
Concept explainers
To match: The given anatomical terms with the given diagram of the respiratory tract.
Introduction: The respiratory tract is a series of structurally complex organs responsible for inhaling oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide. The main function of the respiratory tract is to facilitate gaseous exchange between the organs involved in respiration and the outside environment.
Answer to Problem 1P
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows a diagram of the respiratory tract labeled with the given anatomical terms.
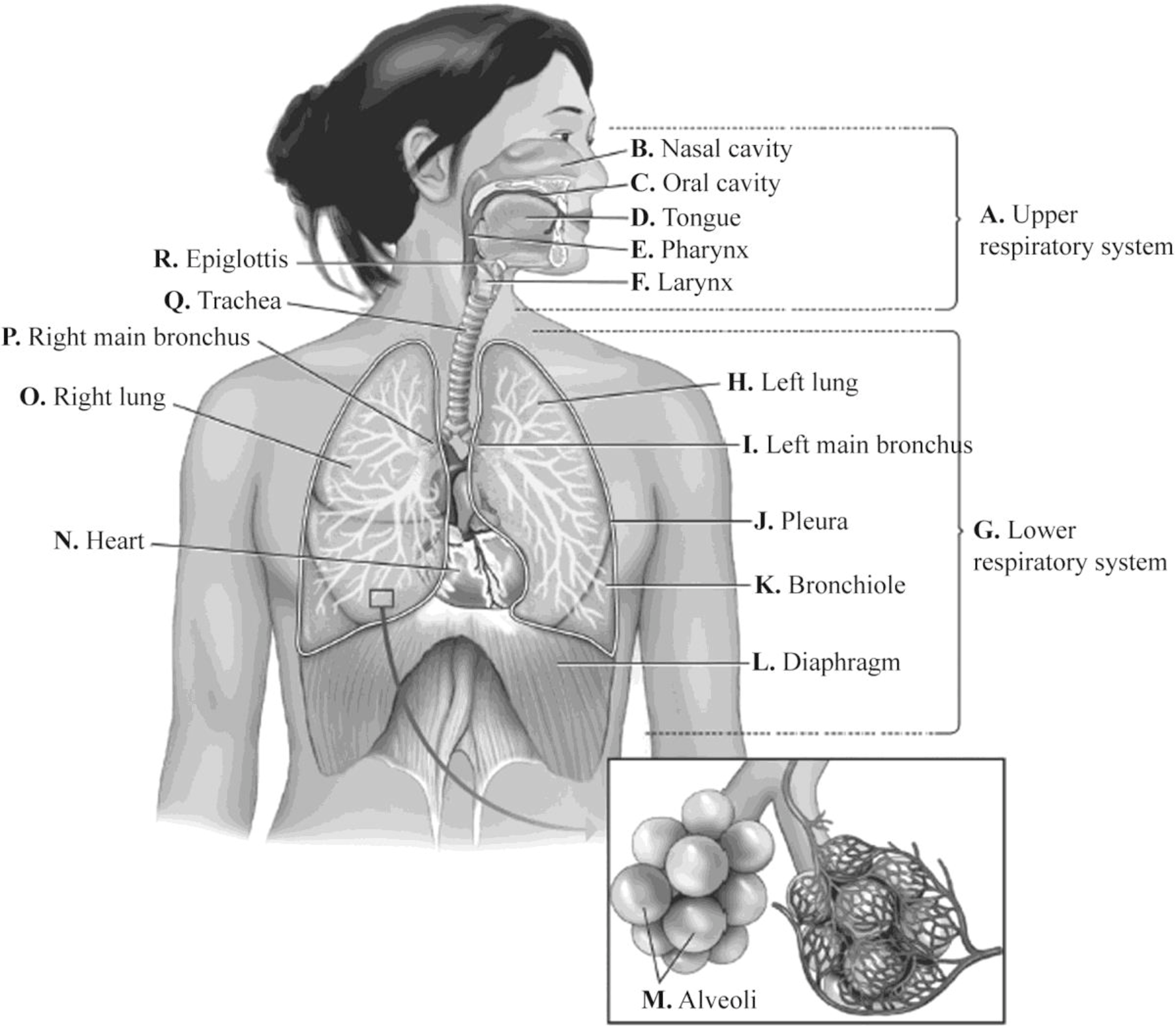
Fig.1: Anatomical structure of the respiratory tract
Explanation of Solution
A. Upper respiratory system: The upper respiratory system provides the passage for the air from the outside to be inhaled and expelled out. The complex muscle structure of the upper respiratory system modulates the respiratory airflow throughout the respiratory cycle in humans.
B. Nasal cavity: The nasal cavity is a small hollow space located within the nose and the skull. It is lined with tiny hairs and a protective mucous membrane. The function of the nasal cavity is to provide warm, moist, and filtered air.
C. Oral cavity: The mouth or the oral cavity acts as the secondary external opening for the respiratory tract. As the mouth lacks the hairs and the mucus to filter the air passing through it and the pathway of air entering the body from the mouth is shorter, there is less time to perform the function of filtering and moistening the air passing through the nasal passage.
D. Tongue: The tongue is anchored to the hyoid bone at the back of the mouth and is responsible for the dual roles of breathing and swallowing functions in humans. The tongue is critical for airway maintenance during quiet breathing and exerts pressure on the food bolus to prevent it from entering the pharynx and the open larynx.
E. Pharynx: The role of the pharynx in respiration is to allow inhaled air to enter the nasal cavity and pass through the respiratory tract where respiration takes place. The mucosal epithelium of the pharynx is thicker as it protects the delicate tissues from abrasion by food passing through for digestion.
