
Gen Combo Ll Basic Biomechanics; Connect Ac; Maxtraq Software Ac
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781264013876
Author: Hall
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13, Problem 4AP
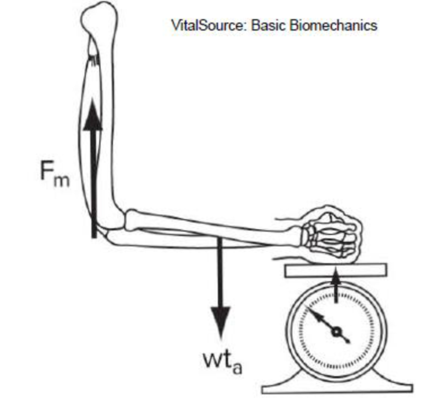
A hand exerts a force of 90 N on a scale at 32 cm from the joint center at the elbow. If the triceps attach to the ulna at a 90° angle and at a distance of 3 cm from the elbow joint center, and if the weight of the forearm and hand is 40 N with the hand/forearm CG located 17 cm from the elbow joint center, how much force is being exerted by the triceps? (Answer: 733.3 N)
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Gen Combo Ll Basic Biomechanics; Connect Ac; Maxtraq Software Ac
Ch. 13 - Why does a force directed through an axis of...Ch. 13 - Why does the orientation of a force acting on a...Ch. 13 - A 23-kg boy sits 1.5 m from the axis of rotation...Ch. 13 - Prob. 4IPCh. 13 - Two people push on opposite sides of a swinging...Ch. 13 - Prob. 6IPCh. 13 - Prob. 7IPCh. 13 - Prob. 8IPCh. 13 - A 10-kg block sits motionless on a table in spite...Ch. 13 - Prob. 10IP
Ch. 13 - A 35-N hand and forearm are held at a 45 angle to...Ch. 13 - A hand exerts a force of 90 N on a scale at 32 cm...Ch. 13 - A patient rehabilitating a knee injury performs...Ch. 13 - A worker leans over and picks up a 90-N box at a...Ch. 13 - A man carries a 3 m, 32-N board over his shoulder....Ch. 13 - A therapist applies a lateral force of 80 N to the...Ch. 13 - Tendon forces Ta and Tb are exerted on the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, bioengineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Movement at the shoulder joint that moves the upper limb laterally away from the body is called ________. elevation eversion abduction lateral rotationarrow_forwardFigure 38.37 Which of the following statements about muscle contraction is true? The power stroke occurs when ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP and phosphate. The power stroke occurs when ADP and phosphate dissociate from the myosin head. The power stroke occurs when ADP and phosphate dissociate from the actin active site. The power stroke occurs when Ca2+ binds the calcium head.arrow_forwardIn a general sense, how do skeletal muscles produce movement?arrow_forward
- The large muscle group that attaches the leg to the pelvic girdle and produces extension of the hip joint is the ________ group. gluteal obturator adductor abductorarrow_forwardA muscle that has a pattern of fascicles running along the long axis of the muscle has which of the following fascicle arrangements? circular pennate parallel rectusarrow_forwardFigure 13.22 To what structures in a skeletal muscle are the endoneurium, perineurium, and epineurium comparable? Figure 13.22 Close-Up of Nerve Trunk Zoom in on this slide of a nerve trunk to examine the endoneurium, perineurium, and epineurium in greater detail (tissue source: simian). LM × 1600. (Micrograph provided by the Regents of University of Michigan Medical School © 2012)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College- Lifetime Physical Fitness & WellnessHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337677509Author:HOEGERPublisher:Cengage

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781337711067
Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna Balac
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College

Lifetime Physical Fitness & Wellness
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781337677509
Author:HOEGER
Publisher:Cengage


GCSE PE - ANTAGONISTIC MUSCLE ACTION - Anatomy and Physiology (Skeletal and Muscular System - 1.5); Author: igpe_complete;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6hm_9jQRoO4;License: Standard Youtube License