
EP BASIC CHEMISTRY-STANDALONE ACCESS
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780134999890
Author: Timberlake
Publisher: PEARSON CO
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 13, Problem 56UTC
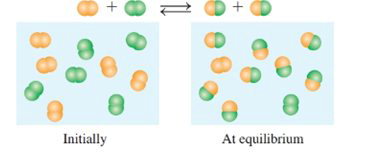
Would the equilibrium constant,
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Alcohols can be synthesized using an acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene. An alkene is combined with aqueous acid (e.. sulfuric acid in water). The
reaction mechanism typically involves a carbocation intermediate.
>
3rd attempt
3343
10
8
Draw arrows to show the reaction between the alkene and hydronium ion.
that
2nd attempt
Feedback
1st attempt
تعمال
Ju See Periodic Table See Hint
F
D
Ju See Periodic Table See Hint
Draw the simplified curved arrow mechanism for the reaction of acetone and CHgLi to give the major product.
4th attempt
Π
Draw the simplified curved arrow mechanism
T
3rd attempt
Feedback
Ju
See Periodic Table See Hint
H
-H
H
-I
H
F
See Periodic Table See Hint
Select the correct reagent to accomplish the first step of this reaction. Then draw a mechanism on the Grignard reagent using curved arrow notation
to show how it is converted to the final product.
4th attempt
Part 1 (0.5 point)
Select the correct reagent to accomplish the first step of this reaction.
Choose one:
OA Mg in ethanol (EtOH)
OB. 2 Li in THF
O C. Li in THF
D. Mg in THF
O E Mg in H2O
Part 2 (0.5 point)
Br
Part 1
Bri
Mg
CH
B
CH,
1 Draw intermediate here, but no arrows.
©
TE
See Periodic Table See Hint
See Hint
ין
H
Chapter 13 Solutions
EP BASIC CHEMISTRY-STANDALONE ACCESS
Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 1PPCh. 13.1 - Prob. 2PPCh. 13.1 - In the following reaction, what happens to the...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 4PPCh. 13.1 - Prob. 5PPCh. 13.1 - Prob. 6PPCh. 13.2 - What is meant by the term reversible reaction?Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 8PPCh. 13.2 - Which of the following are at equilibrium? a. The...Ch. 13.2 - Which of the following are not at equilibrium? a....
Ch. 13.2 - 13.11 The following diagrams show the chemical...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 12PPCh. 13.3 - Write the equilibrium expression for each of the...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 14PPCh. 13.3 - Prob. 15PPCh. 13.3 - Prob. 16PPCh. 13.3 - What is the numerical value of Kc for the...Ch. 13.3 - What is the numerical value of Kc for the...Ch. 13.3 - What is the numerical value of Kc for the...Ch. 13.3 - What is the numerical value of Kc for the...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 21PPCh. 13.3 - Identify each of the following as a homogeneous or...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 23PPCh. 13.3 - Prob. 24PPCh. 13.3 - Prob. 25PPCh. 13.3 - What is the numerical value of Kc for the...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 27PPCh. 13.4 - Prob. 28PPCh. 13.4 - Indicate whether each of the following equilibrium...Ch. 13.4 - Indicale whether each of the following equilibrium...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 31PPCh. 13.4 - The numerical value of the equilibrium constant,...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 33PPCh. 13.4 - The numerical value of the equilibrium constant,...Ch. 13.5 - In the lower atmosphere, oxygen is converted to...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 36PPCh. 13.5 - Hydrogen chloride can be made by reacting hydrogen...Ch. 13.5 - When heated, carbon monoxide reacts with water to...Ch. 13.5 - Use the following equation for the equilibrium of...Ch. 13.5 - Use the following equation for the equilibrium of...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 41PPCh. 13.5 - Prob. 42PPCh. 13.6 - For each of the following slightly soluble ionic...Ch. 13.6 - For each of the following slightly soluble ionic...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 45PPCh. 13.6 - Prob. 46PPCh. 13.6 - A saturated solution of silver carbonate, Ag2CO3 ,...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 48PPCh. 13.6 - Calculate the molar solubility, S , of CuI if it...Ch. 13.6 - Calculate the molar solubility, S , of SnS if it...Ch. 13.6 - The CO2 level in the atmosphere has increased over...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 52PPCh. 13 - Write the equilibrium expression for each of the...Ch. 13 - Write the equilibrium expression for each of the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 55UTCCh. 13 - Would the equilibrium constant, Ke , for the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 57UTCCh. 13 - Prob. 58UTCCh. 13 - Prob. 59APPCh. 13 - Prob. 60APPCh. 13 - For each of the following reactions, indicate if...Ch. 13 - For each of the following reactions, indicate if...Ch. 13 - Consider the reaction: (13.3) 2NH3(g)N2(g)+3H2(g)...Ch. 13 - Prob. 64APPCh. 13 - Prob. 65APPCh. 13 - Prob. 66APPCh. 13 - Prob. 67APPCh. 13 - According to Le Châtelier's principle, does the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 69APPCh. 13 - Prob. 70APPCh. 13 - The numerical value of the equilibrium constant,...Ch. 13 - The numerical value of the equilibrium constant,...Ch. 13 - For each of the following slightly soluble ionic...Ch. 13 - For each of the following slightly soluble ionic...Ch. 13 - Prob. 75APPCh. 13 - Prob. 76APPCh. 13 - Prob. 77APPCh. 13 - Prob. 78APPCh. 13 - What is the molar solubility, S , of CdS if it has...Ch. 13 - Prob. 80APPCh. 13 - Prob. 81CPCh. 13 - Prob. 82CPCh. 13 - Prob. 83CPCh. 13 - Indicate how each of the following will affect the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 85CPCh. 13 - Prob. 86CPCh. 13 - Prob. 87CPCh. 13 - Prob. 88CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Select the product for the following reaction. HO HO PCC OH ○ OH O HO ○ HO HO HOarrow_forward5:45 Х Select the final product for the following reaction sequence. O O 1. Mg. ether 2.D.Oarrow_forwardBased on the chart Two similarities between the molecule with alpha glycosidic linkages. Two similarities between the molecules with beta glycosidtic linkages. Two differences between the alpha and beta glycosidic linkages.arrow_forward
- please help fill in the tablearrow_forwardAnswer F pleasearrow_forward4. Refer to the data below to answer the following questions: The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II. A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive. Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids: Ala, Arg, His, Pro, Sar, Tyr, Val, Val A.Sar is the abbreviation for sarcosine, N-methyl aminoethanoic acid. Draw the structure of sarcosine. B. N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Tyr-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val-Tyr-Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forward
- What is the structure of the DNA backbone?arrow_forwardPLEASE PLEASE PLEASE use hand drawn structures when possarrow_forward. M 1- MATCH each of the following terms to a structure from the list below. There is only one correct structure for each term and structures may be used more than once. Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the corresponding term. A. Sanger dideoxy method C. Watson-Crick B. GAUCGUAAA D. translation E. HOH2C OH OH G. transcription I. AUGGCUGAG 0 K. OPOH2C 0- OH N- H NH2 F. -OPOH2C 0- OH OH H. Maxam-Gilbert method J. replication N L. HOH2C a. b. C. d. e. f. g. B M. AGATCGCTC a pyrimidine nucleoside RNA base sequence with guanine at the 3' end. DNA base sequence with cytosine at the 3' end. a purine nucleoside DNA sequencing method for the human genome 2'-deoxyadenosine 5'-phosphate process by which mRNA directs protein synthesis OH NH2arrow_forward
- Please use hand drawn structures when neededarrow_forwardB. Classify the following amino acid. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. a. acidic b. basic C. neutral C. Consider the following image. Which level of protein structure is shown here? a. primary b. secondary c. tertiary d. quaternary D. Consider the following image. H RH H HR H R HR HR RH Which level of protein structure is shown in the box? a. primary b. secondary R c. tertiary d. quaternary コー Rarrow_forwardBriefly answer three from the followings: a. What are the four structures of the protein? b. Why is the side chain (R) attached to the alpha carbon in the amino acids is important for the function? c. What are the types of amino acids? And how is it depend on the (R) structure? d. Write a reaction to prepare an amino acid. prodarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY
Chemical Equilibria and Reaction Quotients; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1GiZzCzmO5Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY