
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915389
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13.4, Problem 44P
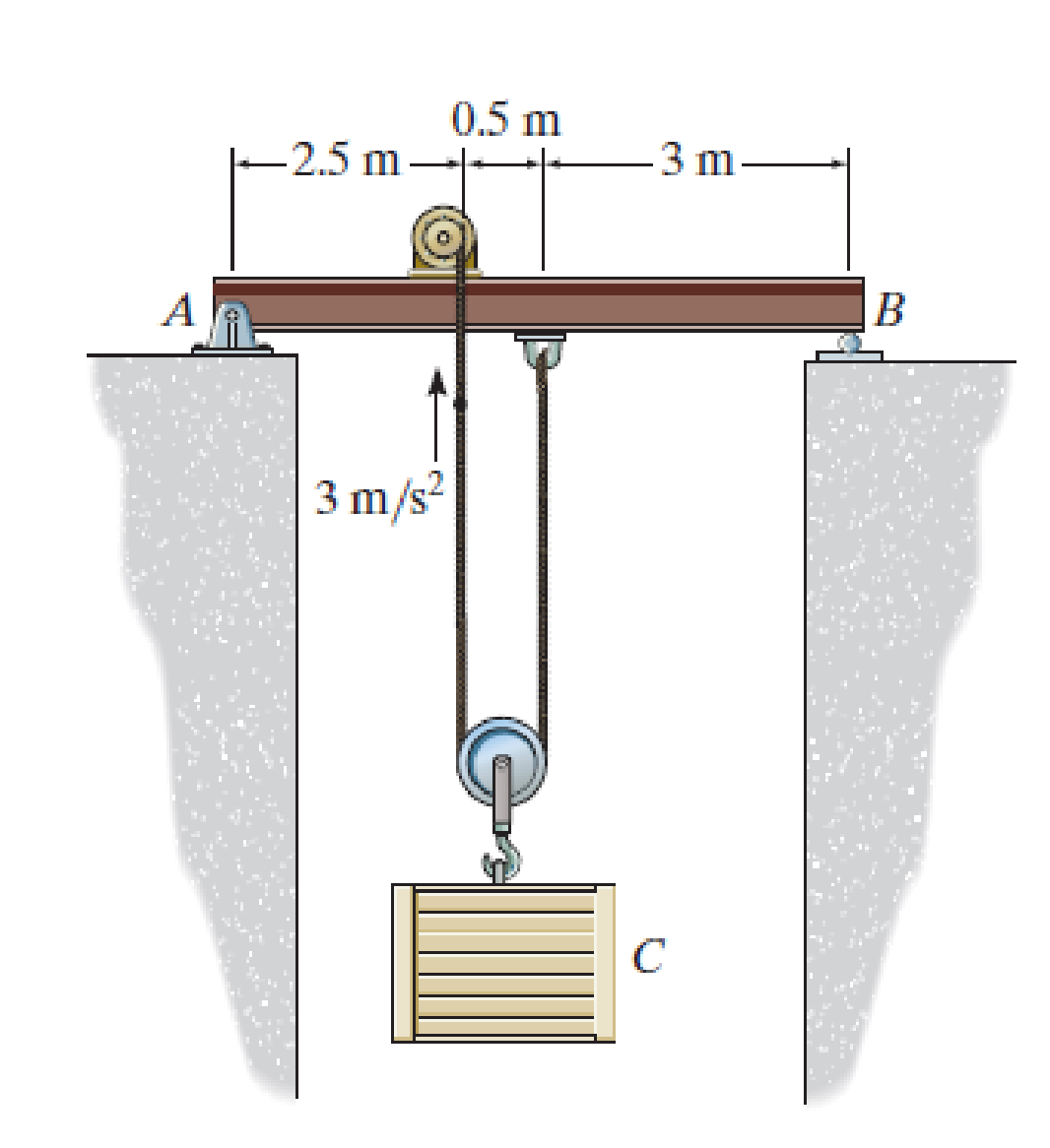
Neglect the mass of the motor and pulleys.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule14:45
Students have asked these similar questions
A boiler with 80% efficiency produces steam at 40bar and 500 C at a rate of 1.128kg/s.
