
Concept explainers
A circular curve of radius R on a highway is banked at an angle θ so that a car can safely traverse the curve without skidding when there is no friction between the mad and the tires. The loss of friction could occur, for example, if the road is covered with a film of water or ice. The rated speed vr of the curve is the maximum speed that a car can attain without skidding. Suppose a car of mass m is traversing the curve at the rated speed vR. Two forces are acting on the car: the vertical force, mg, due to the weight of the car, and a force F exerted by, and normal to, the road (see the figure).
The vertical component of F balances the weight of the car, so that |F| cos θ = mg. The horizontal component of F produces a centripetal force on the car so that, by Newton's Second Law and part (d) of Problem 1,
(a) Show that
(b) Find the rated speed of a circular curve with radius 400 ft that is banked at an angle of 12°.
(c) Suppose the design engineers want to keep the banking at 12°, but wish to increase the rated speed by 50%. What should the radius of the curve be?.
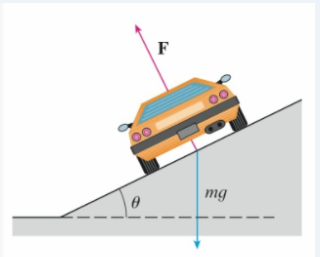
FIGURE FOR PROBLEM 2
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 13 Solutions
Bundle: Calculus: Early Transcendentals, 8th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Stewart's Calculus: Early Transcendentals, 8th Edition, Multi-Term
- the correct answer is A could you show me whyarrow_forwardGood Day, Kindly assist me with this query.arrow_forwardon donne f(x) da fonction derive dhe do fonction fcsos calcule f'(x) orans chacun des Cas sulants: 3 1) f(x)=5x-11, 2- f (x) = ->³ 3-1(x) = x² 12x +π; 4-f(x)=- 5-f(x) = 33-4x6-609)=-3x²+ 7= f(x) = x + 1.8-f(x) = 4 s-f(x) = x++ X+1 -x-1 2 I 3x-4 девоarrow_forward
- The correct answer is Ccould you show me how to do it by finding a0 and and akas well as setting up the piecewise function and integratingarrow_forwardT 1 7. Fill in the blanks to write the calculus problem that would result in the following integral (do not evaluate the interval). Draw a graph representing the problem. So π/2 2 2πxcosx dx Find the volume of the solid obtained when the region under the curve on the interval is rotated about the axis.arrow_forward38,189 5. Draw a detailed graph to and set up, but do not evaluate, an integral for the volume of the solid obtained by rotating the region bounded by the curve: y = cos²x_for_ |x| ≤ and the curve y y = about the line x = =플 2 80 F3 a FEB 9 2 7 0 MacBook Air 3 2 stv DGarrow_forward
- Find f(x) and g(x) such that h(x) = (fog)(x) and g(x) = 3 - 5x. h(x) = (3 –5x)3 – 7(3 −5x)2 + 3(3 −5x) – 1 - - - f(x) = ☐arrow_forwardx-4 Let f(x)=5x-1, h(x) = Find (fo h)(0). 3 (fo h)(0) = (Type an integer or a fraction.)arrow_forwardFill in the blanks to write the calculus problem that would result in the following integral (do not evaluate the interval). Draw a graph representing the problem. π/2 So/² 2xcosx dx Find the volume of the solid obtained when the region under the curve 38,189 on the interval is rotated about the axis.arrow_forward
- Let f(x) = -5x-1, g(x) = x² + 5, h(x) = · x+4 3 Find (hog of)(1). (hogof)(1)= (Simplify your answer. Type an integer or a decimal.)arrow_forwardFor the given function, find (a) the equation of the secant line through the points where x has the given values and (b) the equation of the tangent line when x has the first value. y= f(x) = x²+x; x=-1,x=2 a. Which of the following formulas can be used to find the slope of the secant line? ○ A. 2-(-1) f(2) f(-1) 2+(-1) C. 1(2)+(-1) The equation of the secant line is 1(2)+(-1) О в. 2+(-1) f(2)-(-1) D. 2-(-1)arrow_forwardplease do not use chat gptarrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning  Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning





