
Mechanics of Materials
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780137605460
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Pearson Education (US)
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13.3, Problem 5FP
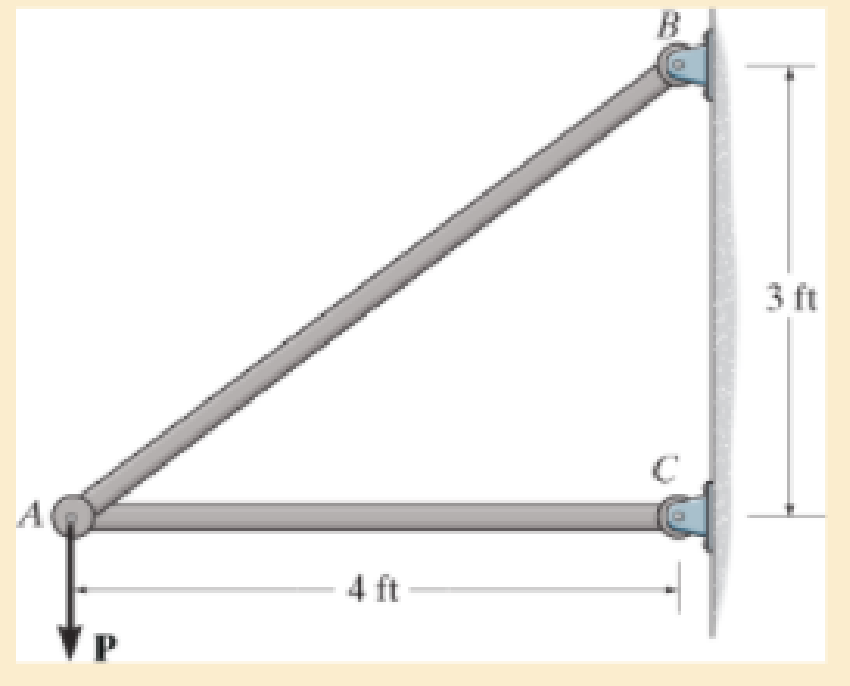
Determine the maximum force P that can be supported by the assembly without causing member AC to buckle. The member is made of A992 steel and has a diameter of 2 in. Take F.S. = 2 against buckling.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
using the theorem of three moments, find all the reactions and supports
(An ellipsoidal trapping region for the Lorenz equations) Show that there is a certain ellipsoidal region E of the form rx2 + σy2 + σ(z − 2r)2 ≤ C such that all trajectories of the Lorenz equations eventually enter E and stay in there forever. For a much stiffer challenge, try to obtain the smallest possible value of C with this property.
A) In a factory, an s-type pitot tube was used to calculate the velocity of dry air for a point
inside a stack.
Calculate the velocity at that point (ft/sec) using following conditions:
●
•
•
Pressure = 30.23 ± 0.01 in Hg (ambient)
Pitot tube coefficient = 0.847 ± 0.03
Temperature = 122 ± 0.1 F (stack)
Temperature = 71.2 ± 0.1 F (ambient)
AP = 0.324 ± 0.008 in H2O (pitot tube)
•
AP = 0.891 ± 0.002 in H2O (stack)
B) Find the dominant error(s) when determining precision for the problem.
C) For part A, what is the precision in ft/sec for the velocity?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials
Ch. 13.3 - A 50-in long steel rod has a diameter of 1 in....Ch. 13.3 - A 12-ft wooden rectangular column has the...Ch. 13.3 - The A992 steel column can be considered pinned at...Ch. 13.3 - A steel pipe is fixed supported at its ends. If it...Ch. 13.3 - Determine the maximum force P that can be...Ch. 13.3 - The A992 steel rod BC has a diameter of 50 mm and...Ch. 13.3 - Determine the critical buckling load for the...Ch. 13.3 - The 10-ft wooden rectangular column has the...Ch. 13.3 - The 10-fl wooden column has the dimensions shown....Ch. 13.3 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...
Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 34PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 35PCh. 13.3 - The members of the truss are assumed to be pin...Ch. 13.3 - Solve Prob. 1336 for member AB, which has a radius...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 40PCh. 13.3 - The ideal column has a weight w (force/length) and...Ch. 13.3 - The ideal column is subjected to the force F at...Ch. 13.3 - The column with constant El has the end...Ch. 13.3 - Consider an ideal column as in Fig.13-10 c, having...Ch. 13.3 - Consider an ideal column as in Fig. 13-10d, having...Ch. 13.5 - The aluminium column is fixed at the bottom and...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 50PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 51PCh. 13.5 - The aluminum rod is fixed at its base and free and...Ch. 13.5 - Assume that the wood column is pin connected at...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 54PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 59PCh. 13.5 - The wood column is pinned at its base and top. If...Ch. 13.5 - The brass rod is fixed at one end and free at the...Ch. 13.5 - The brass rod is fixed at one end and free at the...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 65PCh. 13.5 - The W14 53 structural A992 steel column is fixed...Ch. 13.5 - The W14 53 column is fixed at its base and free...Ch. 13.5 - The stress-strain diagram for the material of a...Ch. 13.5 - Construct the buckling curve, P/A versus L/ r, for...Ch. 13.5 - The stress-strain diagram of the material can be...Ch. 13.5 - The stress-strain diagram of the material can be...Ch. 13.6 - Using the AISC equations, select from AppendixB...Ch. 13.6 - Take Y = 50 ksi.Ch. 13.6 - Using the AISC equations, select from AppendixB...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 83PCh. 13.6 - Using the AISC equations, select from AppendixB...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 97PCh. 13.6 - Prob. 98PCh. 13.6 - The tube is 0.25 in. thick, is made of 2014-T6...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 100PCh. 13.6 - A rectangular wooden column has the cross section...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 102PCh. 13.7 - The W8 15 wide-flange A-36 steel column is...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 110PCh. 13.7 - A 20-ft-long column is made of aluminum alloy...Ch. 13.7 - A 20-ft-long column is made of aluminum alloy...Ch. 13.7 - The 2014-T6 aluminum hollow column is fixed at its...Ch. 13.7 - The 2014-T6 aluminum hollow column is fixed at its...Ch. 13 - The wood column has a thickness of 4 in. and a...Ch. 13 - The wood column has a thickness of 4 in. and a...Ch. 13 - A steel column has a length of 5 m and is free at...Ch. 13 - The square structural A992 steel tubing has outer...Ch. 13 - If the A-36 steel solid circular rod BD has a...Ch. 13 - If P = 15 kip, determine the required minimum...Ch. 13 - The steel pipe is fixed supported at its ends. If...Ch. 13 - The W200 46 wide-flange A992-steel column can be...Ch. 13 - The wide-flange A992 steel column has the cross...Ch. 13 - The wide-flange A992 steel column has the cross...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
A nozzle at A discharges water with an initial velocity of 36 ft/s at an angle with the horizontal. Determine ...
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
What types of coolant are used in vehicles?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Look at the following description of a problem domain:
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
The ____________ is always transparent.
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q1/ For what value of x do the power series converge: 8 (-1)n-1. x2n-1 2n-1 x3 x5 = X n=1 3 Q2/ Find the Interval of convergence and Radius of convergence of the series: 8 n Σ 3+1 n=1 (x)"arrow_forwardExample-1: l D A uniform rotor of length 0.6 m and diameter 0.4 m is made of steel (density 7810 kg/m³) is supported by identical short bearings of stiffness 1 MN/m in the horizontal and vertical directions. If the distance between the bearings is 0.7 m, determine the natural frequencies and plot whirl speed map. Solution: Barrow_forwardfind the laplace transform for the flowing function 2(1-e) Ans. F(s)=- S 12) k 0 Ans. F(s)= k s(1+e) 0 a 2a 3a 4a 13) 2+ Ans. F(s)= 1 s(1+e") 3 14) f(t)=1, 0arrow_forwardFind the solution of the following Differential Equations Using Laplace Transforms 1) 4y+2y=0. y(0)=2. y'(0)=0. 2) y+w²y=0, (0)=A, y'(0)=B. 3) +2y-8y 0. y(0)=1. y'(0)-8. 4)-2-3y=0, y(0)=1. y'(0)=7. 5) y-ky'=0, y(0)=2, y'(0)=k. 6) y+ky'-2k²y=0, y(0)=2, y'(0) = 2k. 7) '+4y=0, y(0)=2.8 8) y+y=17 sin(21), y(0)=-1. 9) y-y-6y=0, y(0)=6, y'(0)=13. 10) y=0. y(0)=4, y' (0)=0. 11) -4y+4y-0, y(0)=2.1. y'(0)=3.9 12) y+2y'+2y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=-3. 13) +7y+12y=21e". y(0)=3.5. y'(0)=-10. 14) "+9y=10e". y(0)=0, y'(0)=0. 15) +3y+2.25y=91' +64. y(0)=1. y'(0) = 31.5 16) -6y+5y-29 cos(2t). y(0)=3.2, y'(0)=6.2 17) y+2y+2y=0, y(0)=0. y'(0)=1. 18) y+2y+17y=0, y(0)=0. y'(0)=12. 19) y"-4y+5y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=2. 20) 9y-6y+y=0, (0)-3, y'(0)=1. 21) -2y+10y=0, y(0)=3, y'(0)=3. 22) 4y-4y+37y=0, y(0)=3. y'(0)=1.5 23) 4y-8y+5y=0, y(0)=0, y'(0)=1. 24) ++1.25y-0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=-0.5 25) y 2 cos(r). y(0)=2. y'(0) = 0. 26) -4y+3y-0, y(0)=3, y(0) 7. 27) y+2y+y=e y(0)=0. y'(0)=0. 28) y+2y-3y=10sinh(27), y(0)=0. y'(0)=4. 29)…arrow_forwardAuto Controls A union feedback control system has the following open loop transfer function where k>0 is a variable proportional gain i. for K = 1 , derive the exact magnitude and phase expressions of G(jw). ii) for K = 1 , identify the gaincross-over frequency (Wgc) [where IG(jo))| 1] and phase cross-overfrequency [where <G(jw) = - 180]. You can use MATLAB command "margin" to obtain there quantities. iii) Calculate gain margin (in dB) and phase margin (in degrees) ·State whether the closed-loop is stable for K = 1 and briefly justify your answer based on the margin . (Gain marginPhase margin) iv. what happens to the gain margin and Phase margin when you increase the value of K?you You can use for loop in MATLAB to check that.Helpful matlab commands : if, bode, margin, rlocus NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forwardThe 120 kg wheel has a radius of gyration of 0.7 m. A force P with a magnitude of 50 N is applied at the edge of the wheel as seen in the diagram. The coefficient of static friction is 0.3, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.25. Find the acceleration and angular acceleration of the wheel.arrow_forwardAuto Controls Using MATLAB , find the magnitude and phase plot of the compensators NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forward4-81 The corner shown in Figure P4-81 is initially uniform at 300°C and then suddenly exposed to a convection environment at 50°C with h 60 W/m². °C. Assume the = 2 solid has the properties of fireclay brick. Examine nodes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 and deter- mine the maximum time increment which may be used for a transient numerical calculation. Figure P4-81 1 2 3 4 1 cm 5 6 1 cm 2 cm h, T + 2 cmarrow_forwardAuto Controls A union feedback control system has the following open loop transfer function where k>0 is a variable proportional gain i. for K = 1 , derive the exact magnitude and phase expressions of G(jw). ii) for K = 1 , identify the gaincross-over frequency (Wgc) [where IG(jo))| 1] and phase cross-overfrequency [where <G(jw) = - 180]. You can use MATLAB command "margin" to obtain there quantities. iii) Calculate gain margin (in dB) and phase margin (in degrees) ·State whether the closed-loop is stable for K = 1 and briefly justify your answer based on the margin . (Gain marginPhase margin) iv. what happens to the gain margin and Phase margin when you increase the value of K?you You can use for loop in MATLAB to check that.Helpful matlab commands : if, bode, margin, rlocus NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forwardAuto Controls Hand sketch the root Focus of the following transfer function How many asymptotes are there ?what are the angles of the asymptotes?Does the system remain stable for all values of K NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forward-400" 150" in Datum 80" 90" -280"arrow_forwardUsing hand drawing both of themarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Column buckling; Author: Amber Book;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AvvaCi_Nn94;License: Standard Youtube License