
Concept explainers
a.
To graph: The Venn diagram that represents the number of patients of lung cancer and patients of chronic smokers.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The number of patients diagnosed with lung cancer are 40, number of patient who are chronic smokers are 30. 25 patients have both lung cancer and smoke.
Graph:
Consider the information that the number of patients diagnosed with lung cancer are 40, number of patient who are chronic smokers are 30. 25 patients have both lung cancer and smoke.
Let A represents the patient only with lung cancer.
So,
Let C represents only the chronic smoker patients.
So,
The Venn diagram that represent the situation is
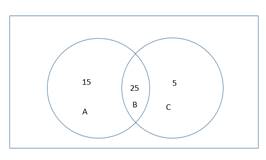
The portion A represents the patient only with lung cancer.
The portion C represents only the chronic smoker patients.
The portion B represents the both that is patients have both lung cancer and smoke.
Interpretation:
The sum total of portion A and B is equal to patient with lung cancer. The sum total of portion B and C is equal to chronic smoker patients.
b.
To calculate: The probability that patient has lung cancer provided that patient smokes.
b.
Answer to Problem 38E
The probability that patient has lung cancer provided that patient smokes is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The number of patients diagnosed with lung cancer are 40, number of patient who are chronic smokers are 30. 25 patients have both lung cancer and smoke.
Formula used:
Probability of an event E is
Given an event Q, the conditional probability of event A is
Calculation:
Consider the provided information that the number of patients diagnosed with lung cancer are 40, number of patient who are chronic smokers are 30. 25 patients have both lung cancer and smoke.
Total number of patients are 200.
Let A be an event that patient has lung cancer and B be an event that patient smokes.
Recall that probability of an event E is
Probability that patient smokes,
Probability that patient has lung cancer and patient smokes,
Recall that given an event Q, the conditional probability of event A is
The probability that patient has lung cancer provided that patient smokes.
Thus, the probability that patient has lung cancer provided that patient smokes is
Chapter 13 Solutions
Advanced Mathematical Concepts: Precalculus with Applications, Student Edition
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
- 8–23. Sketching vector fields Sketch the following vector fieldsarrow_forward25-30. Normal and tangential components For the vector field F and curve C, complete the following: a. Determine the points (if any) along the curve C at which the vector field F is tangent to C. b. Determine the points (if any) along the curve C at which the vector field F is normal to C. c. Sketch C and a few representative vectors of F on C. 25. F = (2½³, 0); c = {(x, y); y − x² = 1} 26. F = x (23 - 212) ; C = {(x, y); y = x² = 1}) , 2 27. F(x, y); C = {(x, y): x² + y² = 4} 28. F = (y, x); C = {(x, y): x² + y² = 1} 29. F = (x, y); C = 30. F = (y, x); C = {(x, y): x = 1} {(x, y): x² + y² = 1}arrow_forward٣/١ B msl kd 180 Ka, Sin (1) I sin () sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120 x 50 G 5005 1000 s = 1000-950 Copper bosses 5kW Rotor input 5 0.05 : loo kw 6) 1 /0001 ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please وه اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط ١٥٠ DC 7) rotor a ' (y+xlny + xe*)dx + (xsiny + xlnx + dy = 0. Q1// Find the solution of: ( 357arrow_forward
- ۳/۱ R₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase 3/31 B. 180 msl Kas Sin (I) 1sin() sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30): 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speeds 120×50 looo G 1000-950 1000 Copper losses 5kw Rotor input 5 loo kw 0.05 6) 1 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotor DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please 0 64 Find the general solution of the following equations: QI//y(4)-16y= 0. Find the general solution of the following equations: Q2ll yll-4y/ +13y=esinx.arrow_forwardR₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B-180 60 msl kd Kas Sin () 2 I sin (6) sin(30) Sin (30) اذا مريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3 Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating ined sove in peaper 5) Synchronous speed s 120×50 6 s = 1000-950 1000 Copper losses 5kw Rotor input 5 0.05 6) 1 loo kw اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط Look 7) rotov DC I need a detailed solution on paper please 0 64 Solve the following equations: 0 Q1// Find the solution of: ( y • with y(0) = 1. dx x²+y²arrow_forwardR₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/3 1 B-180-60 msl Ka Sin (1) Isin () sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120 x 50 s = 1000-950 1000 Copper losses 5kw Rotor input 5 6) 1 0.05 G 50105 loo kw اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotov DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please 064 2- A hot ball (D=15 cm ) is cooled by forced air T.-30°C, the rate of heat transfer from the ball is 460.86 W. Take for the air -0.025 Wim °C and Nu=144.89, find the ball surface temperature a) 300 °C 16 b) 327 °C c) 376 °C d) None か = 750 01arrow_forward
- Don't do 14. Please solve 19arrow_forwardPlease solve 14 and 15arrow_forward1. Consider the following system of equations: x13x2 + 4x3 - 5x4 = 7 -2x13x2 + x3 - 6x4 = 7 x16x213x3 - 21x4 = 28 a) Solve the system. Write your solution in parametric and vector form. b) What is a geometric description of the solution. 7 c) Is v = 7 in the span of the set S= [28. 1 HE 3 -5 3 ·6 ? If it is, write v 6 as a linear combination of the vectors in S. Justify. d) How many solutions are there to the associated homogeneous system for the system above? Justify. e) Let A be the coefficient matrix from the system above. Find the set of all solutions to Ax = 0. f) Is there a solution to Ax=b for all b in R³? Justify.arrow_forward
- 4. Suppose that A is made up of 5 column vectors in R³, and suppose that the rank(A)=3. a. How many solutions are there to Ax=0? Justify. b. What is a geometric description for the nullspace(A)? Justify. c. Do the column vectors of A span R³? Justify. d. Is A invertible? Justify.arrow_forward3. Suppose that A is 5 x 5 and rank(A)=4. Use this information to answer the following. a. Give a geometric description of nullspace(A). Justify. b. Is A invertible? Justify. c. Give a geometric description of the span of the column vectors of A. What space are the column vectors of A in? Justify. d. What is determinant of A? Justify.arrow_forward2. Consider the matrix: A || 1 1 -3 14 2 1 01 4 1 2 2 -26 1 -3 1 5] a) What is rank(A)? b) Is A invertible? Justify. c) Find the nullspace(A). Justify. d) Is the trivial solution the only solution to Ax=0? Justify. e) What is the span of the column vectors of A? Justify.arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





