
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The compound that is more soluble in water should be determined.
CH3 OH or CH3 OCH3.
Concept Introduction:
Water solubility is known as the measurement of the chemical substance which can dissolve into the water at the specific temperature. The solubility’s unit is mg/L or ppm i.e. parts per million. Water solubility is the most vital properties which affects the environmental fate and bioavailability of the chemical substances.
(b)
Interpretation:
The compound that is more soluble in water should be determined.
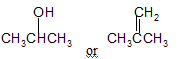
Concept Introduction:
Water solubility is known as the measurement of the chemical substance which can dissolve into the water at the specific temperature. The solubility’s unit is mg/L or ppm i.e. parts per million. Water solubility is the most vital properties which affects the environmental fate and bioavailability of the chemical substances.
(c)
Interpretation:
The compound that is more soluble in water should be determined.
CH3 CH2 CH2 SH or CH3 CH2 CH2 OH.
Concept Introduction:
Water solubility is known as the measurement of the chemical substance which can dissolve into the water at the specific temperature. The solubility’s unit is mg/L or ppm i.e. parts per million. Water solubility is the most vital properties which affects the environmental fate and bioavailability of the chemical substances.
(d)
Interpretation:
The compound that is more soluble in water should be determined.
CH3 CH2 Cl or NaCl.
Concept Introduction:
Water solubility is known as the measurement of the chemical substance which can dissolve into the water at the specific temperature. The solubility’s unit is mg/L or ppm i.e. parts per million. Water solubility is the most vital properties which affects the environmental fate and bioavailability of the chemical substances.
(e)
Interpretation:
The compound that is more soluble in water should be determined.
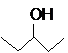 or
or 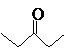
Concept Introduction:
Water solubility is known as the measurement of the chemical substance which can dissolve into the water at the specific temperature. The solubility’s unit is mg/L or ppm i.e. parts per million. Water solubility is the most vital properties which affects the environmental fate and bioavailability of the chemical substances.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 13 Solutions
EP INTRO.TO GENERAL,ORGANIC...-OWL ACCE
- b. CH3 H3C CH3 CH3 H3C an unexpected product, containing a single 9- membered ring the expected product, containing two fused rings H3C-I (H3C)2CuLi an enolatearrow_forwardb. H3C CH3 1. 2. H3O+ H3C MgBr H3Carrow_forwardPredict the major products of this reaction: excess H+ NaOH ? A Note that the first reactant is used in excess, that is, there is much more of the first reactant than the second. If there won't be any products, just check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privarrow_forward
- 1. For each of the reaction "railroads" below, you are either asked to give the structure(s) of the starting material(s) or product(s), or provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the transformation, as indicated by the boxes. a. NaOMe H+ .CO,H HO₂C MeOH (excess) MeOH H3C Br يع CH3 1. LiAlH4 2. H3O+ 3. PBг3 H3C 1. Et-Li 2. H3O+ -CO₂Me -CO₂Me OH CH3 CH3 ল CH3arrow_forwardPredict the intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this organic reaction: NaOMe ག1, ད།་, - + H You can draw 1 and 2 in any arrangement you like. 2 work up Note: if either 1 or 2 consists of a pair of enantiomers, just draw one structure using line bonds instead of 3D (dash and wedge) bonds at the chiral center. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Parrow_forwardWhat is the total energy cost associated with the compound below adopting the shown conformation? CH3 HH DH CH3arrow_forward
- ΗΝ, Draw Final Product C cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Edit Enamine H3O+ CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H Edit Iminium Ionarrow_forwardHow many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?arrow_forwardIdentify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forward
- Identify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