F. Larynx (voice box): The larynx commonly, called as the voice box, is a tubular structure connected to the wind pipe and is responsible for producing vocal sounds. The larynx allows air to be directed to the respiratory organs for gaseous exchange. The larynx plays an important role in preventing food from entering the respiratory system.
G. Lower respiratory system: The lower respiratory system is responsible for sucking in air from the upper respiratory system, absorbing the oxygen from the air, and releasing carbon dioxide in exchange.
H. Left lung: The left lung is a sack of tissue located just below the rib cage, above the diaphragm and is covered by the pleural membrane. The lungs are not the same size; the left lung is narrower to create space for the heart and consists of two lobes. The main function of the lung is the process of gas exchange called breathing.
I. Left main bronchus: The left main bronchus is smaller, about 5cm long and enters the root of the left lung at a point called the hilum. The alveoli and the ducts of the left bronchus consist of squamous epithelium which permits the rapid diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
J. Pleura: The pleura are membranes of the thoracic cavity that aid in the optimal functioning of the lungs during breathing. The pleural cavity contains a fluid that fills the pleural space between the lungs and the ribcage which reduces the friction created by the movement of the lungs during respiration.
K. Bronchiole: The bronchioles are the small passages through which air is directed from the nose and mouth to the alveoli (air sacs) in the lungs. Bronchioles are 1mm or less in diameter, and their walls consist of a layer of smooth muscle.
L. Diaphragm: The diaphragm is a thin skeletal muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. The function of the diaphragm is to contract during respiration increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity that creates a negative pressure drawing air into the lungs.
M. Alveoli: Alveoli are small balloon-shaped structures and are located at the terminal portion of the lungs. The walls of the alveoli consist of a single layer of squamous epithelial tissue. The oxygen from the air that is inhaled passes through the thin walls of the alveoli to the surrounding capillaries.
N. Heart: The heart is located between the lungs in the chest compartment and is divided into four chambers: the upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. The heart is a muscular organ which pumps oxygenated blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system and brings back deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
O. Right lung: The right lung is a sack of tissue located just below the rib cage, above the diaphragm, and covered by the pleural membrane. The lungs are not the same size; the right lung is shorter than the left lung to create space for the liver and consists of three lobes. The main function of the lung is the process of gas exchange called breathing.
P. Right main bronchus: The right main bronchus is about 2.5cm in length, is shorter, wider, and enters the right lung at the hilum. The right main bronchus is subdivided into three secondary bronchi which deliver oxygen to the three lobes of the right lung.
Q. Trachea: The trachea or the wind pipe is a wide hollow tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs. It performs the vital function of conducting air to and from the lungs for respiration. The tracheal walls are made of hyaline cartilage rings that prevent the trachea from collapsing but are flexible enough to allow bending and elongation.
R. Epiglottis: The epiglottis is a small flap at the back of the throat that prevents food from entering the windpipe and the lungs. The epiglottis opens during breathing and allows air into the larynx. It functions as the valve that diverts the passage of air to the trachea.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions
- what causes a variation in vital signs and how can we make adjustments?arrow_forwardAnalyze the traits that define a profession that nursing has attained?arrow_forwardHello, Can you help me please with the next case: Assessment (Recognizing Cues) Which client information is relevant? What client data is most important? Which client information is of immediate concern? Consider signs and symptoms, lab work, client statements, H & P, and others. Consider subjective and objective data. Analysis (Analyzing Cues) Which client conditions are consistent with the cues? Do the cues support a particular client condition? What cues are a cause for concern? What other information would help to establish the significance of a cue? Analysis (Prioritizing Hypotheses) What explanations are most likely? What is the most serious explanation? What is the priority order for safe and effective care? In order of priority, identify the top 3 client conditions. Thank you in advnce!arrow_forward
- Adult Case 1: Day 2—Questions 1. Write the Day 2 PN bag using a 2-in-1 formulation. 2. Would you increase dextrose to goal? 3. Would you add/continue ILE on Day 2? Why or why not? If so, what amount? 4. Assess and determine electrolyte additives. Assess calcium–phosphate compatibility. 5. What other additives would you include in the Day 2 PN? 6. Are there any additional interventions you would make? 7. What follow-up laboratory test results might be important to obtain for tomorrow morning?arrow_forwardAnalyze the traits that define a profession that nursing has attained?arrow_forwardEvaluate ways nursing has failed to attain its status as a profession?arrow_forward
- Discuss the difference between an occupation and a profession?arrow_forward1. Write goal PN macronutrients using a 2-in-1 formulation. 2. What consideration for amino acid concentration needs to be assessed? 3. Would you start this patient on goal dextrose for Day 1? 4. Would you add ILE on Day 1? Why or why not? If so, what amount? 5. Assess and determine electrolyte additives. Assess calcium–phosphate compatibility. 6. What other additives would you include in the Day 1 PN?arrow_forwardWhat impact do regulatory and accreditation standards have on the risk management process within health care organizations? Why do you think it’s important to understand how regulatory and accreditation standards affect risk management? Provide examples.arrow_forward
- you are a school nurse. in the last2 weeks, 9 cases of head lice have been reported in four different classrooms. The potential for spread is high, and both parents and teachers are growing anxious. compose a memo for distribution to the teachers. your goals are to inform, reassure, and direct future inqueries.arrow_forwardasked but not answers yet Language of Medicine 13th edition chapter 1 sections A-E exercise with answers onlyarrow_forwardwhat are the different types of assessments in the nursing process and when are they performed?arrow_forward
 Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC.
Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC. Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders
Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer,
Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer, Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science
Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning





