
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PRINT MULTI TERM
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781119832614
Author: Klein
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 13.8, Problem 14ATS
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation: For the given reaction, the structure of compound 2 needs to be drawn. Also, reagents used for converting 1 into 3 need to be identified.
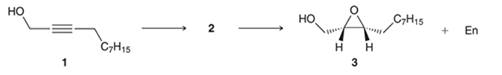
Concept introduction:
Preparation of epoxide-
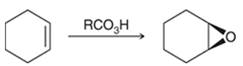
Peroxy acids generally used in this process are MCPBA and peroxyacetic acid. The formation of epoxide via peroxy acid is a stereospecific process; thus, cis substituents in alkene (starting material) remain at cis to each other in the epoxide (product). Similarly, trans substituents in alkene remain at trans to each other.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I have a question about this problem involving mechanisms and drawing curved arrows for acids and bases. I know we need to identify the nucleophile and electrophile, but are there different types of reactions? For instance, what about Grignard reagents and other types that I might not be familiar with? Can you help me with this? I want to identify the names of the mechanisms for problems 1-14, such as Gilman reagents and others. Are they all the same? Also, could you rewrite it so I can better understand? The handwriting is pretty cluttered. Additionally, I need to label the nucleophile and electrophile, but my main concern is whether those reactions differ, like the "Brønsted-Lowry acid-base mechanism, Lewis acid-base mechanism, acid-catalyzed mechanisms, acid-catalyzed reactions, base-catalyzed reactions, nucleophilic substitution mechanisms (SN1 and SN2), elimination reactions (E1 and E2), organometallic mechanisms, and so forth."
Show work with explanation. Don't give Ai generated solution
Show work. don't give Ai generated solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PRINT MULTI TERM
Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 1LTSCh. 13.2 - Prob. 1PTSCh. 13.2 - Prob. 2PTSCh. 13.2 - Prob. 3ATSCh. 13.4 - Prob. 4CCCh. 13.5 - Prob. 2LTSCh. 13.5 - Prob. 5PTSCh. 13.5 - Prob. 6ATSCh. 13.5 - Prob. 7CCCh. 13.5 - Prob. 8CC
Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 9CCCh. 13.6 - Prob. 10CCCh. 13.7 - Prob. 11CCCh. 13.7 - Prob. 12CCCh. 13.8 - Prob. 3LTSCh. 13.8 - Prob. 13PTSCh. 13.8 - Prob. 14ATSCh. 13.9 - Prob. 15CCCh. 13.10 - Prob. 4LTSCh. 13.10 - Prob. 17ATSCh. 13.10 - Prob. 5LTSCh. 13.10 - Prob. 19ATSCh. 13.11 - Prob. 20CCCh. 13.12 - Prob. 6LTSCh. 13.12 - Prob. 7LTSCh. 13 - Prob. 26PPCh. 13 - Prob. 27PPCh. 13 - Prob. 28PPCh. 13 - Prob. 29PPCh. 13 - Prob. 30PPCh. 13 - Prob. 31PPCh. 13 - Prob. 32PPCh. 13 - Prob. 33PPCh. 13 - Prob. 34PPCh. 13 - Prob. 35PPCh. 13 - Prob. 36PPCh. 13 - Prob. 37PPCh. 13 - Prob. 38PPCh. 13 - Prob. 39PPCh. 13 - Prob. 40PPCh. 13 - Prob. 41PPCh. 13 - Prob. 42PPCh. 13 - Prob. 43PPCh. 13 - Prob. 44PPCh. 13 - Prob. 45PPCh. 13 - Prob. 46ASPCh. 13 - Prob. 47ASPCh. 13 - Prob. 48ASPCh. 13 - Prob. 49ASPCh. 13 - Prob. 50ASPCh. 13 - Prob. 51ASPCh. 13 - Prob. 52ASPCh. 13 - Prob. 53ASPCh. 13 - Prob. 54IPCh. 13 - Prob. 59IPCh. 13 - Prob. 60IPCh. 13 - Prob. 61IPCh. 13 - Prob. 62IPCh. 13 - Prob. 63IPCh. 13 - Prob. 64IPCh. 13 - Prob. 65IPCh. 13 - Prob. 66IPCh. 13 - Prob. 69IPCh. 13 - Prob. 70IPCh. 13 - Prob. 71IPCh. 13 - Prob. 72IPCh. 13 - Prob. 73IPCh. 13 - Prob. 74IPCh. 13 - Prob. 77CPCh. 13 - Prob. 79CPCh. 13 - Prob. 80CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Use the average molarity of acetic acid (0.0867M) to calculate the concentration in % (m/v). Then calculate the % difference between the calculated concentrations of your unknown vinegar solution with the 5.00% (w/v%) vinegar solution (check the formula for % difference in the previous lab or online). Before calculating the difference with vinegar, remember that this %(m/v) is of the diluted solution. It has been diluted 10 times.arrow_forwardWhat deprotonates or what can be formed? Please help me understand the problem.arrow_forwardShow work with explanation. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- I have a question about this problem involving mechanisms and drawing curved arrows for acids and bases. I know we need to identify the nucleophile and electrophile, but are there different types of reactions? For instance, what about Grignard reagents and other types that I might not be familiar with? Can you help me with this? I want to identify the names of the mechanisms for problems 1-14, such as Gilman reagents and others. Are they all the same? Also, could you rewrite it so I can better understand? The handwriting is pretty cluttered. Additionally, I need to label the nucleophile and electrophile, but my main concern is whether those reactions differ, like the "Brønsted-Lowry acid-base mechanism, Lewis acid-base mechanism, acid-catalyzed mechanisms, acid-catalyzed reactions, base-catalyzed reactions, nucleophilic substitution mechanisms (SN1 and SN2), elimination reactions (E1 and E2), organometallic mechanisms, and so forth."arrow_forwardSolve the spectroarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward2. 200 LOD For an unknown compound with a molecular ion of 101 m/z: a. Use the molecular ion to propose at least two molecular formulas. (show your work) b. What is the DU for each of your possible formulas? (show your work) C. Solve the structure and assign each of the following spectra. 8 6 4 2 (ppm) 150 100 50 ō (ppm) 4000 3000 2000 1500 1000 500 HAVENUMBERI-11arrow_forwardComplete the spectroscopy with structurearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Characteristic Reactions of Benzene and Phenols; Author: Linda Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tjEqEjDd87E;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
An Overview of Aldehydes and Ketones: Crash Course Organic Chemistry #27; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-fBPX-4kFlw;License: Standard Youtube License