
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977237
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13.1, Problem 13.41P
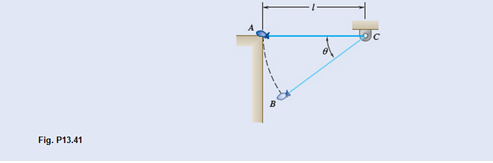
A bag is gently pushed off the top of a wall at A and swings in a vertical plane at the end of a rope of length l. Determine the angle
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A triangular distributed load of max intensity w =460 N/m
acts on beam AB. The beam is supported by a pin at A and
member CD, which is connected by pins at C and D
respectively. Determine the reaction forces at A and C.
Enter your answers in Cartesian components. Assume the
masses of both beam AB and member CD are negligible.
cc 040
BY NC SA
2016 Eric Davishahl
W
A
C
D
-a-
B
Ул
-b-
x
Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following
table. Note the figure may not be to scale.
Variable Value
α
5.4 m
b
8.64 m
C
3.24 m
The reaction at A is A =
i+
ĴN.
λ =
i+
Ĵ N.
The reaction at C is C =
56
Clamps like the one shown are commonly used in
woodworking applications. This clamp has the dimensions
given in the table below the figure, and its jaws are
mm thick (in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the
picture).
a.) The screws of the clamp are adjusted so that there is a
uniform pressure of P = 150 kPa being applied to the
workpieces by the jaws. Determine the force carried in each
screw. Hint: the uniform pressure can be modeled in 2-D as a
uniform distributed load with intensity w = Pt (units of
N/m) acting over the length of contact between the jaw and
the workpiece.
b.) Determine the minimum vertical force (parallel to the
jaws) required to pull either one of the workpieces out of the
clamp jaws. Use a coefficient of static friction between all
contacting surfaces of μs = 0.56 and the same clamping
pressure given for part (a).
2013 Michael Swanbom
A
B
C
a
Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following
table. Note the figure may not be to scale.…
Determine the force in each member of the space truss given
F=5 kN. Use positive to indicate tension and negative to
indicate compression.
F
E
Z
-2 m.
B
3 m
C
5 m
3 m
A
-4 m.
AB
=
KN
FAC =
FAD =
KN
KN
KN
FBC =
KN
FBD
FBE
=
=
KN
F
Chapter 13 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Ch. 13.1 - Block A is traveling with a speed v0 on a smooth...Ch. 13.1 - A 400-kg satellite is placed in a circular orbit...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.2PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.3PCh. 13.1 - A 500-kg communications satellite is in a circular...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.5PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.6PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.7PCh. 13.1 - A 2000-kg automobile starts from rest at point A...Ch. 13.1 - An athlete is holding 30 lb of weights at a height...
Ch. 13.1 - A 1.4-kg model rocket is launched vertically from...Ch. 13.1 - Packages are thrown down an incline at A with a...Ch. 13.1 - A package is thrown down an incline at A with a...Ch. 13.1 - Boxes are transported by a conveyor belt with a...Ch. 13.1 - Boxes are transported by a conveyor belt with a...Ch. 13.1 - A 1200-kg trailer is hitched to a 1400-kg car. The...Ch. 13.1 - A trailer truck enters a 2 percent uphill grade...Ch. 13.1 - The subway train shown is traveling at a speed of...Ch. 13.1 - The subway train shown is travelling at a speed of...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.19PCh. 13.1 - The system shown is at rest when a constant 30-lb...Ch. 13.1 - Car B is towing car A at a constant speed of 10...Ch. 13.1 - The motor applies a constant downward force F=1050...Ch. 13.1 - The motor applies a constant downward force F to...Ch. 13.1 - Two blocks A and B, of mass 4 kg and 5 kg....Ch. 13.1 - Four 15-kg packages are placed as shown on a...Ch. 13.1 - A 3-kg block rests on top of a 2-kg block...Ch. 13.1 - Solve Prob. 13.26. assuming that the 2-kg block is...Ch. 13.1 - People with mobility impairments can gain great...Ch. 13.1 - A 7.5-lb collar is released from rest in the...Ch. 13.1 - A 10-kg block is attached to spring A and...Ch. 13.1 - A 5-kg collar A is at rest on top of, but not...Ch. 13.1 - A 0.75-lb brass (nonmagnetic) block A and a 0.5-lb...Ch. 13.1 - An uncontrolled automobile travelling at 65 mph...Ch. 13.1 - Two types of energy-absorbing fenders designed to...Ch. 13.1 - Nonlinear springs are classified as hard or soft,...Ch. 13.1 - A meteor starts from rest at a very great distance...Ch. 13.1 - Express the acceleration of gravity gh, at an...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.38PCh. 13.1 - The sphere at A is given a downward velocity v0 of...Ch. 13.1 - The sphere at Ais given a downward velocity v0and...Ch. 13.1 - A bag is gently pushed off the top of a wall at A...Ch. 13.1 - A roller coaster starts from rest at A, rolls down...Ch. 13.1 - In Prob. 13.42. determine the range of values of h...Ch. 13.1 - A small block slides at a speed v on a horizontal...Ch. 13.1 - A small block slides at a speed v=8 ft/s on a...Ch. 13.1 - A chairlift is designed to transport 1000 skiers...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.47PCh. 13.1 - The velocity of the lift of Prob. 13.47 increases...Ch. 13.1 - (a) A 120-lb woman rides a 15-lb bicycle up a...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.50PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.51PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.52PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.53PCh. 13.1 - The elevator E has a weight of 6600 lb when fully...Ch. 13.2 - Two small balls A and B with masses 2m and m,...Ch. 13.2 - A small blocks is released from rest and slides...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.55PCh. 13.2 - A loaded railroad car of mass m is rolling at a...Ch. 13.2 - A 750-g collar can slide along the horizontal rod...Ch. 13.2 - A 2-lb collar C may slide without friction along a...Ch. 13.2 - Solve Prob. 13.58 assuming the spring CD has been...Ch. 13.2 - A 500-g collar can slide without friction on the...Ch. 13.2 - For the adapted shuffleboard device in Prob 13.28....Ch. 13.2 - An elastic cable is to be designed for bungee...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.63PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.64PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.65PCh. 13.2 - A thin circular rod is supported in a vertical...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.67PCh. 13.2 - A spring is used to stop a 50-kg package that is...Ch. 13.2 - Solve Prob. 13.68 assuming the coefficient of...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.70PCh. 13.2 - A roller coaster starts from rest at A, rolls down...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.72PCh. 13.2 - A 10-lb collar is attached to a spring and slides...Ch. 13.2 - An 8-oz package is projected upward with a...Ch. 13.2 - If the package of Prob. 13.74 is not to hit the...Ch. 13.2 - A small package of weight W is projected into a...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.77PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.78PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.79PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.80PCh. 13.2 - A force F acts on a particle P(x, y) which moves...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.82PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.83PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.84PCh. 13.2 - (a) Determine the kinetic energy per unit mass...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.86PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.87PCh. 13.2 - How much energy per pound should be imparted to a...Ch. 13.2 - Knowing that the velocity of an experimental space...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.90PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.91PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.92PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.93PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.94PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.95PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.96PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.97PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.98PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.99PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.100PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.101PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.102PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.103PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.104PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.105PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.106PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.107PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.108PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.109PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.110PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.111PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.112PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.113PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.114PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.115PCh. 13.2 - A spacecraft of mass mdescribes a circular orbit...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.117PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.118PCh. 13.3 - A large insect impacts the front windshield of a...Ch. 13.3 - The expected damages associated with two types of...Ch. 13.3 - The initial velocity of the block in position A is...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.F2PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.F3PCh. 13.3 - Car A was traveling west at a speed of 15 m/s and...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.F5PCh. 13.3 - A 35.000-Mg ocean liner has an initial velocity of...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.120PCh. 13.3 - A sailboat weighing 980 lb with its occupants is...Ch. 13.3 - A truck is hauling a 300-kg log out of a ditch...Ch. 13.3 - The coefficients of friction between the load and...Ch. 13.3 - Steep safety ramps are built beside mountain...Ch. 13.3 - Baggage on the floor of the baggage car of a...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.126PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.127PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.128PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.129PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.130PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.131PCh. 13.3 - The motor applies a constant downward force F=550...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.133PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.134PCh. 13.3 - A 60-g model rocket is fired vertically. The...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.136PCh. 13.3 - A crash test is performed between an SUV A and a...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.138PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.139PCh. 13.3 - A 1.6 2-oz golf ball is hit with a golf club and...Ch. 13.3 - The triple jump is a track-and-field event in...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.142PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.143PCh. 13.3 - A 28-g steel-jacketed bullet is fired with a...Ch. 13.3 - A 120-ton tugboat is moving at 6 ft/s with a slack...Ch. 13.3 - At an intersection, car B was traveling south and...Ch. 13.3 - The 650-kg hammer of a drop-hammer pile driver...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.148PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.149PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.150PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.151PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.152PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.153PCh. 13.3 - In order to test the resistance of a chain to...Ch. 13.4 - A 5 -kg ball A strikes a 1-kg ball B that is...Ch. 13.4 - F6 A sphere with a speed v0 rebounds after...Ch. 13.4 - An 80-Mg railroad engine A coasting at 6.5 km/h...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.F8PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.F9PCh. 13.4 - Block A of mass mA strikes ball B of mass mB with...Ch. 13.4 - Two steel blocks slide without friction on a...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.156PCh. 13.4 - One of the requirements for tennis balls to be...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.158PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.159PCh. 13.4 - Packages in an automobile parts supply house are...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.161PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.162PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.163PCh. 13.4 - Two identical billiard balls can move freely on a...Ch. 13.4 - Two identical 40-lb curling stones have diameters...Ch. 13.4 - A 600-g ball A is moving with a velocity of...Ch. 13.4 - Two identical hockey pucks are moving on a hockey...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.168PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.169PCh. 13.4 - The Mars Pathfinder spacecraft used large airbags...Ch. 13.4 - A girl throws a ball at an inclined wall from a...Ch. 13.4 - Rockfalls can cause major damage to roads and...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.173PCh. 13.4 - cars of the same mass run head-on into each other...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.175PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.176PCh. 13.4 - After having been pushed by an airline employee,...Ch. 13.4 - Blocks A and B each weigh 0.8 lb and block C...Ch. 13.4 - A 5-kg sphere is dropped from a height of y=2 m to...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.180PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.181PCh. 13.4 - Block A is released from rest and slides down the...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.183PCh. 13.4 - A test machine that kicks soccer balls has a 5-lb...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.185PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.186PCh. 13.4 - A 2-kg sphere moving to the right with a velocity...Ch. 13.4 - When the rope is at an angle of a=30 , the 1-Ib...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.189PCh. 13 - 34,000-Ib airplane lands on an aircraft carrier...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.191RPCh. 13 - A satellite describes an elliptic orbit about a...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.193RPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.194RPCh. 13 - A 300-g block is released from rest after a spring...Ch. 13 - A kicking-simulation attachment goes on the front...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.197RPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.198RPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.199RPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.200RPCh. 13 - The 2-Ib ball at A is suspended by an inextensible...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A short brass cyclinder (denisty=8530 kg/m^3, cp=0.389 kJ/kgK, k=110 W/mK, and alpha=3.39*10^-5 m^2/s) of diameter 4 cm and height 20 cm is initially at uniform temperature of 150 degrees C. The cylinder is now placed in atmospheric air at 20 degrees C, where heat transfer takes place by convection with a heat transfer coefficent of 40 W/m^2K. Calculate (a) the center temp of the cylinder, (b) the center temp of the top surface of the cylinder, and (c) the total heat transfer from the cylinder 15 min after the start of the cooling. Solve this problem using the analytical one term approximation method. (Answer: (a) 45.7C, (b)45.3C, (c)87.2 kJ)arrow_forwardA short brass cyclinder (denisty=8530 kg/m^3, cp=0.389 kJ/kgK, k=110 W/mK, and alpha=3.39*10^-5 m^2/s) of diameter 4 cm and height 20 cm is initially at uniform temperature of 150 degrees C. The cylinder is now placed in atmospheric air at 20 degrees C, where heat transfer takes place by convection with a heat transfer coefficent of 40 W/m^2K. Calculate (a) the center temp of the cylinder, (b) the center temp of the top surface of the cylinder, and (c) the total heat transfer from the cylinder 15 min after the start of the cooling. Solve this problem using the analytical one term approximation method.arrow_forwardA 6 cm high rectangular ice block (k=2.22 W/mK, and alpha=0.124*10^-7 m^2/s) initially at -18 degrees C is placed on a table on its square base 4 cm by 4cm in size in a room at 18 degrees C. The heat transfer coefficent on the exposed surfaces of the ice block is 12 W/m^2K. Disregarding any heat transfer from the base to the table, determine how long it will be before the ice block starts melting. Where on the ice block will the first liquid droplets appear? Solve this problem using the analytical one-term approximation method.arrow_forward
- Consider a piece of steel undergoing a decarburization process at 925 degrees C. the mass diffusivity of carbon in steel at 925 degrees C is 1*10^-7 cm^2/s. Determine the depth below the surface of the steel at which the concentration of carbon is reduced to 40 percent from its initial value as a result of the decarburization process for (a) an hour and (b) 10 hours. Assume the concnetration of carbon at the surface is zero throughout the decarburization process.arrow_forwardPlease do not rely too much on chatgpt, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer. You can borrow ideas from gpt, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful! Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!arrow_forwardMultiple Choice Circle the best answer to each statement. 1. Which geometry attribute deviation(s) can be limited with a profile of a surface tolerance? A. Location B. Orientation C. Form D. All of the above 2. A true profile may be defined with: A. Basic radii B. Basic angles C. Formulas D. All of the above 3. Which modifier may be applied to the profile tolerance value? A B C. D. All of the above 4. The default tolerance zone for a profile tolerance is: A. Non-uniform B. Unilateral C. Bilateral equal distribution D. Bilateral-unequal distribution 5. An advantage of using a profile tolerance in place of a coordinate tolerance is: A. A bonus tolerance is permitted. B. A datum feature sequence may be specified C. A profile tolerance always controls size D. All of the above 6. The shape of the tolerance zone for a profile tolerance is: A. Two parallel planes B. The same as the true profile of the toleranced surface C. Equal bilateral D. Cylindrical when the diameter symbol is speci- fied…arrow_forward
- One thousand kg/h of a (50-50 wt%) acetone-in-water solution is to be extracted at 25C in a continuous, countercurrent system with pure 1,1,2-trichloroethane to obtain a raffinate containing 10 wt% acetone. Using the following equilibrium data, determine with an equilateral-triangle diagram: a- the minimum flow rate of solvent; b- the number of stages required for a solvent rate equal to 1.5 times minimum, and composition of each streamleaving each stage. c- Repeat the calculation of (a) and (b) if the solvent used has purity 93wt% (4wr% acetone, 3wt% water impurities) acetone water 1,1,2-trichloroethane Raffinate. Weight Extract. Weight 0.6 0.13 0.27 Fraction Acetone Fraction Acetone 0.5 0.04 0.46 0.44 0.56 0.4 0.03 0.57 0.29 0.40 0.3 0.02 0.68 0.12 0.18 0.2 0.015 0.785 0.0 0.0 0.1 0.01 0.89 0.55 0.35 0.1 0.5 0.43 0.07 0.4 0.57 0.03 0.3 0.68 0.02 0.2 0.79 0.01 0.1 0.895 0.005arrow_forward2500 kg/hr of (20-80) nicotine water solution is to be extracted with benzene containing 0.5% nicotine in the 1st and 2ed stages while the 3rd stage is free of nicotine. Cross- current operation is used with different amounts of solvent for each stages 2000kg/hr in the 1st stage, 2300 kg/hr in the 2nd stage, 2600 kg/hr in the 3rd, determine: - a- The final raffinate concentration and % extraction. b- b- The minimum amount of solvent required for counter-current operation if the minimum concentration will be reduced to 5% in the outlet raffinate. Equilibrium data Wt % Nicotine in water Wt % Nicotine in benzene 0 4 16 25 0 4 21 30arrow_forwardQuiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1=6mm, for w2 h2 5mm, and for w3 is h3 -5.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=22 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E90xx). 140 101.15 REDMI NOTE 8 PRO AI QUAD CAMERA Farrow_forward
- (read image)arrow_forwardProblem 3.30 A piston-cylinder device contains 0.85 kg of refrigerant- 134a at -10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Determine (a) the final pressure, (b) the change in the volume of the refrigerant, and (c) the change in the enthalpy of the refrigerant-134a. please show Al work step by steparrow_forwardPart 1 The storage tank contains lubricating oil of specific gravity 0.86 In one inclined side of the tank, there is a 0.48 m diameter circular inspection door, mounted on a horizontal shaft along the centre line of the gate. The oil level in the tank rests 8.8 m above the mounted shaft. (Please refer table 01 for relevant SG, D and h values). Describe the hydrostatic force and centre of pressure with the aid of a free body diagram of the inspection door. Calculate the magnitude of the hydrostatic force and locate the centre of pressure. 45° Estimate the moment that would have to be applied to the shaft to open the gate. Stop B If the oil level raised by 2 m from the current level, calculate the new moment required to open the gate. Figure 01arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY