
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the given reaction between 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene and hydrogen bromide is to be determined. The reaction energy coordinate diagram that illustrates kinetic and thermodynamic pathways is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
舧 Electrophiles are electron-deficient species, which has positive or partially positive charge. Lewis acids are electrophiles, which accept electron pair.
舧 Nucleophiles are electron-rich species, which has negative or partially negative charge. Lewis bases are nucleophiles, which donate electron pair.
舧 Free radical is an atom, molecule, or ion that has an unpaired electron, which makes it highly chemically reactive.
舧 Substitution reaction: A reaction in which one of the hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon or a
舧 Elimination reaction: A reaction in which two substituent groups are detached and a double bond is formed is called elimination reaction.
舧 Addition reaction: It is the reaction in which unsaturated bonds are converted to saturated molecules by the addition of molecules.
舧 The reaction in which there is addition of hydrogen molecule is called hydrogenation reaction.
舧
舧 Hydrogenation with platinum as a catalyst is used to convert unsaturated carbohydrates to saturated hydrocarbons
舧 Oxidation of
舧 Ozonolysis helps convert the carbon – carbon double bonds to carbon – oxygen double bond (carbonyl compounds).
舧 Dimethyl sulfide is used as a reducing agent that decomposes the intermediate formed into the carbonyl group.
舧 NBS (nitro-bromo succinimide) is a special reagent used for bromination of allylic carbocations.
舧 Bromine replaces the hydrogen attached to the carbon adjacent to the carbon bearing double bond.
舧 This method of using NBS can produce allylic bromides without bromine reacting with the double bond.
舧 Dehydration of a primary alcohol in the presence of a mineral acid like concentrated sulfuric acid results in the formation of alkene via E2 elimination.
舧 1,2–addition of hydrohalogenation (HX) to a diene is the addition of hydrogen to the carbon designated as 1 and halogen to the carbon designated as 2. The positions of carbon as 1 and 2 are not according to the IUPAC numbering of the molecule, but as a conjugated diene. The mechanism is similar to 1,4-addition. The mechanism of 1,2-addition and 1,4-addition of hydrohalogenation is given below:
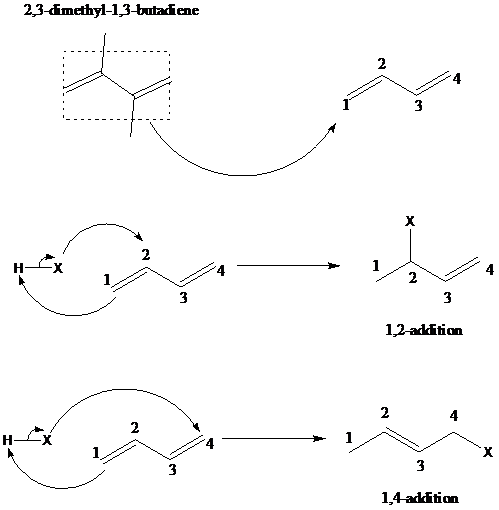
舧 When conjugated diene is attacked by an electrophile, the resultant products are formed via 1,2-addition and 1,4-addition reaction mechanism. Kinetics and
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Indicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. OC2H5 + CoHs-NH-NH,arrow_forwardExplain how substitutions at the 5-position of barbituric acid increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forwardExplain how substitutions at the 5-position of phenobarbital increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forward
- Name an interesting derivative of barbituric acid, describing its structure.arrow_forwardBriefly describe the synthesis mechanism of barbituric acid from the condensation of urea with a β-diketone.arrow_forwardGiven the hydrazones indicated, draw the structures of the enamines that can be formed. Indicate the most stable enamine (explain). C6H5 C6H5 H C6H5 Harrow_forward
- 4. Propose a Synthesis for the molecule below. You may use any starting materials containing 6 carbons or less (reagents that aren't incorporated into the final molecule such as PhзP do not count towards this total, and the starting material can have whatever non-carbon functional groups you want), and any of the reactions you have learned so far in organic chemistry I, II, and III. Your final answer should show each step separately, with intermediates and conditions clearly drawn.arrow_forwardIndicate the importance of the indole ring. Find a representative example and list 5 structures.arrow_forwardΌΗ 1) V2 CO 3 or Nalt In منهarrow_forward
- 6. The equilibrium constant for the reaction 2 HBr (g) → H2(g) + Br2(g) Can be expressed by the empirical formula 11790 K In K-6.375 + 0.6415 In(T K-¹) - T Use this formula to determine A,H as a function of temperature. Calculate A,-H at 25 °C and at 100 °C.arrow_forward3. Nitrosyl chloride, NOCI, decomposes according to 2 NOCI (g) → 2 NO(g) + Cl2(g) Assuming that we start with no moles of NOCl (g) and no NO(g) or Cl2(g), derive an expression for Kp in terms of the equilibrium value of the extent of reaction, Seq, and the pressure, P. Given that K₂ = 2.00 × 10-4, calculate Seq/ of 29/no when P = 0.080 bar. What is the new value по ƒª/ at equilibrium when P = 0.160 bar? Is this result in accord with Le Châtelier's Principle?arrow_forwardConsider the following chemical equilibrium: 2SO2(g) + O2(g) = 2SO3(g) • Write the equilibrium constant expression for this reaction. Now compare it to the equilibrium constant expression for the related reaction: • . 1 SO2(g) + O2(g) = SO3(g) 2 How do these two equilibrium expressions differ? What important principle about the dependence of equilibrium constants on the stoichiometry of a reaction can you learn from this comparison?arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


