
A piece of metal has a measured mass of 5.00 g in air, 3.00 g in water, and 3.24 g in benzene. Determine the mass density of the metal and of the benzene.
The apparent mass of a
Answer to Problem 55SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The side of metal cube is
The apparent mass of metal cube in water is
The specific gravity of glycerineis
Formula used:
The volume of a cube is expressed as
Here,
The density of a body is calculated using the expression
Here,
Archimedes’ principle states that the apparent upward force experienced by the solid immersed in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it. This upward buoyant force on the solid is expressed as
Here,
The weight of a body is expressed as
Here,
The apparent weight of a body submerged in a liquid is calculated as
Here,
The specific gravity of a liquid is expressed as
Here,
Explanation:
Draw a figure to represent the system when the cube is submerged in water:
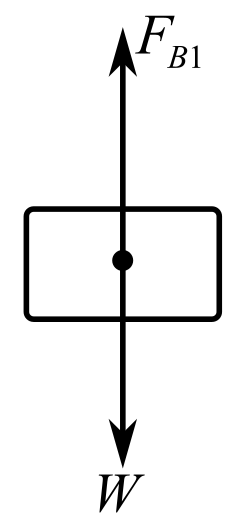
Here,
Recall the formula for calculating the volume of the metal cube:
Substitute
Recall the formula for calculating the density of a metal cube:
Rearrange the above expression for
Substitute
Recall expression for the weight of themetal cube:
Substitute
It is understood that the cube is completely submerged in water, therefore, the expression for the volume of a cube submerged in water becomes
Substitute
Recall the expression for buoyant force exerted by water on the metal cube:
Here,
Consider the standard value of
Substitute
Write the expression for the apparent weight of the cube in water in terms of apparent mass:
Here,
Substitute
Recall the expression for the apparent weight of the cube in water in terms of buoyant force:
Substitute
Further solve as
Consider the situation when the cube is submerged in glycerine anddraw its free body diagram:
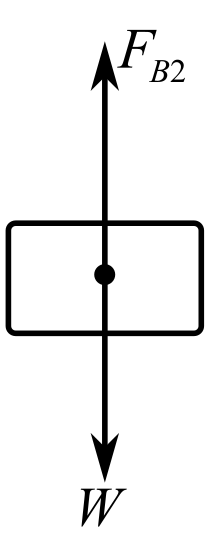
Here,
Recall the expression for the specific gravity of glycerine:
Substitute
Recall the expression for calculating the buoyant force exerted by glycerine on the metal cube:
Substitute
Write the expression for apparent weight of the cube in glycerine in terms of apparent mass:
Here,
Substitute
Recall the expression for the apparent weight of the cube in glycerine in terms of buoyant force:
Substitute
Substitute
Further solve as
Conclusion:
The apparent mass of the cube in glycerine is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Schaum's Outline of College Physics, Twelfth Edition (Schaum's Outlines)
- Correct answer No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardStatistical thermodynamics. The number of imaginary replicas of a system of N particlesa) cannot be greater than Avogadro's numberb) must always be greater than Avogadro's number.c) has no relation to Avogadro's number.arrow_forwardLab-Based Section Use the following information to answer the lab based scenario. A student performed an experiment in an attempt to determine the index of refraction of glass. The student used a laser and a protractor to measure a variety of angles of incidence and refraction through a semi-circular glass prism. The design of the experiment and the student's results are shown below. Angle of Incidence (°) Angle of Refraction (º) 20 11 30 19 40 26 50 31 60 36 70 38 2a) By hand (i.e., without using computer software), create a linear graph on graph paper using the student's data. Note: You will have to manipulate the data in order to achieve a linear function. 2b) Graphically determine the index of refraction of the semi-circular glass prism, rounding your answer to the nearest hundredth.arrow_forward
- Use the following information to answer the next two questions. A laser is directed at a prism made of zircon (n = 1.92) at an incident angle of 35.0°, as shown in the diagram. 3a) Determine the critical angle of zircon. 35.0° 70° 55 55° 3b) Determine the angle of refraction when the laser beam leaves the prism.arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next two questions. A laser is directed at a prism made of zircon (n = 1.92) at an incident angle of 35.0°, as shown in the diagram. 3a) Determine the critical angle of zircon. 35.0° 70° 55 55° 3b) Determine the angle of refraction when the laser beam leaves the prism.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- A beam of alpha-particles of energy 7.3MeV is used.The protons emitted at an angle of zero degree are found to have energy of 9.34MeV.Find the Q-value of this reaction .arrow_forwardAn aluminum rod and a copper rod have the same length of 100cm at 5C. At what temperatures would one of the rods be 0.5 mm longer than the other? Which rod is longer at such temperature?arrow_forwardROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Question 01 A solid circular cylinder and a solid spherical ball of the same mass and radius are rolling together down the same inclined. Calculate the ratio of their kinetic energy. Assume pure rolling motion Question 02 A sphere and cylinder of the same mass and radius start from ret at the same point and more down the same plane inclined at 30° to the horizontal Which body gets the bottom first and what is its acceleration b) What angle of inclination of the plane is needed to give the slower body the same acceleration Question 03 i) Define the angular velocity of a rotating body and give its SI unit A car wheel has its angular velocity changing from 2rads to 30 rads seconds. If the radius of the wheel is 400mm. calculate ii) The angular acceleration iii) The tangential linear acceleration of a point on the rim of the wheel Question 04 in 20arrow_forward
- Question B3 Consider the following FLRW spacetime: t2 ds² = -dt² + (dx² + dy²+ dz²), t2 where t is a constant. a) State whether this universe is spatially open, closed or flat. [2 marks] b) Determine the Hubble factor H(t), and represent it in a (roughly drawn) plot as a function of time t, starting at t = 0. [3 marks] c) Taking galaxy A to be located at (x, y, z) = (0,0,0), determine the proper distance to galaxy B located at (x, y, z) = (L, 0, 0). Determine the recessional velocity of galaxy B with respect to galaxy A. d) The Friedmann equations are 2 k 8πG а 4πG + a² (p+3p). 3 a 3 [5 marks] Use these equations to determine the energy density p(t) and the pressure p(t) for the FLRW spacetime specified at the top of the page. [5 marks] e) Given the result of question B3.d, state whether the FLRW universe in question is (i) radiation-dominated, (ii) matter-dominated, (iii) cosmological-constant-dominated, or (iv) none of the previous. Justify your answer. f) [5 marks] A conformally…arrow_forwardSECTION B Answer ONLY TWO questions in Section B [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-B sub question.] Question B1 Consider the line element where w is a constant. ds²=-dt²+e2wt dx², a) Determine the components of the metric and of the inverse metric. [2 marks] b) Determine the Christoffel symbols. [See the Appendix of this document.] [10 marks] c) Write down the geodesic equations. [5 marks] d) Show that e2wt it is a constant of geodesic motion. [4 marks] e) Solve the geodesic equations for null geodesics. [4 marks]arrow_forwardPage 2 SECTION A Answer ALL questions in Section A [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-A sub question.] Question A1 SPA6308 (2024) Consider Minkowski spacetime in Cartesian coordinates th = (t, x, y, z), such that ds² = dt² + dx² + dy² + dz². (a) Consider the vector with components V" = (1,-1,0,0). Determine V and V. V. (b) Consider now the coordinate system x' (u, v, y, z) such that u =t-x, v=t+x. [2 marks] Write down the line element, the metric, the Christoffel symbols and the Riemann curvature tensor in the new coordinates. [See the Appendix of this document.] [5 marks] (c) Determine V", that is, write the object in question A1.a in the coordinate system x'. Verify explicitly that V. V is invariant under the coordinate transformation. Question A2 [5 marks] Suppose that A, is a covector field, and consider the object Fv=AAμ. (a) Show explicitly that F is a tensor, that is, show that it transforms appropriately under a coordinate transformation. [5 marks] (b)…arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





