
EP INTRO.TO GENERAL,ORGANIC...-OWL ACCE
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781337915984
Author: Bettelheim
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13, Problem 60P
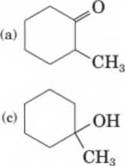
14-70 Show how to prepare each compound from 2-methylcyclohexanol.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Using the graphs could you help me explain the answers. I assumed that both graphs are proportional to the inverse of time, I think. Could you please help me.
Synthesis of Dibenzalacetone
[References]
Draw structures for the carbonyl electrophile and enolate nucleophile that react to give the enone below.
Question 1
1 pt
Question 2
1 pt
Question 3
1 pt
H
Question 4
1 pt
Question 5
1 pt
Question 6
1 pt
Question 7
1pt
Question 8
1 pt
Progress:
7/8 items
Que Feb 24 at
You do not have to consider stereochemistry.
. Draw the enolate ion in its carbanion form.
• Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner.
⚫ Separate multiple reactants using the + sign from the drop-down menu.
?
4
Shown below is the mechanism presented for the formation of biasplatin in reference 1 from the Background and Experiment document. The amounts used of each reactant are shown. Either draw or describe a better alternative to this mechanism. (Note that the first step represents two steps combined and the proton loss is not even shown; fixing these is not the desired improvement.) (Hints: The first step is correct, the second step is not; and the amount of the anhydride is in large excess to serve a purpose.)
Chapter 13 Solutions
EP INTRO.TO GENERAL,ORGANIC...-OWL ACCE
Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.1QCCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.2QCCh. 13.2 - Problem 14-3 Draw structural formulas for the...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.4QCCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.5QCCh. 13.3 - Problem 14-6 Write the common name for each ether.Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.7QCCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.8QCCh. 13 - 14-8 Answer true or false. The functional group of...Ch. 13 - 14-9 What is the difference in structure between a...
Ch. 13 - 14-10 Which of the following are secondary...Ch. 13 - 14-11 Which of the alcohols in Problem 14-10 are...Ch. 13 - 14-12 Write the 1UPAC name of each compound. (e)...Ch. 13 - Prob. 6PCh. 13 - Prob. 7PCh. 13 - 14-15 Both alcohols and phenols contain an —OH...Ch. 13 - Prob. 9PCh. 13 - 14-17 Explain in terms of noncovalent interactions...Ch. 13 - Prob. 11PCh. 13 - Prob. 12PCh. 13 - 14-20 Show hydrogen bonding between methanol and...Ch. 13 - 14-21 Show hydrogen bonding between the oxygen of...Ch. 13 - 14-22 Arrange these compounds in order of...Ch. 13 - 14-23 Arrange these compounds in order of...Ch. 13 - 14-24 2-Propanol (isopropyl alcohol) is commonly...Ch. 13 - Prob. 18PCh. 13 - Prob. 19PCh. 13 - Prob. 20PCh. 13 - 14-28 Give the structural formula of an alkene or...Ch. 13 - Prob. 22PCh. 13 - 14-30 Show how to distinguish between cyclohexanol...Ch. 13 - 14-31 Compare the acidity of alcohols and phenols,...Ch. 13 - 14-32 Both 2,6-diisopropylcyclohexanol and the...Ch. 13 - 14-33 Write equations for the reaction of...Ch. 13 - 14-34 Write equations for the reaction of...Ch. 13 - 14-35 Write equations for the reaction of each of...Ch. 13 - 14-36 Show how to convert cyclohexanol to these...Ch. 13 - Prob. 30PCh. 13 - Prob. 31PCh. 13 - 14-39 Name two important alcohols derived from...Ch. 13 - 14-40 Name two important alcohols derived from...Ch. 13 - Prob. 34PCh. 13 - 14-42 Write the common name for each ether. ch3...Ch. 13 - Prob. 36PCh. 13 - 14-44 Answer true or false. (a) The functional...Ch. 13 - Prob. 38PCh. 13 - Write the common name for each thiol in Problem 38...Ch. 13 - 14-47 Following are structural formulas for...Ch. 13 - 14-48 Explain why methanethiol, CH3SH, has a lower...Ch. 13 - 14-49 Answer true or false. Today, the major...Ch. 13 - (Chemical Connections 13A ) As stated in the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 44PCh. 13 - Prob. 45PCh. 13 - Prob. 46PCh. 13 - Prob. 47PCh. 13 - (Chemical Connections 13D ) Show that enflurane...Ch. 13 - Prob. 49PCh. 13 - 14-60 Write a balanced equation for the complete...Ch. 13 - 14-61 Knowing what you do about electronegativity,...Ch. 13 - 14-62 Draw structural formulas and write IUPAC...Ch. 13 - Prob. 53PCh. 13 - 14-64 Explain why the boiling point of ethylene...Ch. 13 - Prob. 55PCh. 13 - 14-66 1,4-Butanediol, hexane, and 1-pentanol have...Ch. 13 - 14-67 Of the three compounds given in Problem...Ch. 13 - Prob. 58PCh. 13 - 14-69 Show how to prepare each compound from...Ch. 13 - 14-70 Show how to prepare each compound from...Ch. 13 - 14-71 The mechanism of the acid-catalyzed...Ch. 13 - Prob. 62PCh. 13 - 14-73 Lipoic acid is a growth factor for many...Ch. 13 - 14-74 Following is a structural formula for the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 65PCh. 13 - Prob. 66PCh. 13 - Prob. 67PCh. 13 - 14-78 Consider alkenes A, B, and C. each of which...Ch. 13 - Prob. 69P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Hi I need help on the question provided in the image.arrow_forwardDraw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the following reaction: CH3 CH3 Et-OH Et Edit the reaction by drawing all steps in the appropriate boxes and connecting them with reaction arrows. Add charges where needed. Electron-flow arrows should start on the electron(s) of an atom or a bond and should end on an atom, bond, or location where a new bond should be created. H± EXP. L CONT. י Α [1] осн CH3 а CH3 :Ö Et H 0 N о S 0 Br Et-ÖH | P LL Farrow_forward
- 20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.025 M HCl is titrated with 0.035 M KOH. What volume of KOH is needed?arrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Acid-Base Titration | Acids, Bases & Alkalis | Chemistry | FuseSchool; Author: FuseSchool - Global Education;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yFqx6_Y6c2M;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY