, and the pH at 150.0 mL NaOH added is 8.0, determine the values
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 14 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach, Loose-leaf Version, 2nd + OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics of Everyday Phenomena
Organic Chemistry
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
Loose Leaf For Integrated Principles Of Zoology
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
- Arrange the following compounds / ions in increasing nucleophilicity (least to most nucleophilic) CH3NH2 CH3C=C: CH3COO 1 2 3 5 Multiple Choice 1 point 1, 2, 3 2, 1, 3 3, 1, 2 2, 3, 1 The other answers are not correct 0000arrow_forwardcurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. using the provided starting and product structures, draw the cured electron-pushing arrows for thw following reaction or mechanistic steps. be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond making stepsarrow_forwardUsing the graphs could you help me explain the answers. I assumed that both graphs are proportional to the inverse of time, I think. Could you please help me.arrow_forward
- Synthesis of Dibenzalacetone [References] Draw structures for the carbonyl electrophile and enolate nucleophile that react to give the enone below. Question 1 1 pt Question 2 1 pt Question 3 1 pt H Question 4 1 pt Question 5 1 pt Question 6 1 pt Question 7 1pt Question 8 1 pt Progress: 7/8 items Que Feb 24 at You do not have to consider stereochemistry. . Draw the enolate ion in its carbanion form. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. ⚫ Separate multiple reactants using the + sign from the drop-down menu. ? 4arrow_forwardShown below is the mechanism presented for the formation of biasplatin in reference 1 from the Background and Experiment document. The amounts used of each reactant are shown. Either draw or describe a better alternative to this mechanism. (Note that the first step represents two steps combined and the proton loss is not even shown; fixing these is not the desired improvement.) (Hints: The first step is correct, the second step is not; and the amount of the anhydride is in large excess to serve a purpose.)arrow_forwardHi I need help on the question provided in the image.arrow_forward
- Draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the following reaction: CH3 CH3 Et-OH Et Edit the reaction by drawing all steps in the appropriate boxes and connecting them with reaction arrows. Add charges where needed. Electron-flow arrows should start on the electron(s) of an atom or a bond and should end on an atom, bond, or location where a new bond should be created. H± EXP. L CONT. י Α [1] осн CH3 а CH3 :Ö Et H 0 N о S 0 Br Et-ÖH | P LL Farrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemical Principles in the LaboratoryChemistryISBN:9781305264434Author:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert RossiPublisher:Brooks Cole
Chemical Principles in the LaboratoryChemistryISBN:9781305264434Author:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert RossiPublisher:Brooks Cole