The temperature of the feed water is raised from 25 C to 125 C in the economizer and the
ambient air is drawn to the boiler at a rate of 2.70 kg/s at 16 C. The flue gases leave the
chimney at rate of 3 kg/s at 150 C with specific heat of 1.01 kJ/kg.K. The dryness fraction
of steam collected in the steam drum is 0.95.
1- Determine the heat value of the fuel.
2- The equivalence evaporation.
3- Draw the heat balance sheet.
A rotating shaft is made of 42 mm by 4 mm thick cold-drawn round steel tubing and has a 6 mm diameter
hole drilled transversely through it. The shaft is subjected to a pulsating torque fluctuating from 20 to 160
Nm and a completely reversed bending moment of 200 Nm. The steel tubing has a minimum strength of Sut
= 410 MPa (60 ksi). The static stress-concentration factor for the hole is 2.4 for bending and 1.9 for torsion.
The maximum operating temperature is 400˚C and a reliability of 99.9% is to be assumed. Find the factor of
safety for infinite life using the modified Goodman failure criterion.
I need help with a MATLAB code. This code just keeps running and does not give me any plots. I even reduced the tolerance from 1e-9 to 1e-6. Can you help me fix this? Please make sure your solution runs.
% Initial Conditions
rev = 0:0.001:2;
g1 = deg2rad(1);
g2 = deg2rad(3);
g3 = deg2rad(6);
g4 = deg2rad(30);
g0 = deg2rad(0);
Z0 = 0;
w0 = [0; Z0*cos(g0); -Z0*sin(g0)];
Z1 = 5;
w1 = [0; Z1*cos(g1); -Z1*sin(g1)];
Z2 = 11;
w2 = [0; Z2*cos(g2); -Z2*sin(g2)];
[v3, psi3, eta3] = Nut_angle(Z2, g2, w2);
plot(v3, psi3)
function dwedt = K_DDE(~, w_en)
% Extracting the initial condtions to a variable
% Extracting the initial condtions to a variable
w = w_en(1:3);
e = w_en(4:7);
Z = w_en(8);
I = 0.060214;
J = 0.015707;
x = (J/I) - 1;
y = Z - 1;
s = Z;
% Kinematic Differential Equations
dedt = zeros(4,1);
dedt(1) = pi*(e(3)*(s-w(2)-1) + e(2)*w(3) + e(4)*w(1));
dedt(2) = pi*(e(4)*(w(2)-1-s) + e(3)*w(1) - e(1)*w(3));
dedt(3) = pi*(-e(1)*(s-w(2)-1) - e(2)*w(1) + e(4)*w(3));…
Chapter 13 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 13.4 - In each case, determine its velocity when t = 2 s...Ch. 13.4 - In each case, determine its velocity at s = 8 m if...Ch. 13.4 - Determine the initial acceleration of the 10-kg...Ch. 13.4 - Write the equations of motion in the x and y...Ch. 13.4 - The motor winds n the cable with a constant...Ch. 13.4 - If motor M exerts a force of F = (10t2 + 100) N on...Ch. 13.4 - A spring of stiffness k = 500 N/m is mounted...Ch. 13.4 - The spring has a stiffness k = 200 N/m and is...Ch. 13.4 - Block B rests upon a smooth surface. If the...Ch. 13.4 - The 6-lb particle is subjected to the action of...
Ch. 13.4 - The two boxcars A and B have a weight of 20 000 lb...Ch. 13.4 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 13.4 - If the 50-kg crate starts from rest and achieves a...Ch. 13.4 - If blocks A and B of mass 10 kg and 6 kg...Ch. 13.4 - The 10-lb block has a speed of 4 ft/s when the...Ch. 13.4 - The 10-lb block has a speed of 4 ft/s when the...Ch. 13.4 - The speed of the 3500-lb sports car is plotted...Ch. 13.4 - The conveyor belt is moving at 4 m/s. If the...Ch. 13.4 - The conveyor belt is designed to transport...Ch. 13.4 - Determine the time needed to pull the cord at B...Ch. 13.4 - Cylinder B has a mass m and is hoisted using the...Ch. 13.4 - Block A has a weight of 8 lb and block B has a...Ch. 13.4 - The 2-Mg truck is traveling at 15 m/s when the...Ch. 13.4 - The motor lifts the 50-kg crate with an...Ch. 13.4 - The 75-kg man pushes on the 150-kg crate with a...Ch. 13.4 - The coefficient of kinetic friction is k, and the...Ch. 13.4 - A 40-lb suitcase slides from rest 20 ft down the...Ch. 13.4 - Solve Prob. 13-18 if the suitcase has an initial...Ch. 13.4 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between...Ch. 13.4 - The conveyor belt delivers each 12-kg crate to the...Ch. 13.4 - The 50-kg block A is released from rest. Determine...Ch. 13.4 - If the supplied force F = 150 N, determine the...Ch. 13.4 - A 60-kg suitcase slides from rest 5 m down the...Ch. 13.4 - Solve Prob. 13-24 if the suitcase has an initial...Ch. 13.4 - The 1.5 Mg sports car has a tractive force of F =...Ch. 13.4 - The conveyor belt is moving downward at 4 m/s. If...Ch. 13.4 - At the instant shown the 100-lb block A is moving...Ch. 13.4 - Determine the velocity of the 200-lb crate when t...Ch. 13.4 - Determine the velocity of the 400-kg crate A when...Ch. 13.4 - The tractor is used to lift the 150-kg load B with...Ch. 13.4 - If the tractor travels to the right with an...Ch. 13.4 - Block A and B each have a mass m. Determine the...Ch. 13.4 - The 4-kg smooth cylinder is supported by the...Ch. 13.4 - The coefficient of static friction between the...Ch. 13.4 - If the spring is unstretched when s = 0 and the...Ch. 13.4 - Neglecting the mass of the rope and pulley, and...Ch. 13.4 - Determine the force in the cable when t = 5 s, if...Ch. 13.4 - An electron of mass m is discharged with an...Ch. 13.4 - The 400-lb cylinder at A is hoisted using the...Ch. 13.4 - What is their velocity at this instant?Ch. 13.4 - Block A has a mass mA and is attached to a spring...Ch. 13.4 - A parachutist having a mass m opens his parachute...Ch. 13.4 - Neglect the mass of the motor and pulleys.Ch. 13.4 - If the force exerted on cable AB by the motor is F...Ch. 13.4 - Blocks A and B each have a mass m. Determine the...Ch. 13.4 - Blocks A and Beach have a mass m. Determine the...Ch. 13.4 - If the board AC pushes on the block at an angle ...Ch. 13.4 - If a horizontal force P = 12lb is applied to block...Ch. 13.4 - A freight elevator, including its load, has a mass...Ch. 13.4 - The block A has a mass mA and rests on the pan B,...Ch. 13.5 - P13-5.Set up the n, t axes and write the equations...Ch. 13.5 - P13-6.Set up the n, b, t axes and write the...Ch. 13.5 - The block rests at a distance of 2 m from the...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 8FPCh. 13.5 - A pilot weighs 150 lb and is traveling at a...Ch. 13.5 - The sports car is traveling along a 30 banked road...Ch. 13.5 - If the 10-kg ball has a velocity of 3m/ s when it...Ch. 13.5 - The motorcycle has a mass of 0.5 Mg and a...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 52PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 53PCh. 13.5 - The 2-kg block B and 15-kg cylinder A are...Ch. 13.5 - Determine the maximum constant speed at which the...Ch. 13.5 - Cartons having a mass of 5 kg are required to move...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 57PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 58PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 59PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 60PCh. 13.5 - At the instant B = 60, the boys center of mass G...Ch. 13.5 - A girl having a mass of 25 kg sits at the edge of...Ch. 13.5 - The pendulum bob B has a weight of 5 lb and is...Ch. 13.5 - The pendulum bob B has a mass m and is released...Ch. 13.5 - Determine the constant speed of the passengers on...Ch. 13.5 - A motorcyclist in a circus rides his motorcycle...Ch. 13.5 - The vehicle is designed to combine the feel of a...Ch. 13.5 - The 0.8-Mg car travels over the hill having the...Ch. 13.5 - The 0.8-Mg car travels over the hill having the...Ch. 13.5 - When it reaches the curved portion AB, it is...Ch. 13.5 - Determine the resultant normal and frictional...Ch. 13.5 - If he rotates about the z axis with a constant...Ch. 13.5 - Determine the maximum speed at which the car with...Ch. 13.5 - Determine the maximum constant speed at which the...Ch. 13.5 - The box has a mass m and slides down the smooth...Ch. 13.5 - Prove that if the block is released from rest at...Ch. 13.5 - The cylindrical plug has a weight of 2 lb and it...Ch. 13.5 - When crossing an intersection, a motorcyclist...Ch. 13.5 - The airplane, traveling at a constant speed of 50...Ch. 13.5 - The 2-kg pendulum bob moves in the vertical plane...Ch. 13.5 - The 2-kg pendulum bob moves in the vertical plane...Ch. 13.5 - If it has a speed of 1.5 m/s when y = 0.2 m,...Ch. 13.5 - The ball has a mass m and is attached to the cord...Ch. 13.6 - If the attached spring has a stiffness k = 2...Ch. 13.6 - Determine the constant angular velocity of the...Ch. 13.6 - If = ( t2) rad, where t is in seconds, determine...Ch. 13.6 - The 2-Mg car is traveling along the curved road...Ch. 13.6 - The 0.2-kg pin P is constrained to move in the...Ch. 13.6 - If the cam is rotating at a constant rate of 6...Ch. 13.6 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 13.6 - Determine the magnitude of the unbalanced force...Ch. 13.6 - Rod OA rotates counterclockwise with a constant...Ch. 13.6 - The boy of mass 40 kg is sliding down the spiral...Ch. 13.6 - Using a forked rod, a 0.5-kg smooth peg P is...Ch. 13.6 - The arm is rotating at a rate of = 4 rad/s when ...Ch. 13.6 - If arm OA rotates with a constant clockwise...Ch. 13.6 - Determine the normal and frictional driving forces...Ch. 13.6 - A smooth can C, having a mass of 3 kg, is lifted...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 96PCh. 13.6 - Prob. 97PCh. 13.6 - The particle has a mass of 0.5 kg and is confined...Ch. 13.6 - A car of a roller coaster travels along a track...Ch. 13.6 - The 0.5-lb ball is guided along the vertical...Ch. 13.6 - The ball of mass misguided along the vertical...Ch. 13.6 - Using a forked rod, a smooth cylinder P, having a...Ch. 13.6 - The pilot of the airplane executes a vertical loop...Ch. 13.6 - The collar has a mass of 2 kg and travels along...Ch. 13.6 - The particle has a mass of 0.5 kg and is confined...Ch. 13.6 - Solve Prob. 13-105 If the arm has an angular...Ch. 13.6 - The forked rod is used to move the smooth 2-lb...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 108PCh. 13.6 - Rod OA rotates counterclockwise at a constant...Ch. 13.6 - Solve Prob. 13-109 if motion is in the vertical...Ch. 13.7 - If his speed is a constant vP = 80 ft/s, determine...Ch. 13.7 - The earth has an orbit with eccentricity 0.0167...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 114PCh. 13.7 - Determine the speed of a satellite launched...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 116PCh. 13.7 - Prove Keplers third law of motion. Hint: Use Eqs....Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 118PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 119PCh. 13.7 - Determine the constant speed of satellite S so...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 121PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 122PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 123PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 124PCh. 13.7 - The rocket is traveling around the earth in free...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 127PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 128PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 129PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 130PCh. 13.7 - The rocket is traveling around the earth in free...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 132PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 3CPCh. 13.7 - If the trailer has a mass of 250 kg and coasts 45...Ch. 13.7 - The coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 13.7 - Block B rests on a smooth surface. If the...Ch. 13.7 - If the motor draws in the cable at a rate of v =...Ch. 13.7 - The ball has a mass of 30 kg and a speed v = 4 m/s...Ch. 13.7 - If the coefficient of static friction between the...Ch. 13.7 - If at the instant it reaches point A it has a...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1.1 List 10 uses. for surveying in areas other than land
sunreying-
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Describe two properties that each candidate key must satisfy.
Modern Database Management
What is the difference between the methods System.out.println and System.out.print?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
In what year was Plankalkl designed? In what year was that design published?
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Look at the following pseudocode: Constant Integer SIZE = 3 Declare Integer numbers[SIZE] = 1, 2, 3 a. What val...
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
What is an algorithm?
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- alpha 1 is not zero alpha 1 can equal alpha 2 use velocity triangle to solve for alpha 1 USE MATLAB ONLY provide typed code solve for velocity triangle and dont provide copied answer Turbomachienery . GIven: vx = 185 m/s, flow angle = 60 degrees, (leaving a stator in axial flow) R = 0.5, U = 150 m/s, b2 = -a3, a2 = -b3 Find: velocity triangle , a. magnitude of abs vel leaving rotor (m/s) b. flow absolute angles (a1, a2, a3) 3. flow rel angles (b2, b3) d. specific work done e. use code to draw vel. diagram Use this code for plot % plots Velocity Tri. in Ch4 function plotveltri(al1,al2,al3,b2,b3) S1L = [0 1]; V1x = [0 0]; V1s = [0 1*tand(al3)]; S2L = [2 3]; V2x = [0 0]; V2s = [0 1*tand(al2)]; W2s = [0 1*tand(b2)]; U2x = [3 3]; U2y = [1*tand(b2) 1*tand(al2)]; S3L = [4 5]; V3x = [0 0]; V3r = [0 1*tand(al3)]; W3r = [0 1*tand(b3)]; U3x = [5 5]; U3y = [1*tand(b3) 1*tand(al3)]; plot(S1L,V1x,'k',S1L,V1s,'r',... S2L,V2x,'k',S2L,V2s,'r',S2L,W2s,'b',U2x,U2y,'g',...…arrow_forward3. Find a basis of eigenvectors and diagonalize. 4 0 -19 7 a. b. 1-42 16 12-20 [21-61arrow_forward2. Find the eigenvalues. Find the corresponding eigenvectors. 6 2 -21 [0 -3 1 3 31 a. 2 5 0 b. 3 0 -6 C. 1 1 0 -2 0 7 L6 6 0 1 1 2. (Hint: λ = = 3)arrow_forward
- USE MATLAB ONLY provide typed code solve for velocity triangle and dont provide copied answer Turbomachienery . GIven: vx = 185 m/s, flow angle = 60 degrees, (leaving a stator in axial flow) R = 0.5, U = 150 m/s, b2 = -a3, a2 = -b3 Find: velocity triangle , a. magnitude of abs vel leaving rotor (m/s) b. flow absolute angles (a1, a2, a3) 3. flow rel angles (b2, b3) d. specific work done e. use code to draw vel. diagram Use this code for plot % plots Velocity Tri. in Ch4 function plotveltri(al1,al2,al3,b2,b3) S1L = [0 1]; V1x = [0 0]; V1s = [0 1*tand(al3)]; S2L = [2 3]; V2x = [0 0]; V2s = [0 1*tand(al2)]; W2s = [0 1*tand(b2)]; U2x = [3 3]; U2y = [1*tand(b2) 1*tand(al2)]; S3L = [4 5]; V3x = [0 0]; V3r = [0 1*tand(al3)]; W3r = [0 1*tand(b3)]; U3x = [5 5]; U3y = [1*tand(b3) 1*tand(al3)]; plot(S1L,V1x,'k',S1L,V1s,'r',... S2L,V2x,'k',S2L,V2s,'r',S2L,W2s,'b',U2x,U2y,'g',... S3L,V3x,'k',S3L,V3r,'r',S3L,W3r,'b',U3x,U3y,'g',...... 'LineWidth',2,'MarkerSize',10),...…arrow_forwardUSE MATLAB ONLY provide typed code solve for velocity triangle and dont provide copied answer Turbomachienery . GIven: vx = 185 m/s, flow angle = 60 degrees, R = 0.5, U = 150 m/s, b2 = -a3, a2 = -b3 Find: velocity triangle , a. magnitude of abs vel leaving rotor (m/s) b. flow absolute angles (a1, a2, a3) 3. flow rel angles (b2, b3) d. specific work done e. use code to draw vel. diagram Use this code for plot % plots Velocity Tri. in Ch4 function plotveltri(al1,al2,al3,b2,b3) S1L = [0 1]; V1x = [0 0]; V1s = [0 1*tand(al3)]; S2L = [2 3]; V2x = [0 0]; V2s = [0 1*tand(al2)]; W2s = [0 1*tand(b2)]; U2x = [3 3]; U2y = [1*tand(b2) 1*tand(al2)]; S3L = [4 5]; V3x = [0 0]; V3r = [0 1*tand(al3)]; W3r = [0 1*tand(b3)]; U3x = [5 5]; U3y = [1*tand(b3) 1*tand(al3)]; plot(S1L,V1x,'k',S1L,V1s,'r',... S2L,V2x,'k',S2L,V2s,'r',S2L,W2s,'b',U2x,U2y,'g',... S3L,V3x,'k',S3L,V3r,'r',S3L,W3r,'b',U3x,U3y,'g',...... 'LineWidth',2,'MarkerSize',10),... axis([-1 6 -4 4]), ...…arrow_forwardThe answer should equal to 1157. Please sent me the solution. Thank you!arrow_forward
- BONUS: If the volume of the 8cm x 6.5cm x 6cm Block of Aluminum was 312cm3 before machining, find how much material was removed when the fixture below was machined. +2 2.00 cm 6.00 cm 2.50 cm 6.50 cm 1.00 cm 2.50 cm 11.00 cm 8.00 cm 30 CP 9411 FL.4) (m² 1157 Area of triangle = 1/2*B*H Area of circle = лR² Circumference of a circle = 2πR 6.00 cm 6.50 cm 1.50 cm Radius 1.50 cm 1.00 cmarrow_forwardConsider a 5m by 5m wet concret patio with an average water film thickness of .2mm. Now wind at 50 km/h is blowing over the surface. If the air is at 1 atm, 15oC and 35 percent relative humidity, determine how long it will take for the patio to completely dry.arrow_forward70. Compute the number of cubic centimeters of iron required for the cast-iron plate shown. The plate is 3.50 centimeters thick. Round the answer to the nearest cubic centimeter. 50.0 cm 40.0 cm Radius 150° 115.0 cm- 81.0 cmarrow_forward
- Law of Sines Solve the following problems using the Law of Sin 7. Find side x. All dimensions are in inches. -°-67°-37° 81° x Sin A 8.820 X 67°00' 32°00' a sin A b C sin B sin Carrow_forward35. a. Determine B. b. Determine side b. c. Determine side c. 5.330 in.- ZB 73°30'arrow_forwardConsider a 12 cm internal diameter, 14 m long circular duct whose interior surface is wet. The duct is to be dried by forcing dry air at 1 atm and 15 degrees C throught it at an average velocity of 3m/s. The duct passes through a chilled roo, and it remains at an average temp of 15 degrees C at all time. Determine the mass transfer coeeficient in the duct.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Electrical Transformers and Rotating MachinesMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305494817Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Electrical Transformers and Rotating MachinesMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305494817Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781133612315Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob ThompsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781133612315Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob ThompsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning

Electrical Transformers and Rotating Machines
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305494817
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781133612315
Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob Thompson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305578296
Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanical Design (Machine Design) Clutches, Brakes and Flywheels Intro (S20 ME470 Class 15); Author: Professor Ted Diehl;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eMvbePrsT34;License: Standard Youtube License